[English] 日本語
 Yorodumi
Yorodumi- EMDB-40914: Cryo-EM structure of cinacalcet-bound active-state human calcium-... -
+ Open data
Open data
- Basic information
Basic information
| Entry |  | |||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Title | Cryo-EM structure of cinacalcet-bound active-state human calcium-sensing receptor CaSR in lipid nanodiscs | |||||||||
 Map data Map data | ||||||||||
 Sample Sample |
| |||||||||
 Keywords Keywords | Family C GPCR / Calcium-sensing Receptor (CaSR) / Lipid Nanodiscs / Positive Allosteric Modulator / Membrane Protein / SIGNALING PROTEIN | |||||||||
| Function / homology |  Function and homology information Function and homology informationregulation of presynaptic membrane potential / bile acid secretion / chemosensory behavior / response to fibroblast growth factor / cellular response to peptide / cellular response to vitamin D / Class C/3 (Metabotropic glutamate/pheromone receptors) / positive regulation of positive chemotaxis / fat pad development / cellular response to hepatocyte growth factor stimulus ...regulation of presynaptic membrane potential / bile acid secretion / chemosensory behavior / response to fibroblast growth factor / cellular response to peptide / cellular response to vitamin D / Class C/3 (Metabotropic glutamate/pheromone receptors) / positive regulation of positive chemotaxis / fat pad development / cellular response to hepatocyte growth factor stimulus / amino acid binding / branching morphogenesis of an epithelial tube / positive regulation of calcium ion import / positive regulation of NLRP3 inflammasome complex assembly / regulation of calcium ion transport / positive regulation of vasoconstriction / cellular response to low-density lipoprotein particle stimulus / anatomical structure morphogenesis / detection of calcium ion / JNK cascade / axon terminus / ossification / chloride transmembrane transport / response to ischemia / cellular response to glucose stimulus / positive regulation of insulin secretion / G protein-coupled receptor activity / adenylate cyclase-inhibiting G protein-coupled receptor signaling pathway / integrin binding / vasodilation / intracellular calcium ion homeostasis / presynaptic membrane / cellular response to hypoxia / G alpha (i) signalling events / basolateral plasma membrane / phospholipase C-activating G protein-coupled receptor signaling pathway / G alpha (q) signalling events / transmembrane transporter binding / positive regulation of ERK1 and ERK2 cascade / apical plasma membrane / G protein-coupled receptor signaling pathway / neuronal cell body / positive regulation of cell population proliferation / calcium ion binding / positive regulation of gene expression / protein kinase binding / glutamatergic synapse / cell surface / protein homodimerization activity / identical protein binding / plasma membrane Similarity search - Function | |||||||||
| Biological species |  Homo sapiens (human) Homo sapiens (human) | |||||||||
| Method | single particle reconstruction / cryo EM / Resolution: 2.8 Å | |||||||||
 Authors Authors | He F / Wu C / Gao Y / Skiniotis G | |||||||||
| Funding support |  United States, 1 items United States, 1 items
| |||||||||
 Citation Citation |  Journal: Nature / Year: 2024 Journal: Nature / Year: 2024Title: Allosteric modulation and G-protein selectivity of the Ca-sensing receptor. Authors: Feng He / Cheng-Guo Wu / Yang Gao / Sabrina N Rahman / Magda Zaoralová / Makaía M Papasergi-Scott / Ting-Jia Gu / Michael J Robertson / Alpay B Seven / Lingjun Li / Jesper M Mathiesen / Georgios Skiniotis /    Abstract: The calcium-sensing receptor (CaSR) is a family C G-protein-coupled receptor (GPCR) that has a central role in regulating systemic calcium homeostasis. Here we use cryo-electron microscopy and ...The calcium-sensing receptor (CaSR) is a family C G-protein-coupled receptor (GPCR) that has a central role in regulating systemic calcium homeostasis. Here we use cryo-electron microscopy and functional assays to investigate the activation of human CaSR embedded in lipid nanodiscs and its coupling to functional G versus G proteins in the presence and absence of the calcimimetic drug cinacalcet. High-resolution structures show that both G and G drive additional conformational changes in the activated CaSR dimer to stabilize a more extensive asymmetric interface of the seven-transmembrane domain (7TM) that involves key protein-lipid interactions. Selective G and G coupling by the receptor is achieved through substantial rearrangements of intracellular loop 2 and the C terminus, which contribute differentially towards the binding of the two G-protein subtypes, resulting in distinct CaSR-G-protein interfaces. The structures also reveal that natural polyamines target multiple sites on CaSR to enhance receptor activation by zipping negatively charged regions between two protomers. Furthermore, we find that the amino acid L-tryptophan, a well-known ligand of CaSR extracellular domains, occupies the 7TM bundle of the G-protein-coupled protomer at the same location as cinacalcet and other allosteric modulators. Together, these results provide a framework for G-protein activation and selectivity by CaSR, as well as its allosteric modulation by endogenous and exogenous ligands. | |||||||||
| History |
|
- Structure visualization
Structure visualization
| Supplemental images |
|---|
- Downloads & links
Downloads & links
-EMDB archive
| Map data |  emd_40914.map.gz emd_40914.map.gz | 394.5 MB |  EMDB map data format EMDB map data format | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Header (meta data) |  emd-40914-v30.xml emd-40914-v30.xml emd-40914.xml emd-40914.xml | 20.1 KB 20.1 KB | Display Display |  EMDB header EMDB header |
| Images |  emd_40914.png emd_40914.png | 86.2 KB | ||
| Filedesc metadata |  emd-40914.cif.gz emd-40914.cif.gz | 6.8 KB | ||
| Others |  emd_40914_additional_1.map.gz emd_40914_additional_1.map.gz emd_40914_additional_2.map.gz emd_40914_additional_2.map.gz | 212.1 MB 211.4 MB | ||
| Archive directory |  http://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/structures/EMD-40914 http://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/structures/EMD-40914 ftp://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/structures/EMD-40914 ftp://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/structures/EMD-40914 | HTTPS FTP |
-Related structure data
| Related structure data |  8szfMC  8szgC  8szhC  8sziC C: citing same article ( M: atomic model generated by this map |
|---|---|
| Similar structure data | Similarity search - Function & homology  F&H Search F&H Search |
- Links
Links
| EMDB pages |  EMDB (EBI/PDBe) / EMDB (EBI/PDBe) /  EMDataResource EMDataResource |
|---|---|
| Related items in Molecule of the Month |
- Map
Map
| File |  Download / File: emd_40914.map.gz / Format: CCP4 / Size: 421.9 MB / Type: IMAGE STORED AS FLOATING POINT NUMBER (4 BYTES) Download / File: emd_40914.map.gz / Format: CCP4 / Size: 421.9 MB / Type: IMAGE STORED AS FLOATING POINT NUMBER (4 BYTES) | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Projections & slices | Image control
Images are generated by Spider. | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Voxel size | X=Y=Z: 0.8677 Å | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
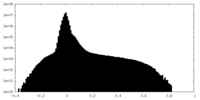
| Density |
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Symmetry | Space group: 1 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Details | EMDB XML:
|
-Supplemental data
-Additional map: Local unsharpened refinement map of CaSR VFT and CRD domains
| File | emd_40914_additional_1.map | ||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Annotation | Local unsharpened refinement map of CaSR VFT and CRD domains | ||||||||||||
| Projections & Slices |
| ||||||||||||
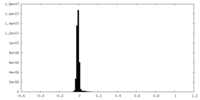
| Density Histograms |
-Additional map: Local unsharpened refinement map of CaSR CRD and 7TM domains
| File | emd_40914_additional_2.map | ||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Annotation | Local unsharpened refinement map of CaSR CRD and 7TM domains | ||||||||||||
| Projections & Slices |
| ||||||||||||
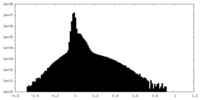
| Density Histograms |
- Sample components
Sample components
-Entire : Cinacalcet-bound active-state human calcium-sensing receptor CaSR...
| Entire | Name: Cinacalcet-bound active-state human calcium-sensing receptor CaSR dimer in lipid nanodiscs |
|---|---|
| Components |
|
-Supramolecule #1: Cinacalcet-bound active-state human calcium-sensing receptor CaSR...
| Supramolecule | Name: Cinacalcet-bound active-state human calcium-sensing receptor CaSR dimer in lipid nanodiscs type: complex / ID: 1 / Parent: 0 / Macromolecule list: #1-#2 |
|---|---|
| Source (natural) | Organism:  Homo sapiens (human) Homo sapiens (human) |
-Macromolecule #1: Extracellular calcium-sensing receptor
| Macromolecule | Name: Extracellular calcium-sensing receptor / type: protein_or_peptide / ID: 1 / Number of copies: 1 / Enantiomer: LEVO |
|---|---|
| Source (natural) | Organism:  Homo sapiens (human) Homo sapiens (human) |
| Molecular weight | Theoretical: 123.820969 KDa |
| Recombinant expression | Organism:  |
| Sequence | String: DYKDDDDKAA AYGPDQRAQK KGDIILGGLF PIHFGVAAKD QDLKSRPESV ECIRYNFRGF RWLQAMIFAI EEINSSPALL PNLTLGYRI FDTCNTVSKA LEATLSFVAQ NKIDSLNLDE FCNCSEHIPS TIAVVGATGS GVSTAVANLL GLFYIPQVSY A SSSRLLSN ...String: DYKDDDDKAA AYGPDQRAQK KGDIILGGLF PIHFGVAAKD QDLKSRPESV ECIRYNFRGF RWLQAMIFAI EEINSSPALL PNLTLGYRI FDTCNTVSKA LEATLSFVAQ NKIDSLNLDE FCNCSEHIPS TIAVVGATGS GVSTAVANLL GLFYIPQVSY A SSSRLLSN KNQFKSFLRT IPNDEHQATA MADIIEYFRW NWVGTIAADD DYGRPGIEKF REEAEERDIC IDFSELISQY SD EEEIQHV VEVIQNSTAK VIVVFSSGPD LEPLIKEIVR RNITGKIWLA SEAWASSSLI AMPQYFHVVG GTIGFALKAG QIP GFREFL KKVHPRKSVH NGFAKEFWEE TFNCHLQEGA KGPLPVDTFL RGHEESGDRF SNSSTAFRPL CTGDENISSV ETPY IDYTH LRISYNVYLA VYSIAHALQD IYTCLPGRGL FTNGSCADIK KVEAWQVLKH LRHLNFTNNM GEQVTFDECG DLVGN YSII NWHLSPEDGS IVFKEVGYYN VYAKKGERLF INEEKILWSG FSREVPFSNC SRDCLAGTRK GIIEGEPTCC FECVEC PDG EYSDETDASA CNKCPDDFWS NENHTSCIAK EIEFLSWTEP FGIALTLFAV LGIFLTAFVL GVFIKFRNTP IVKATNR EL SYLLLFSLLC CFSSSLFFIG EPQDWTCRLR QPAFGISFVL CISCILVKTN RVLLVFEAKI PTSFHRKWWG LNLQFLLV F LCTFMQIVIC VIWLYTAPPS SYRNQELEDE IIFITCHEGS LMALGFLIGY TCLLAAICFF FAFKSRKLPE NFNEAKFIT FSMLIFFIVW ISFIPAYAST YGKFVSAVEV IAILAASFGL LACIFFNKIY IILFKPSRNT IEEVRCSTAA HAFKVAARAT LRRSNVTST SVTSVNQAST SRLEGLQSEN HRLRMKITEL DKDLEEVTMQ LQDTPEKKTN SGGSVFTLED FVGDWEQTAA Y NLDQVLEQ GGVSSLLQNL AVSVTPIQRI VRSGENALKI DIHVIIPYEG LSADQMAQIE EVFKVVYPVD DHHFKVILPY GT LVIDGVT PNMLNYFGRP YEGIAVFDGK KITVTGTLWN GNKIIDERLI TPDGSMLFRV TINS UniProtKB: Extracellular calcium-sensing receptor |
-Macromolecule #2: Extracellular calcium-sensing receptor
| Macromolecule | Name: Extracellular calcium-sensing receptor / type: protein_or_peptide / ID: 2 / Number of copies: 1 / Enantiomer: LEVO |
|---|---|
| Source (natural) | Organism:  Homo sapiens (human) Homo sapiens (human) |
| Molecular weight | Theoretical: 108.023055 KDa |
| Recombinant expression | Organism:  |
| Sequence | String: WSHPQFEKGG GSGGGSGGSA WSHPQFEKGS AAAYGPDQRA QKKGDIILGG LFPIHFGVAA KDQDLKSRPE SVECIRYNFR GFRWLQAMI FAIEEINSSP ALLPNLTLGY RIFDTCNTVS KALEATLSFV AQNKIDSLNL DEFCNCSEHI PSTIAVVGAT G SGVSTAVA ...String: WSHPQFEKGG GSGGGSGGSA WSHPQFEKGS AAAYGPDQRA QKKGDIILGG LFPIHFGVAA KDQDLKSRPE SVECIRYNFR GFRWLQAMI FAIEEINSSP ALLPNLTLGY RIFDTCNTVS KALEATLSFV AQNKIDSLNL DEFCNCSEHI PSTIAVVGAT G SGVSTAVA NLLGLFYIPQ VSYASSSRLL SNKNQFKSFL RTIPNDEHQA TAMADIIEYF RWNWVGTIAA DDDYGRPGIE KF REEAEER DICIDFSELI SQYSDEEEIQ HVVEVIQNST AKVIVVFSSG PDLEPLIKEI VRRNITGKIW LASEAWASSS LIA MPQYFH VVGGTIGFAL KAGQIPGFRE FLKKVHPRKS VHNGFAKEFW EETFNCHLQE GAKGPLPVDT FLRGHEESGD RFSN SSTAF RPLCTGDENI SSVETPYIDY THLRISYNVY LAVYSIAHAL QDIYTCLPGR GLFTNGSCAD IKKVEAWQVL KHLRH LNFT NNMGEQVTFD ECGDLVGNYS IINWHLSPED GSIVFKEVGY YNVYAKKGER LFINEEKILW SGFSREVPFS NCSRDC LAG TRKGIIEGEP TCCFECVECP DGEYSDETDA SACNKCPDDF WSNENHTSCI AKEIEFLSWT EPFGIALTLF AVLGIFL TA FVLGVFIKFR NTPIVKATNR ELSYLLLFSL LCCFSSSLFF IGEPQDWTCR LRQPAFGISF VLCISCILVK TNRVLLVF E AKIPTSFHRK WWGLNLQFLL VFLCTFMQIV ICVIWLYTAP PSSYRNQELE DEIIFITCHE GSLMALGFLI GYTCLLAAI CFFFAFKSRK LPENFNEAKF ITFSMLIFFI VWISFIPAYA STYGKFVSAV EVIAILAASF GLLACIFFNK IYIILFKPSR NTIEEVRCS TAAHAFKVAA RATLRRSNVT GSSTNNNEEE KSRLLEKENR ELEKIIAEKE ERVSELRHQL QSRQQLKKTN UniProtKB: Extracellular calcium-sensing receptor |
-Macromolecule #4: 2-acetamido-2-deoxy-beta-D-glucopyranose
| Macromolecule | Name: 2-acetamido-2-deoxy-beta-D-glucopyranose / type: ligand / ID: 4 / Number of copies: 5 / Formula: NAG |
|---|---|
| Molecular weight | Theoretical: 221.208 Da |
| Chemical component information |  ChemComp-NAG: |
-Macromolecule #5: TRYPTOPHAN
| Macromolecule | Name: TRYPTOPHAN / type: ligand / ID: 5 / Number of copies: 2 / Formula: TRP |
|---|---|
| Molecular weight | Theoretical: 204.225 Da |
| Chemical component information | 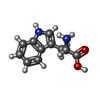 ChemComp-TRP: |
-Macromolecule #6: CALCIUM ION
| Macromolecule | Name: CALCIUM ION / type: ligand / ID: 6 / Number of copies: 4 / Formula: CA |
|---|---|
| Molecular weight | Theoretical: 40.078 Da |
-Macromolecule #7: PHOSPHATE ION
| Macromolecule | Name: PHOSPHATE ION / type: ligand / ID: 7 / Number of copies: 2 / Formula: PO4 |
|---|---|
| Molecular weight | Theoretical: 94.971 Da |
| Chemical component information |  ChemComp-PO4: |
-Macromolecule #8: N-[(1R)-1-(naphthalen-1-yl)ethyl]-3-[3-(trifluoromethyl)phenyl]pr...
| Macromolecule | Name: N-[(1R)-1-(naphthalen-1-yl)ethyl]-3-[3-(trifluoromethyl)phenyl]propan-1-amine type: ligand / ID: 8 / Number of copies: 2 / Formula: YP4 |
|---|---|
| Molecular weight | Theoretical: 357.412 Da |
| Chemical component information |  ChemComp-YP4: |
-Macromolecule #9: SPERMINE
| Macromolecule | Name: SPERMINE / type: ligand / ID: 9 / Number of copies: 1 / Formula: SPM |
|---|---|
| Molecular weight | Theoretical: 202.34 Da |
| Chemical component information | 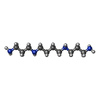 ChemComp-SPM: |
-Experimental details
-Structure determination
| Method | cryo EM |
|---|---|
 Processing Processing | single particle reconstruction |
| Aggregation state | particle |
- Sample preparation
Sample preparation
| Concentration | 7.00 mg/mL |
|---|---|
| Buffer | pH: 7.5 |
| Vitrification | Cryogen name: ETHANE |
- Electron microscopy
Electron microscopy
| Microscope | FEI TITAN KRIOS |
|---|---|
| Image recording | Film or detector model: GATAN K3 BIOQUANTUM (6k x 4k) / Average electron dose: 50.0 e/Å2 |
| Electron beam | Acceleration voltage: 300 kV / Electron source:  FIELD EMISSION GUN FIELD EMISSION GUN |
| Electron optics | Illumination mode: FLOOD BEAM / Imaging mode: BRIGHT FIELD / Nominal defocus max: 1.5 µm / Nominal defocus min: 0.5 µm |
| Experimental equipment |  Model: Titan Krios / Image courtesy: FEI Company |
- Image processing
Image processing
| Startup model | Type of model: PDB ENTRY PDB model - PDB ID: |
|---|---|
| Final reconstruction | Resolution.type: BY AUTHOR / Resolution: 2.8 Å / Resolution method: FSC 0.143 CUT-OFF / Number images used: 234170 |
| Initial angle assignment | Type: MAXIMUM LIKELIHOOD |
| Final angle assignment | Type: MAXIMUM LIKELIHOOD |
 Movie
Movie Controller
Controller























 Z (Sec.)
Z (Sec.) Y (Row.)
Y (Row.) X (Col.)
X (Col.)