+ Open data
Open data
- Basic information
Basic information
| Entry |  | |||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Title | Cryo-EM Structure of the CAND1-Cul3-Rbx1 complex | |||||||||
 Map data Map data | ||||||||||
 Sample Sample |
| |||||||||
 Keywords Keywords | ligase / complex | |||||||||
| Function / homology |  Function and homology information Function and homology informationSCF complex assembly / positive regulation of mitotic cell cycle phase transition / trophectodermal cellular morphogenesis / liver morphogenesis / POZ domain binding / negative regulation of catalytic activity / nuclear protein quality control by the ubiquitin-proteasome system / polar microtubule / regulation protein catabolic process at postsynapse / COPII vesicle coating ...SCF complex assembly / positive regulation of mitotic cell cycle phase transition / trophectodermal cellular morphogenesis / liver morphogenesis / POZ domain binding / negative regulation of catalytic activity / nuclear protein quality control by the ubiquitin-proteasome system / polar microtubule / regulation protein catabolic process at postsynapse / COPII vesicle coating / anaphase-promoting complex-dependent catabolic process / cullin-RING-type E3 NEDD8 transferase / NEDD8 transferase activity / cullin-RING ubiquitin ligase complex / RHOBTB3 ATPase cycle / embryonic cleavage / positive regulation of mitotic metaphase/anaphase transition / Cul7-RING ubiquitin ligase complex / cell projection organization / ubiquitin-dependent protein catabolic process via the C-end degron rule pathway / cellular response to chemical stress / Loss of Function of FBXW7 in Cancer and NOTCH1 Signaling / Notch binding / positive regulation of protein autoubiquitination / RNA polymerase II transcription initiation surveillance / protein neddylation / fibroblast apoptotic process / NEDD8 ligase activity / RHOBTB1 GTPase cycle / VCB complex / negative regulation of response to oxidative stress / Cul5-RING ubiquitin ligase complex / SCF ubiquitin ligase complex / ubiquitin-ubiquitin ligase activity / negative regulation of type I interferon production / stem cell division / SCF-dependent proteasomal ubiquitin-dependent protein catabolic process / Cul2-RING ubiquitin ligase complex / mitotic metaphase chromosome alignment / Cul3-RING ubiquitin ligase complex / Cul4A-RING E3 ubiquitin ligase complex / negative regulation of Rho protein signal transduction / Cul4-RING E3 ubiquitin ligase complex / stress fiber assembly / negative regulation of mitophagy / positive regulation of cytokinesis / Prolactin receptor signaling / Cul4B-RING E3 ubiquitin ligase complex / ubiquitin ligase complex scaffold activity / cullin family protein binding / positive regulation of RNA polymerase II transcription preinitiation complex assembly / protein monoubiquitination / endoplasmic reticulum to Golgi vesicle-mediated transport / ubiquitin ligase complex / RHOBTB2 GTPase cycle / sperm flagellum / protein K48-linked ubiquitination / protein autoubiquitination / Nuclear events stimulated by ALK signaling in cancer / transcription-coupled nucleotide-excision repair / gastrulation / positive regulation of TORC1 signaling / regulation of cellular response to insulin stimulus / negative regulation of insulin receptor signaling pathway / intrinsic apoptotic signaling pathway / post-translational protein modification / TBP-class protein binding / cyclin binding / T cell activation / Regulation of BACH1 activity / positive regulation of protein ubiquitination / integrin-mediated signaling pathway / cellular response to amino acid stimulus / kidney development / Degradation of DVL / Degradation of GLI1 by the proteasome / G1/S transition of mitotic cell cycle / Iron uptake and transport / negative regulation of canonical Wnt signaling pathway / GSK3B and BTRC:CUL1-mediated-degradation of NFE2L2 / Negative regulation of NOTCH4 signaling / Recognition of DNA damage by PCNA-containing replication complex / Hedgehog 'on' state / Vif-mediated degradation of APOBEC3G / FBXL7 down-regulates AURKA during mitotic entry and in early mitosis / Degradation of GLI2 by the proteasome / GLI3 is processed to GLI3R by the proteasome / RING-type E3 ubiquitin transferase / protein destabilization / Degradation of beta-catenin by the destruction complex / DNA Damage Recognition in GG-NER / Oxygen-dependent proline hydroxylation of Hypoxia-inducible Factor Alpha / Evasion by RSV of host interferon responses / NOTCH1 Intracellular Domain Regulates Transcription / Constitutive Signaling by NOTCH1 PEST Domain Mutants / Constitutive Signaling by NOTCH1 HD+PEST Domain Mutants / Dual Incision in GG-NER / Transcription-Coupled Nucleotide Excision Repair (TC-NER) / Formation of TC-NER Pre-Incision Complex / Regulation of expression of SLITs and ROBOs Similarity search - Function | |||||||||
| Biological species |  Homo sapiens (human) Homo sapiens (human) | |||||||||
| Method | single particle reconstruction / cryo EM / Resolution: 3.76 Å | |||||||||
 Authors Authors | Hu Y / Mao Q / Chen Z / Sun L | |||||||||
| Funding support |  China, 1 items China, 1 items
| |||||||||
 Citation Citation |  Journal: Nat Struct Mol Biol / Year: 2024 Journal: Nat Struct Mol Biol / Year: 2024Title: Dynamic molecular architecture and substrate recruitment of cullin3-RING E3 ligase CRL3. Authors: Yuxia Hu / Zhao Zhang / Qiyu Mao / Xiang Zhang / Aihua Hao / Yu Xun / Yeda Wang / Lin Han / Wuqiang Zhan / Qianying Liu / Yue Yin / Chao Peng / Eva Marie Y Moresco / Zhenguo Chen / Bruce Beutler / Lei Sun /   Abstract: Phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase α, a heterodimer of catalytic p110α and one of five regulatory subunits, mediates insulin- and insulin like growth factor-signaling and, frequently, oncogenesis. ...Phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase α, a heterodimer of catalytic p110α and one of five regulatory subunits, mediates insulin- and insulin like growth factor-signaling and, frequently, oncogenesis. Cellular levels of the regulatory p85α subunit are tightly controlled by regulated proteasomal degradation. In adipose tissue and growth plates, failure of K48-linked p85α ubiquitination causes diabetes, lipodystrophy and dwarfism in mice, as in humans with SHORT syndrome. Here we elucidated the structures of the key ubiquitin ligase complexes regulating p85α availability. Specificity is provided by the substrate receptor KBTBD2, which recruits p85α to the cullin3-RING E3 ubiquitin ligase (CRL3). CRL3 forms multimers, which disassemble into dimers upon substrate binding (CRL3-p85α) and/or neddylation by the activator NEDD8 (CRL3~N8), leading to p85α ubiquitination and degradation. Deactivation involves dissociation of NEDD8 mediated by the COP9 signalosome and displacement of KBTBD2 by the inhibitor CAND1. The hereby identified structural basis of p85α regulation opens the way to better understanding disturbances of glucose regulation, growth and cancer. | |||||||||
| History |
|
- Structure visualization
Structure visualization
| Supplemental images |
|---|
- Downloads & links
Downloads & links
-EMDB archive
| Map data |  emd_34473.map.gz emd_34473.map.gz | 57.1 MB |  EMDB map data format EMDB map data format | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Header (meta data) |  emd-34473-v30.xml emd-34473-v30.xml emd-34473.xml emd-34473.xml | 21.9 KB 21.9 KB | Display Display |  EMDB header EMDB header |
| Images |  emd_34473.png emd_34473.png | 81 KB | ||
| Filedesc metadata |  emd-34473.cif.gz emd-34473.cif.gz | 7.6 KB | ||
| Others |  emd_34473_half_map_1.map.gz emd_34473_half_map_1.map.gz emd_34473_half_map_2.map.gz emd_34473_half_map_2.map.gz | 49.7 MB 49.7 MB | ||
| Archive directory |  http://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/structures/EMD-34473 http://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/structures/EMD-34473 ftp://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/structures/EMD-34473 ftp://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/structures/EMD-34473 | HTTPS FTP |
-Validation report
| Summary document |  emd_34473_validation.pdf.gz emd_34473_validation.pdf.gz | 675.6 KB | Display |  EMDB validaton report EMDB validaton report |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Full document |  emd_34473_full_validation.pdf.gz emd_34473_full_validation.pdf.gz | 675.2 KB | Display | |
| Data in XML |  emd_34473_validation.xml.gz emd_34473_validation.xml.gz | 12.2 KB | Display | |
| Data in CIF |  emd_34473_validation.cif.gz emd_34473_validation.cif.gz | 14.5 KB | Display | |
| Arichive directory |  https://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/validation_reports/EMD-34473 https://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/validation_reports/EMD-34473 ftp://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/validation_reports/EMD-34473 ftp://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/validation_reports/EMD-34473 | HTTPS FTP |
-Related structure data
| Related structure data | 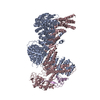 8h3qMC 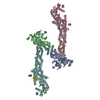 8gq6C  8h33C  8h34C  8h35C  8h36C  8h37C  8h38C  8h3aC  8h3fC  8h3rC M: atomic model generated by this map C: citing same article ( |
|---|---|
| Similar structure data | Similarity search - Function & homology  F&H Search F&H Search |
- Links
Links
| EMDB pages |  EMDB (EBI/PDBe) / EMDB (EBI/PDBe) /  EMDataResource EMDataResource |
|---|---|
| Related items in Molecule of the Month |
- Map
Map
| File |  Download / File: emd_34473.map.gz / Format: CCP4 / Size: 64 MB / Type: IMAGE STORED AS FLOATING POINT NUMBER (4 BYTES) Download / File: emd_34473.map.gz / Format: CCP4 / Size: 64 MB / Type: IMAGE STORED AS FLOATING POINT NUMBER (4 BYTES) | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Projections & slices | Image control
Images are generated by Spider. | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Voxel size | X=Y=Z: 1.044 Å | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Density |
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Symmetry | Space group: 1 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Details | EMDB XML:
|
-Supplemental data
-Half map: #2
| File | emd_34473_half_map_1.map | ||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Projections & Slices |
| ||||||||||||
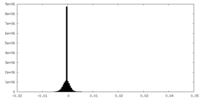
| Density Histograms |
-Half map: #1
| File | emd_34473_half_map_2.map | ||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Projections & Slices |
| ||||||||||||
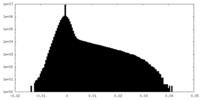
| Density Histograms |
- Sample components
Sample components
-Entire : CAND1-Cul3-Rbx1 complex
| Entire | Name: CAND1-Cul3-Rbx1 complex |
|---|---|
| Components |
|
-Supramolecule #1: CAND1-Cul3-Rbx1 complex
| Supramolecule | Name: CAND1-Cul3-Rbx1 complex / type: complex / ID: 1 / Parent: 0 / Macromolecule list: #1-#3 |
|---|---|
| Source (natural) | Organism:  Homo sapiens (human) Homo sapiens (human) |
-Supramolecule #2: CAND1
| Supramolecule | Name: CAND1 / type: complex / ID: 2 / Parent: 1 / Macromolecule list: #1 |
|---|
-Supramolecule #3: Cul3, Rbx1
| Supramolecule | Name: Cul3, Rbx1 / type: complex / ID: 3 / Parent: 1 / Macromolecule list: #2-#3 |
|---|
-Macromolecule #1: Cullin-associated NEDD8-dissociated protein 1
| Macromolecule | Name: Cullin-associated NEDD8-dissociated protein 1 / type: protein_or_peptide / ID: 1 / Number of copies: 1 / Enantiomer: LEVO |
|---|---|
| Source (natural) | Organism:  Homo sapiens (human) Homo sapiens (human) |
| Molecular weight | Theoretical: 136.529297 KDa |
| Recombinant expression | Organism:  |
| Sequence | String: MASASYHISN LLEKMTSSDK DFRFMATNDL MTELQKDSIK LDDDSERKVV KMILKLLEDK NGEVQNLAVK CLGPLVSKVK EYQVETIVD TLCTNMLSDK EQLRDISSIG LKTVIGELPP ASSGSALAAN VCKKITGRLT SAIAKQEDVS VQLEALDIMA D MLSRQGGL ...String: MASASYHISN LLEKMTSSDK DFRFMATNDL MTELQKDSIK LDDDSERKVV KMILKLLEDK NGEVQNLAVK CLGPLVSKVK EYQVETIVD TLCTNMLSDK EQLRDISSIG LKTVIGELPP ASSGSALAAN VCKKITGRLT SAIAKQEDVS VQLEALDIMA D MLSRQGGL LVNFHPSILT CLLPQLTSPR LAVRKRTIIA LGHLVMSCGN IVFVDLIEHL LSELSKNDSM STTRTYIQCI AA ISRQAGH RIGEYLEKII PLVVKFCNVD DDELREYCIQ AFESFVRRCP KEVYPHVSTI INICLKYLTY DPNYNYDDED EDE NAMDAD GGDDDDQGSD DEYSDDDDMS WKVRRAAAKC LDAVVSTRHE MLPEFYKTVS PALISRFKER EENVKADVFH AYLS LLKQT RPVQSWLCDP DAMEQGETPL TMLQSQVPNI VKALHKQMKE KSVKTRQCCF NMLTELVNVL PGALTQHIPV LVPGI IFSL NDKSSSSNLK IDALSCLYVI LCNHSPQVFH PHVQALVPPV VACVGDPFYK ITSEALLVTQ QLVKVIRPLD QPSSFD ATP YIKDLFTCTI KRLKAADIDQ EVKERAISCM GQIICNLGDN LGSDLPNTLQ IFLERLKNEI TRLTTVKALT LIAGSPL KI DLRPVLGEGV PILASFLRKN QRALKLGTLS ALDILIKNYS DSLTAAMIDA VLDELPPLIS ESDMHVSQMA ISFLTTLA K VYPSSLSKIS GSILNELIGL VRSPLLQGGA LSAMLDFFQA LVVTGTNNLG YMDLLRMLTG PVYSQSTALT HKQSYYSIA KCVAALTRAC PKEGPAVVGQ FIQDVKNSRS TDSIRLLALL SLGEVGHHID LSGQLELKSV ILEAFSSPSE EVKSAASYAL GSISVGNLP EYLPFVLQEI TSQPKRQYLL LHSLKEIISS ASVVGLKPYV ENIWALLLKH CECAEEGTRN VVAECLGKLT L IDPETLLP RLKGYLISGS SYARSSVVTA VKFTISDHPQ PIDPLLKNCI GDFLKTLEDP DLNVRRVALV TFNSAAHNKP SL IRDLLDT VLPHLYNETK VRKELIREVE MGPFKHTVDD GLDIRKAAFE CMYTLLDSCL DRLDIFEFLN HVEDGLKDHY DIK MLTFLM LVRLSTLCPS AVLQRLDRLV EPLRATCTTK VKANSVKQEF EKQDELKRSA MRAVAALLTI PEAEKSPLMS EFQS QISSN PELAAIFESI QKDSSSTNLE SMDTS UniProtKB: Cullin-associated NEDD8-dissociated protein 1 |
-Macromolecule #2: Cullin-3
| Macromolecule | Name: Cullin-3 / type: protein_or_peptide / ID: 2 / Number of copies: 1 / Enantiomer: LEVO |
|---|---|
| Source (natural) | Organism:  Homo sapiens (human) Homo sapiens (human) |
| Molecular weight | Theoretical: 89.063328 KDa |
| Recombinant expression | Organism:  |
| Sequence | String: MSNLSKGTGS RKDTKMRIRA FPMTMDEKYV NSIWDLLKNA IQEIQRKNNS GLSFEELYRN AYTMVLHKHG EKLYTGLREV VTEHLINKV REDVLNSLNN NFLQTLNQAW NDHQTAMVMI RDILMYMDRV YVQQNNVENV YNLGLIIFRD QVVRYGCIRD H LRQTLLDM ...String: MSNLSKGTGS RKDTKMRIRA FPMTMDEKYV NSIWDLLKNA IQEIQRKNNS GLSFEELYRN AYTMVLHKHG EKLYTGLREV VTEHLINKV REDVLNSLNN NFLQTLNQAW NDHQTAMVMI RDILMYMDRV YVQQNNVENV YNLGLIIFRD QVVRYGCIRD H LRQTLLDM IARERKGEVV DRGAIRNACQ MLMILGLEGR SVYEEDFEAP FLEMSAEFFQ MESQKFLAEN SASVYIKKVE AR INEEIER VMHCLDKSTE EPIVKVVERE LISKHMKTIV EMENSGLVHM LKNGKTEDLG CMYKLFSRVP NGLKTMCECM SSY LREQGK ALVSEEGEGK NPVDYIQGLL DLKSRFDRFL LESFNNDRLF KQTIAGDFEY FLNLNSRSPE YLSLFIDDKL KKGV KGLTE QEVETILDKA MVLFRFMQEK DVFERYYKQH LARRLLTNKS VSDDSEKNMI SKLKTECGCQ FTSKLEGMFR DMSIS NTTM DEFRQHLQAT GVSLGGVDLT VRVLTTGYWP TQSATPKCNI PPAPRHAFEI FRRFYLAKHS GRQLTLQHHM GSADLN ATF YGPVKKEDGS EVGVGGAQVT GSNTRKHILQ VSTFQMTILM LFNNREKYTF EEIQQETDIP ERELVRALQS LACGKPT QR VLTKEPKSKE IENGHIFTVN DQFTSKLHRV KIQTVAAKQG ESDPERKETR QKVDDDRKHE IEAAIVRIMK SRKKMQHN V LVAEVTQQLK ARFLPSPVVI KKRIEGLIER EYLARTPEDR KVYTYVA UniProtKB: Cullin-3 |
-Macromolecule #3: E3 ubiquitin-protein ligase RBX1
| Macromolecule | Name: E3 ubiquitin-protein ligase RBX1 / type: protein_or_peptide / ID: 3 / Number of copies: 1 / Enantiomer: LEVO / EC number: RING-type E3 ubiquitin transferase |
|---|---|
| Source (natural) | Organism:  Homo sapiens (human) Homo sapiens (human) |
| Molecular weight | Theoretical: 12.289977 KDa |
| Recombinant expression | Organism:  |
| Sequence | String: MAAAMDVDTP SGTNSGAGKK RFEVKKWNAV ALWAWDIVVD NCAICRNHIM DLCIECQANQ ASATSEECTV AWGVCNHAFH FHCISRWLK TRQVCPLDNR EWEFQKYGH UniProtKB: E3 ubiquitin-protein ligase RBX1 |
-Macromolecule #4: ZINC ION
| Macromolecule | Name: ZINC ION / type: ligand / ID: 4 / Number of copies: 3 / Formula: ZN |
|---|---|
| Molecular weight | Theoretical: 65.409 Da |
-Experimental details
-Structure determination
| Method | cryo EM |
|---|---|
 Processing Processing | single particle reconstruction |
| Aggregation state | particle |
- Sample preparation
Sample preparation
| Buffer | pH: 7.8 |
|---|---|
| Vitrification | Cryogen name: ETHANE |
- Electron microscopy
Electron microscopy
| Microscope | FEI TITAN KRIOS |
|---|---|
| Image recording | Film or detector model: GATAN K2 SUMMIT (4k x 4k) / Detector mode: SUPER-RESOLUTION / Average electron dose: 53.0 e/Å2 |
| Electron beam | Acceleration voltage: 300 kV / Electron source:  FIELD EMISSION GUN FIELD EMISSION GUN |
| Electron optics | Illumination mode: FLOOD BEAM / Imaging mode: BRIGHT FIELD / Nominal defocus max: 2.2 µm / Nominal defocus min: 1.2 µm |
| Experimental equipment |  Model: Titan Krios / Image courtesy: FEI Company |
 Movie
Movie Controller
Controller













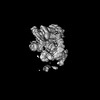








 Z (Sec.)
Z (Sec.) Y (Row.)
Y (Row.) X (Col.)
X (Col.)