+ Open data
Open data
- Basic information
Basic information
| Entry | 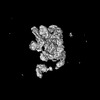 | |||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Title | Cryo-EM Structure of the KBTBD2-CRL3~N8(removed)-CSN complex | |||||||||
 Map data Map data | ||||||||||
 Sample Sample |
| |||||||||
 Keywords Keywords | ligase / complex | |||||||||
| Function / homology |  Function and homology information Function and homology informationpositive regulation of mitotic cell cycle phase transition / trophectodermal cellular morphogenesis / liver morphogenesis / COP9 signalosome assembly / POZ domain binding / trophectodermal cell proliferation / macrophage migration inhibitory factor binding / regulation of IRE1-mediated unfolded protein response / exosomal secretion / GTPase inhibitor activity ...positive regulation of mitotic cell cycle phase transition / trophectodermal cellular morphogenesis / liver morphogenesis / COP9 signalosome assembly / POZ domain binding / trophectodermal cell proliferation / macrophage migration inhibitory factor binding / regulation of IRE1-mediated unfolded protein response / exosomal secretion / GTPase inhibitor activity / deNEDDylase activity / nuclear protein quality control by the ubiquitin-proteasome system / polar microtubule / regulation protein catabolic process at postsynapse / COPII vesicle coating / protein deneddylation / anaphase-promoting complex-dependent catabolic process / regulation of protein neddylation / activation of NF-kappaB-inducing kinase activity / eukaryotic translation initiation factor 3 complex / cullin-RING-type E3 NEDD8 transferase / NEDD8 transferase activity / COP9 signalosome / cullin-RING ubiquitin ligase complex / RHOBTB3 ATPase cycle / embryonic cleavage / positive regulation of mitotic metaphase/anaphase transition / Cul7-RING ubiquitin ligase complex / cell projection organization / ubiquitin-dependent protein catabolic process via the C-end degron rule pathway / cellular response to chemical stress / Loss of Function of FBXW7 in Cancer and NOTCH1 Signaling / Notch binding / positive regulation of protein autoubiquitination / RNA polymerase II transcription initiation surveillance / protein neddylation / fibroblast apoptotic process / regulation of JNK cascade / NEDD8 ligase activity / Hydrolases; Acting on peptide bonds (peptidases) / RHOBTB1 GTPase cycle / metal-dependent deubiquitinase activity / VCB complex / negative regulation of response to oxidative stress / regulation of DNA damage response, signal transduction by p53 class mediator / Cul5-RING ubiquitin ligase complex / inner cell mass cell proliferation / SCF ubiquitin ligase complex / ubiquitin-ubiquitin ligase activity / negative regulation of type I interferon production / stem cell division / SCF-dependent proteasomal ubiquitin-dependent protein catabolic process / Cul2-RING ubiquitin ligase complex / mitotic metaphase chromosome alignment / Cul3-RING ubiquitin ligase complex / Cul4A-RING E3 ubiquitin ligase complex / negative regulation of Rho protein signal transduction / Cul4-RING E3 ubiquitin ligase complex / stress fiber assembly / negative regulation of mitophagy / positive regulation of cytokinesis / Prolactin receptor signaling / Cul4B-RING E3 ubiquitin ligase complex / ubiquitin ligase complex scaffold activity / response to light stimulus / cullin family protein binding / skeletal muscle cell differentiation / protein monoubiquitination / endoplasmic reticulum to Golgi vesicle-mediated transport / RHOBTB2 GTPase cycle / sperm flagellum / ubiquitin-like ligase-substrate adaptor activity / protein K48-linked ubiquitination / : / protein autoubiquitination / Nuclear events stimulated by ALK signaling in cancer / JNK cascade / transcription-coupled nucleotide-excision repair / gastrulation / translation initiation factor activity / positive regulation of TORC1 signaling / regulation of cellular response to insulin stimulus / negative regulation of insulin receptor signaling pathway / intrinsic apoptotic signaling pathway / post-translational protein modification / cyclin binding / T cell activation / Regulation of BACH1 activity / positive regulation of protein ubiquitination / integrin-mediated signaling pathway / cellular response to amino acid stimulus / phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase/protein kinase B signal transduction / kidney development / Degradation of DVL / Degradation of GLI1 by the proteasome / G1/S transition of mitotic cell cycle / negative regulation of canonical Wnt signaling pathway / GSK3B and BTRC:CUL1-mediated-degradation of NFE2L2 / Negative regulation of NOTCH4 signaling / Recognition of DNA damage by PCNA-containing replication complex Similarity search - Function | |||||||||
| Biological species |  Homo sapiens (human) Homo sapiens (human) | |||||||||
| Method | single particle reconstruction / cryo EM / Resolution: 7.51 Å | |||||||||
 Authors Authors | Hu Y / Mao Q / Chen Z / Sun L | |||||||||
| Funding support |  China, 1 items China, 1 items
| |||||||||
 Citation Citation |  Journal: Nat Struct Mol Biol / Year: 2024 Journal: Nat Struct Mol Biol / Year: 2024Title: Dynamic molecular architecture and substrate recruitment of cullin3-RING E3 ligase CRL3. Authors: Yuxia Hu / Zhao Zhang / Qiyu Mao / Xiang Zhang / Aihua Hao / Yu Xun / Yeda Wang / Lin Han / Wuqiang Zhan / Qianying Liu / Yue Yin / Chao Peng / Eva Marie Y Moresco / Zhenguo Chen / Bruce Beutler / Lei Sun /   Abstract: Phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase α, a heterodimer of catalytic p110α and one of five regulatory subunits, mediates insulin- and insulin like growth factor-signaling and, frequently, oncogenesis. ...Phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase α, a heterodimer of catalytic p110α and one of five regulatory subunits, mediates insulin- and insulin like growth factor-signaling and, frequently, oncogenesis. Cellular levels of the regulatory p85α subunit are tightly controlled by regulated proteasomal degradation. In adipose tissue and growth plates, failure of K48-linked p85α ubiquitination causes diabetes, lipodystrophy and dwarfism in mice, as in humans with SHORT syndrome. Here we elucidated the structures of the key ubiquitin ligase complexes regulating p85α availability. Specificity is provided by the substrate receptor KBTBD2, which recruits p85α to the cullin3-RING E3 ubiquitin ligase (CRL3). CRL3 forms multimers, which disassemble into dimers upon substrate binding (CRL3-p85α) and/or neddylation by the activator NEDD8 (CRL3~N8), leading to p85α ubiquitination and degradation. Deactivation involves dissociation of NEDD8 mediated by the COP9 signalosome and displacement of KBTBD2 by the inhibitor CAND1. The hereby identified structural basis of p85α regulation opens the way to better understanding disturbances of glucose regulation, growth and cancer. | |||||||||
| History |
|
- Structure visualization
Structure visualization
| Supplemental images |
|---|
- Downloads & links
Downloads & links
-EMDB archive
| Map data |  emd_34462.map.gz emd_34462.map.gz | 34.2 MB |  EMDB map data format EMDB map data format | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Header (meta data) |  emd-34462-v30.xml emd-34462-v30.xml emd-34462.xml emd-34462.xml | 31.1 KB 31.1 KB | Display Display |  EMDB header EMDB header |
| Images |  emd_34462.png emd_34462.png | 99.3 KB | ||
| Filedesc metadata |  emd-34462.cif.gz emd-34462.cif.gz | 9.1 KB | ||
| Others |  emd_34462_half_map_1.map.gz emd_34462_half_map_1.map.gz emd_34462_half_map_2.map.gz emd_34462_half_map_2.map.gz | 29.6 MB 29.6 MB | ||
| Archive directory |  http://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/structures/EMD-34462 http://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/structures/EMD-34462 ftp://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/structures/EMD-34462 ftp://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/structures/EMD-34462 | HTTPS FTP |
-Related structure data
| Related structure data |  8h3aMC  8gq6C  8h33C  8h34C  8h35C  8h36C  8h37C  8h38C  8h3fC  8h3qC  8h3rC M: atomic model generated by this map C: citing same article ( |
|---|---|
| Similar structure data | Similarity search - Function & homology  F&H Search F&H Search |
- Links
Links
| EMDB pages |  EMDB (EBI/PDBe) / EMDB (EBI/PDBe) /  EMDataResource EMDataResource |
|---|---|
| Related items in Molecule of the Month |
- Map
Map
| File |  Download / File: emd_34462.map.gz / Format: CCP4 / Size: 38.4 MB / Type: IMAGE STORED AS FLOATING POINT NUMBER (4 BYTES) Download / File: emd_34462.map.gz / Format: CCP4 / Size: 38.4 MB / Type: IMAGE STORED AS FLOATING POINT NUMBER (4 BYTES) | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Projections & slices | Image control
Images are generated by Spider. | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Voxel size | X=Y=Z: 2.088 Å | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
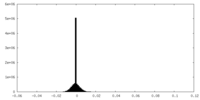
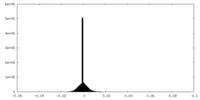
| Density |
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Symmetry | Space group: 1 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Details | EMDB XML:
|
-Supplemental data
-Half map: #2
| File | emd_34462_half_map_1.map | ||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Projections & Slices |
| ||||||||||||
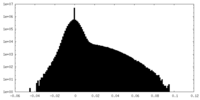
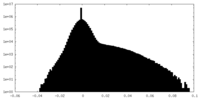
| Density Histograms |
-Half map: #1
| File | emd_34462_half_map_2.map | ||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Projections & Slices |
| ||||||||||||
| Density Histograms |
- Sample components
Sample components
+Entire : Cryo-EM Structure of the KBTBD2-CRL3~N8-CSN complex
+Supramolecule #1: Cryo-EM Structure of the KBTBD2-CRL3~N8-CSN complex
+Supramolecule #2: CSN
+Supramolecule #3: KBTBD2, Cullin-3, Rbx1
+Macromolecule #1: COP9 signalosome complex subunit 5
+Macromolecule #2: COP9 signalosome complex subunit 1
+Macromolecule #3: COP9 signalosome complex subunit 2
+Macromolecule #4: COP9 signalosome complex subunit 3
+Macromolecule #5: COP9 signalosome complex subunit 4
+Macromolecule #6: COP9 signalosome complex subunit 6
+Macromolecule #7: COP9 signalosome complex subunit 7b
+Macromolecule #8: COP9 signalosome complex subunit 8
+Macromolecule #9: Kelch repeat and BTB domain-containing protein 2
+Macromolecule #10: Cullin-3
+Macromolecule #11: E3 ubiquitin-protein ligase RBX1
+Macromolecule #12: ZINC ION
-Experimental details
-Structure determination
| Method | cryo EM |
|---|---|
 Processing Processing | single particle reconstruction |
| Aggregation state | particle |
- Sample preparation
Sample preparation
| Buffer | pH: 7.8 |
|---|---|
| Vitrification | Cryogen name: ETHANE |
- Electron microscopy
Electron microscopy
| Microscope | FEI TITAN KRIOS |
|---|---|
| Image recording | Film or detector model: GATAN K2 SUMMIT (4k x 4k) / Detector mode: SUPER-RESOLUTION / Average electron dose: 53.0 e/Å2 |
| Electron beam | Acceleration voltage: 300 kV / Electron source:  FIELD EMISSION GUN FIELD EMISSION GUN |
| Electron optics | Illumination mode: FLOOD BEAM / Imaging mode: BRIGHT FIELD / Nominal defocus max: 2.2 µm / Nominal defocus min: 1.2 µm |
| Experimental equipment |  Model: Titan Krios / Image courtesy: FEI Company |
- Image processing
Image processing
| Startup model | Type of model: PDB ENTRY PDB model - PDB ID: Details: 6r7f |
|---|---|
| Final reconstruction | Applied symmetry - Point group: C1 (asymmetric) / Resolution.type: BY AUTHOR / Resolution: 7.51 Å / Resolution method: FSC 0.143 CUT-OFF / Software - Name: RELION (ver. 3.0) / Number images used: 55391 |
| Initial angle assignment | Type: PROJECTION MATCHING |
| Final angle assignment | Type: PROJECTION MATCHING |
 Movie
Movie Controller
Controller




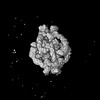
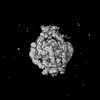
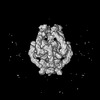



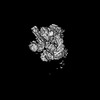


















 Z (Sec.)
Z (Sec.) Y (Row.)
Y (Row.) X (Col.)
X (Col.)
























 Trichoplusia ni (cabbage looper)
Trichoplusia ni (cabbage looper)
