+ Open data
Open data
- Basic information
Basic information
| Entry | Database: EMDB / ID: EMD-3221 | |||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Title | Mammalian 80S HCV-IRES complex, Classical | |||||||||
 Map data Map data | Reconstruction of ribosome complex | |||||||||
 Sample Sample |
| |||||||||
 Keywords Keywords | ribosome / translation initiation / Hepatitis C Virus internal ribosome entry site | |||||||||
| Function / homology |  Function and homology information Function and homology informationnegative regulation of endoplasmic reticulum unfolded protein response / oxidized pyrimidine DNA binding / response to TNF agonist / positive regulation of base-excision repair / positive regulation of respiratory burst involved in inflammatory response / positive regulation of gastrulation / positive regulation of intrinsic apoptotic signaling pathway in response to DNA damage / protein tyrosine kinase inhibitor activity / positive regulation of endodeoxyribonuclease activity / nucleolus organization ...negative regulation of endoplasmic reticulum unfolded protein response / oxidized pyrimidine DNA binding / response to TNF agonist / positive regulation of base-excision repair / positive regulation of respiratory burst involved in inflammatory response / positive regulation of gastrulation / positive regulation of intrinsic apoptotic signaling pathway in response to DNA damage / protein tyrosine kinase inhibitor activity / positive regulation of endodeoxyribonuclease activity / nucleolus organization / IRE1-RACK1-PP2A complex / positive regulation of Golgi to plasma membrane protein transport / TNFR1-mediated ceramide production / negative regulation of RNA splicing / negative regulation of DNA repair / supercoiled DNA binding / NF-kappaB complex / cysteine-type endopeptidase activator activity involved in apoptotic process / neural crest cell differentiation / oxidized purine DNA binding / positive regulation of ubiquitin-protein transferase activity / negative regulation of intrinsic apoptotic signaling pathway in response to hydrogen peroxide / negative regulation of bicellular tight junction assembly / regulation of establishment of cell polarity / ubiquitin-like protein conjugating enzyme binding / rRNA modification in the nucleus and cytosol / erythrocyte homeostasis / negative regulation of phagocytosis / Formation of the ternary complex, and subsequently, the 43S complex / cytoplasmic side of rough endoplasmic reticulum membrane / negative regulation of ubiquitin protein ligase activity / protein kinase A binding / laminin receptor activity / ion channel inhibitor activity / Ribosomal scanning and start codon recognition / pigmentation / Translation initiation complex formation / positive regulation of mitochondrial depolarization / fibroblast growth factor binding / positive regulation of T cell receptor signaling pathway / negative regulation of Wnt signaling pathway / monocyte chemotaxis / negative regulation of translational frameshifting / TOR signaling / BH3 domain binding / Protein hydroxylation / positive regulation of activated T cell proliferation / SARS-CoV-1 modulates host translation machinery / regulation of adenylate cyclase-activating G protein-coupled receptor signaling pathway / iron-sulfur cluster binding / mTORC1-mediated signalling / regulation of cell division / Peptide chain elongation / cellular response to ethanol / positive regulation of GTPase activity / Selenocysteine synthesis / Formation of a pool of free 40S subunits / positive regulation of intrinsic apoptotic signaling pathway by p53 class mediator / endonucleolytic cleavage to generate mature 3'-end of SSU-rRNA from (SSU-rRNA, 5.8S rRNA, LSU-rRNA) / Eukaryotic Translation Termination / protein serine/threonine kinase inhibitor activity / SRP-dependent cotranslational protein targeting to membrane / Response of EIF2AK4 (GCN2) to amino acid deficiency / negative regulation of ubiquitin-dependent protein catabolic process / ubiquitin ligase inhibitor activity / Viral mRNA Translation / negative regulation of respiratory burst involved in inflammatory response / negative regulation of protein binding / positive regulation of signal transduction by p53 class mediator / Nonsense Mediated Decay (NMD) independent of the Exon Junction Complex (EJC) / GTP hydrolysis and joining of the 60S ribosomal subunit / L13a-mediated translational silencing of Ceruloplasmin expression / Major pathway of rRNA processing in the nucleolus and cytosol / regulation of translational fidelity / phagocytic cup / Nonsense Mediated Decay (NMD) enhanced by the Exon Junction Complex (EJC) / positive regulation of intrinsic apoptotic signaling pathway / Protein methylation / spindle assembly / positive regulation of microtubule polymerization / Nuclear events stimulated by ALK signaling in cancer / endonucleolytic cleavage in ITS1 to separate SSU-rRNA from 5.8S rRNA and LSU-rRNA from tricistronic rRNA transcript (SSU-rRNA, 5.8S rRNA, LSU-rRNA) / positive regulation of cell cycle / laminin binding / rough endoplasmic reticulum / ribosomal small subunit export from nucleus / translation regulator activity / translation initiation factor binding / Maturation of protein E / gastrulation / Amplification of signal from unattached kinetochores via a MAD2 inhibitory signal / Maturation of protein E / DNA-(apurinic or apyrimidinic site) endonuclease activity / ER Quality Control Compartment (ERQC) / Myoclonic epilepsy of Lafora / MDM2/MDM4 family protein binding / signaling adaptor activity / FLT3 signaling by CBL mutants / Constitutive Signaling by NOTCH1 HD Domain Mutants / IRAK2 mediated activation of TAK1 complex Similarity search - Function | |||||||||
| Biological species |   Hepatitis C virus Hepatitis C virus | |||||||||
| Method | single particle reconstruction / cryo EM / Resolution: 3.9 Å | |||||||||
 Authors Authors | Yamamoto H / Collier M / Loerke J / Ismer J / Schmidt A / Hilal T / Sprink T / Yamamoto K / Mielke T / Burger J ...Yamamoto H / Collier M / Loerke J / Ismer J / Schmidt A / Hilal T / Sprink T / Yamamoto K / Mielke T / Burger J / Shaikh TR / Dabrowski M / Hildebrand PW / Scheerer P / Spahn CMT | |||||||||
 Citation Citation |  Journal: EMBO J / Year: 2015 Journal: EMBO J / Year: 2015Title: Molecular architecture of the ribosome-bound Hepatitis C Virus internal ribosomal entry site RNA. Authors: Hiroshi Yamamoto / Marianne Collier / Justus Loerke / Jochen Ismer / Andrea Schmidt / Tarek Hilal / Thiemo Sprink / Kaori Yamamoto / Thorsten Mielke / Jörg Bürger / Tanvir R Shaikh / ...Authors: Hiroshi Yamamoto / Marianne Collier / Justus Loerke / Jochen Ismer / Andrea Schmidt / Tarek Hilal / Thiemo Sprink / Kaori Yamamoto / Thorsten Mielke / Jörg Bürger / Tanvir R Shaikh / Marylena Dabrowski / Peter W Hildebrand / Patrick Scheerer / Christian M T Spahn /   Abstract: Internal ribosomal entry sites (IRESs) are structured cis-acting RNAs that drive an alternative, cap-independent translation initiation pathway. They are used by many viruses to hijack the ...Internal ribosomal entry sites (IRESs) are structured cis-acting RNAs that drive an alternative, cap-independent translation initiation pathway. They are used by many viruses to hijack the translational machinery of the host cell. IRESs facilitate translation initiation by recruiting and actively manipulating the eukaryotic ribosome using only a subset of canonical initiation factor and IRES transacting factors. Here we present cryo-EM reconstructions of the ribosome 80S- and 40S-bound Hepatitis C Virus (HCV) IRES. The presence of four subpopulations for the 80S•HCV IRES complex reveals dynamic conformational modes of the complex. At a global resolution of 3.9 Å for the most stable complex, a derived atomic model reveals a complex fold of the IRES RNA and molecular details of its interaction with the ribosome. The comparison of obtained structures explains how a modular architecture facilitates mRNA loading and tRNA binding to the P-site. This information provides the structural foundation for understanding the mechanism of HCV IRES RNA-driven translation initiation. | |||||||||
| History |
|
- Structure visualization
Structure visualization
| Movie |
 Movie viewer Movie viewer |
|---|---|
| Structure viewer | EM map:  SurfView SurfView Molmil Molmil Jmol/JSmol Jmol/JSmol |
| Supplemental images |
- Downloads & links
Downloads & links
-EMDB archive
| Map data |  emd_3221.map.gz emd_3221.map.gz | 11.9 MB |  EMDB map data format EMDB map data format | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Header (meta data) |  emd-3221-v30.xml emd-3221-v30.xml emd-3221.xml emd-3221.xml | 11 KB 11 KB | Display Display |  EMDB header EMDB header |
| Images |  EMD-1-3221.png EMD-1-3221.png | 227.8 KB | ||
| Archive directory |  http://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/structures/EMD-3221 http://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/structures/EMD-3221 ftp://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/structures/EMD-3221 ftp://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/structures/EMD-3221 | HTTPS FTP |
-Related structure data
| Related structure data |  5flxMC 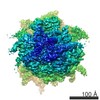 3223C  3224C  3225C  3226C M: atomic model generated by this map C: citing same article ( |
|---|---|
| Similar structure data |
- Links
Links
| EMDB pages |  EMDB (EBI/PDBe) / EMDB (EBI/PDBe) /  EMDataResource EMDataResource |
|---|---|
| Related items in Molecule of the Month |
- Map
Map
| File |  Download / File: emd_3221.map.gz / Format: CCP4 / Size: 204.4 MB / Type: IMAGE STORED AS FLOATING POINT NUMBER (4 BYTES) Download / File: emd_3221.map.gz / Format: CCP4 / Size: 204.4 MB / Type: IMAGE STORED AS FLOATING POINT NUMBER (4 BYTES) | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Annotation | Reconstruction of ribosome complex | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Projections & slices | Image control
Images are generated by Spider. | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Voxel size | X=Y=Z: 1.07 Å | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Density |
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Symmetry | Space group: 1 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Details | EMDB XML:
CCP4 map header:
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
-Supplemental data
- Sample components
Sample components
-Entire : Mammalian 80S-HCV-IRES complex, classical
| Entire | Name: Mammalian 80S-HCV-IRES complex, classical |
|---|---|
| Components |
|
-Supramolecule #1000: Mammalian 80S-HCV-IRES complex, classical
| Supramolecule | Name: Mammalian 80S-HCV-IRES complex, classical / type: sample / ID: 1000 / Number unique components: 2 |
|---|---|
| Molecular weight | Theoretical: 4.6 MDa |
-Supramolecule #1: 80S ribosome
| Supramolecule | Name: 80S ribosome / type: complex / ID: 1 / Recombinant expression: No / Ribosome-details: ribosome-eukaryote: ALL |
|---|---|
| Source (natural) | Organism:  |
| Molecular weight | Theoretical: 4.5 MDa |
-Macromolecule #1: HCV-IRES
| Macromolecule | Name: HCV-IRES / type: rna / ID: 1 / Classification: OTHER / Structure: DOUBLE HELIX / Synthetic?: Yes |
|---|---|
| Source (natural) | Organism:  Hepatitis C virus / synonym: HCV Hepatitis C virus / synonym: HCV |
| Molecular weight | Theoretical: 162 KDa |
| Sequence | String: GCCAGCCCCC UGAUGGGGGC GACACUCCAC CAUGAAUCAC UCCCCUGUGA GGAACUACUG UCUUCACGCA GAAAGCGUCU AGCCAUGGCG UUAGUAUGAG UGUCGUGCAG CCUCCAGGAC CCCCCCUCCC GGGAGAGCCA UAGUGGUCUG CGGAACCGGU GAGUACACCG ...String: GCCAGCCCCC UGAUGGGGGC GACACUCCAC CAUGAAUCAC UCCCCUGUGA GGAACUACUG UCUUCACGCA GAAAGCGUCU AGCCAUGGCG UUAGUAUGAG UGUCGUGCAG CCUCCAGGAC CCCCCCUCCC GGGAGAGCCA UAGUGGUCUG CGGAACCGGU GAGUACACCG GAAUUGCCAG GACGACCGGG UCCUUUCUUG GAUAAACCCG CUCAAUGCCU GGAGAUUUGG GCGUGCCCCC GCAAGACUGC UAGCCGAGUA GUGUUGGGUC GCGAAAGGCC UUGUGGUACU GCCUGAUAGG GUGCUUGCGA GUGCCCCGGG AGGUCUCGUA GACCGUGCAC CAUGAGCACG AAUCCUAAAC CUCAAAGAAA AACCAAACGU AACACCAACC GUCGCCCACA GGACGUCAAG UUCCCGGGUG GCGGUCUAGA CGCCGAGAUC AGAAAUCCCU CUCUCGGAUC GCAUUUGGAC UUCUGCCUUC GGGCACCACG GUCGGAUCCG AAUU |
-Experimental details
-Structure determination
| Method | cryo EM |
|---|---|
 Processing Processing | single particle reconstruction |
| Aggregation state | particle |
- Sample preparation
Sample preparation
| Concentration | 0.15 mg/mL |
|---|---|
| Buffer | pH: 7.6 Details: 20mM Tris-HCl, 7.5mM MgCl2, 100mM KCl, 0.2mM spermidine, 2mM DTT |
| Grid | Details: Quantifoil R3-3 Cu 300 mesh with 2 nm carbon support film |
| Vitrification | Cryogen name: ETHANE / Chamber humidity: 100 % / Chamber temperature: 93 K / Instrument: FEI VITROBOT MARK I / Method: blot for 2-4 seconds before plunging |
- Electron microscopy
Electron microscopy
| Microscope | FEI TITAN KRIOS |
|---|---|
| Date | Oct 16, 2014 |
| Image recording | Category: CCD / Film or detector model: FEI FALCON II (4k x 4k) / Number real images: 7707 / Average electron dose: 20 e/Å2 / Details: Automated data collection on using EPU |
| Electron beam | Acceleration voltage: 300 kV / Electron source:  FIELD EMISSION GUN FIELD EMISSION GUN |
| Electron optics | Calibrated magnification: 130293 / Illumination mode: FLOOD BEAM / Imaging mode: BRIGHT FIELD / Cs: 2.7 mm / Nominal defocus max: 4.0 µm / Nominal defocus min: 1.0 µm / Nominal magnification: 75000 |
| Sample stage | Specimen holder model: FEI TITAN KRIOS AUTOGRID HOLDER |
| Experimental equipment |  Model: Titan Krios / Image courtesy: FEI Company |
- Image processing
Image processing
| CTF correction | Details: CTFFIND3 |
|---|---|
| Final reconstruction | Applied symmetry - Point group: C1 (asymmetric) / Resolution.type: BY AUTHOR / Resolution: 3.9 Å / Resolution method: OTHER / Software - Name: spider, sparx Details: To avoid overfitting, the data was refined in a resolution-limited scheme using SPIDER. A final local refinement and the final reconstruction were calculated in Sparx. Number images used: 171820 |
 Movie
Movie Controller
Controller




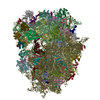


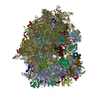
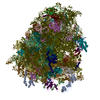































 Z (Sec.)
Z (Sec.) X (Row.)
X (Row.) Y (Col.)
Y (Col.)