+ Open data
Open data
- Basic information
Basic information
| Entry | 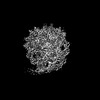 | |||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
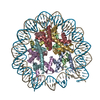
| Title | Telomeric mononucleosome | |||||||||
 Map data Map data | ||||||||||
 Sample Sample |
| |||||||||
 Keywords Keywords | Telomere / nucleosome / chromatin / DNA BINDING PROTEIN / DNA BINDING PROTEIN-DNA complex | |||||||||
| Function / homology |  Function and homology information Function and homology informationnegative regulation of megakaryocyte differentiation / protein localization to CENP-A containing chromatin / Chromatin modifying enzymes / Replacement of protamines by nucleosomes in the male pronucleus / CENP-A containing nucleosome / Packaging Of Telomere Ends / Recognition and association of DNA glycosylase with site containing an affected purine / Cleavage of the damaged purine / Deposition of new CENPA-containing nucleosomes at the centromere / nucleosomal DNA binding ...negative regulation of megakaryocyte differentiation / protein localization to CENP-A containing chromatin / Chromatin modifying enzymes / Replacement of protamines by nucleosomes in the male pronucleus / CENP-A containing nucleosome / Packaging Of Telomere Ends / Recognition and association of DNA glycosylase with site containing an affected purine / Cleavage of the damaged purine / Deposition of new CENPA-containing nucleosomes at the centromere / nucleosomal DNA binding / Recognition and association of DNA glycosylase with site containing an affected pyrimidine / Cleavage of the damaged pyrimidine / Inhibition of DNA recombination at telomere / telomere organization / Meiotic synapsis / Interleukin-7 signaling / RNA Polymerase I Promoter Opening / epigenetic regulation of gene expression / Assembly of the ORC complex at the origin of replication / SUMOylation of chromatin organization proteins / Regulation of endogenous retroelements by the Human Silencing Hub (HUSH) complex / DNA methylation / Condensation of Prophase Chromosomes / SIRT1 negatively regulates rRNA expression / Chromatin modifications during the maternal to zygotic transition (MZT) / ERCC6 (CSB) and EHMT2 (G9a) positively regulate rRNA expression / HCMV Late Events / innate immune response in mucosa / PRC2 methylates histones and DNA / Regulation of endogenous retroelements by KRAB-ZFP proteins / Defective pyroptosis / Regulation of endogenous retroelements by Piwi-interacting RNAs (piRNAs) / HDACs deacetylate histones / Nonhomologous End-Joining (NHEJ) / RNA Polymerase I Promoter Escape / Transcriptional regulation by small RNAs / Formation of the beta-catenin:TCF transactivating complex / RUNX1 regulates genes involved in megakaryocyte differentiation and platelet function / NoRC negatively regulates rRNA expression / Activated PKN1 stimulates transcription of AR (androgen receptor) regulated genes KLK2 and KLK3 / G2/M DNA damage checkpoint / HDMs demethylate histones / B-WICH complex positively regulates rRNA expression / DNA Damage/Telomere Stress Induced Senescence / heterochromatin formation / PKMTs methylate histone lysines / Metalloprotease DUBs / Meiotic recombination / Pre-NOTCH Transcription and Translation / RMTs methylate histone arginines / Activation of anterior HOX genes in hindbrain development during early embryogenesis / HCMV Early Events / Transcriptional regulation of granulopoiesis / structural constituent of chromatin / UCH proteinases / antimicrobial humoral immune response mediated by antimicrobial peptide / nucleosome / nucleosome assembly / E3 ubiquitin ligases ubiquitinate target proteins / antibacterial humoral response / Recruitment and ATM-mediated phosphorylation of repair and signaling proteins at DNA double strand breaks / chromatin organization / RUNX1 regulates transcription of genes involved in differentiation of HSCs / Factors involved in megakaryocyte development and platelet production / HATs acetylate histones / Processing of DNA double-strand break ends / gene expression / Senescence-Associated Secretory Phenotype (SASP) / Oxidative Stress Induced Senescence / defense response to Gram-negative bacterium / Estrogen-dependent gene expression / killing of cells of another organism / chromosome, telomeric region / Ub-specific processing proteases / defense response to Gram-positive bacterium / cadherin binding / protein heterodimerization activity / Amyloid fiber formation / negative regulation of cell population proliferation / protein-containing complex / DNA binding / RNA binding / extracellular space / extracellular exosome / extracellular region / nucleoplasm / membrane / nucleus / cytosol Similarity search - Function | |||||||||
| Biological species |  Homo sapiens (human) Homo sapiens (human) | |||||||||
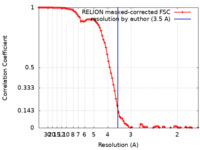
| Method | single particle reconstruction / cryo EM / Resolution: 3.5 Å | |||||||||
 Authors Authors | Soman A | |||||||||
| Funding support |  Singapore, 1 items Singapore, 1 items
| |||||||||
 Citation Citation |  Journal: Nature / Year: 2022 Journal: Nature / Year: 2022Title: Columnar structure of human telomeric chromatin. Authors: Aghil Soman / Sook Yi Wong / Nikolay Korolev / Wahyu Surya / Simon Lattmann / Vinod K Vogirala / Qinming Chen / Nikolay V Berezhnoy / John van Noort / Daniela Rhodes / Lars Nordenskiöld /    Abstract: Telomeres, the ends of eukaryotic chromosomes, play pivotal parts in ageing and cancer and are targets of DNA damage and the DNA damage response. Little is known about the structure of telomeric ...Telomeres, the ends of eukaryotic chromosomes, play pivotal parts in ageing and cancer and are targets of DNA damage and the DNA damage response. Little is known about the structure of telomeric chromatin at the molecular level. Here we used negative stain electron microscopy and single-molecule magnetic tweezers to characterize 3-kbp-long telomeric chromatin fibres. We also obtained the cryogenic electron microscopy structure of the condensed telomeric tetranucleosome and its dinucleosome unit. The structure displayed close stacking of nucleosomes with a columnar arrangement, and an unusually short nucleosome repeat length that comprised about 132 bp DNA wound in a continuous superhelix around histone octamers. This columnar structure is primarily stabilized by the H2A carboxy-terminal and histone amino-terminal tails in a synergistic manner. The columnar conformation results in exposure of the DNA helix, which may make it susceptible to both DNA damage and the DNA damage response. The conformation also exists in an alternative open state, in which one nucleosome is unstacked and flipped out, which exposes the acidic patch of the histone surface. The structural features revealed in this work suggest mechanisms by which protein factors involved in telomere maintenance can access telomeric chromatin in its compact form. | |||||||||
| History |
|
- Structure visualization
Structure visualization
| Supplemental images |
|---|
- Downloads & links
Downloads & links
-EMDB archive
| Map data |  emd_31806.map.gz emd_31806.map.gz | 59.8 MB |  EMDB map data format EMDB map data format | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Header (meta data) |  emd-31806-v30.xml emd-31806-v30.xml emd-31806.xml emd-31806.xml | 21 KB 21 KB | Display Display |  EMDB header EMDB header |
| FSC (resolution estimation) |  emd_31806_fsc.xml emd_31806_fsc.xml | 9.2 KB | Display |  FSC data file FSC data file |
| Images |  emd_31806.png emd_31806.png | 58.4 KB | ||
| Masks |  emd_31806_msk_1.map emd_31806_msk_1.map | 64 MB |  Mask map Mask map | |
| Filedesc metadata |  emd-31806.cif.gz emd-31806.cif.gz | 6 KB | ||
| Others |  emd_31806_half_map_1.map.gz emd_31806_half_map_1.map.gz emd_31806_half_map_2.map.gz emd_31806_half_map_2.map.gz | 49.7 MB 49.7 MB | ||
| Archive directory |  http://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/structures/EMD-31806 http://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/structures/EMD-31806 ftp://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/structures/EMD-31806 ftp://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/structures/EMD-31806 | HTTPS FTP |
-Validation report
| Summary document |  emd_31806_validation.pdf.gz emd_31806_validation.pdf.gz | 1020.3 KB | Display |  EMDB validaton report EMDB validaton report |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Full document |  emd_31806_full_validation.pdf.gz emd_31806_full_validation.pdf.gz | 1019.9 KB | Display | |
| Data in XML |  emd_31806_validation.xml.gz emd_31806_validation.xml.gz | 16.1 KB | Display | |
| Data in CIF |  emd_31806_validation.cif.gz emd_31806_validation.cif.gz | 20.9 KB | Display | |
| Arichive directory |  https://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/validation_reports/EMD-31806 https://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/validation_reports/EMD-31806 ftp://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/validation_reports/EMD-31806 ftp://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/validation_reports/EMD-31806 | HTTPS FTP |
-Related structure data
| Related structure data |  7v90MC  7v96C  7v9cC  7v9jC  7v9kC  7v9sC  7va4C M: atomic model generated by this map C: citing same article ( |
|---|---|
| Similar structure data | Similarity search - Function & homology  F&H Search F&H Search |
- Links
Links
| EMDB pages |  EMDB (EBI/PDBe) / EMDB (EBI/PDBe) /  EMDataResource EMDataResource |
|---|---|
| Related items in Molecule of the Month |
- Map
Map
| File |  Download / File: emd_31806.map.gz / Format: CCP4 / Size: 64 MB / Type: IMAGE STORED AS FLOATING POINT NUMBER (4 BYTES) Download / File: emd_31806.map.gz / Format: CCP4 / Size: 64 MB / Type: IMAGE STORED AS FLOATING POINT NUMBER (4 BYTES) | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Projections & slices | Image control
Images are generated by Spider. | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Voxel size | X=Y=Z: 0.858 Å | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
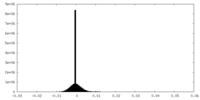
| Density |
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Symmetry | Space group: 1 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Details | EMDB XML:
|
-Supplemental data
-Mask #1
| File |  emd_31806_msk_1.map emd_31806_msk_1.map | ||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Projections & Slices |
| ||||||||||||
| Density Histograms |
-Half map: #1
| File | emd_31806_half_map_1.map | ||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Projections & Slices |
| ||||||||||||
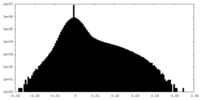
| Density Histograms |
-Half map: #2
| File | emd_31806_half_map_2.map | ||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Projections & Slices |
| ||||||||||||
| Density Histograms |
- Sample components
Sample components
-Entire : Telomeric Mononucleosome
| Entire | Name: Telomeric Mononucleosome |
|---|---|
| Components |
|
-Supramolecule #1: Telomeric Mononucleosome
| Supramolecule | Name: Telomeric Mononucleosome / type: complex / ID: 1 / Parent: 0 / Macromolecule list: all Details: Mononucleosome in open statae in a telomeric tetranucleosome |
|---|---|
| Source (natural) | Organism:  Homo sapiens (human) Homo sapiens (human) |
-Macromolecule #1: Histone H3.1
| Macromolecule | Name: Histone H3.1 / type: protein_or_peptide / ID: 1 / Number of copies: 2 / Enantiomer: LEVO |
|---|---|
| Source (natural) | Organism:  Homo sapiens (human) Homo sapiens (human) |
| Molecular weight | Theoretical: 15.437167 KDa |
| Recombinant expression | Organism:  |
| Sequence | String: MARTKQTARK STGGKAPRKQ LATKAARKSA PATGGVKKPH RYRPGTVALR EIRRYQKSTE LLIRKLPFQR LVREIAQDFK TDLRFQSSA VMALQEACEA YLVGLFEDTN LCAIHAKRVT IMPKDIQLAR RIRGERA UniProtKB: Histone H3.1 |
-Macromolecule #2: Histone H4
| Macromolecule | Name: Histone H4 / type: protein_or_peptide / ID: 2 / Number of copies: 2 / Enantiomer: LEVO |
|---|---|
| Source (natural) | Organism:  Homo sapiens (human) Homo sapiens (human) |
| Molecular weight | Theoretical: 11.394426 KDa |
| Recombinant expression | Organism:  |
| Sequence | String: MSGRGKGGKG LGKGGAKRHR KVLRDNIQGI TKPAIRRLAR RGGVKRISGL IYEETRGVLK VFLENVIRDA VTYTEHAKRK TVTAMDVVY ALKRQGRTLY GFGG UniProtKB: Histone H4 |
-Macromolecule #3: Histone H2A type 1-B/E
| Macromolecule | Name: Histone H2A type 1-B/E / type: protein_or_peptide / ID: 3 / Number of copies: 2 / Enantiomer: LEVO |
|---|---|
| Source (natural) | Organism:  Homo sapiens (human) Homo sapiens (human) |
| Molecular weight | Theoretical: 14.165551 KDa |
| Recombinant expression | Organism:  |
| Sequence | String: MSGRGKQGGK ARAKAKTRSS RAGLQFPVGR VHRLLRKGNY SERVGAGAPV YLAAVLEYLT AEILELAGNA ARDNKKTRII PRHLQLAIR NDEELNKLLG RVTIAQGGVL PNIQAVLLPK KTESHHKAKG K UniProtKB: Histone H2A type 1-B/E |
-Macromolecule #4: Histone H2B type 1-K
| Macromolecule | Name: Histone H2B type 1-K / type: protein_or_peptide / ID: 4 / Number of copies: 2 / Enantiomer: LEVO |
|---|---|
| Source (natural) | Organism:  Homo sapiens (human) Homo sapiens (human) |
| Molecular weight | Theoretical: 11.151906 KDa |
| Recombinant expression | Organism:  |
| Sequence | String: KKRKRSRKES YSVYVYKVLK QVHPDTGISS KAMGIMNSFV NDIFERIAGE ASRLAHYNKR STITSREIQT AVRLLLPGEL AKHAVSEGT KAVTKYTSAK UniProtKB: Histone H2B type 1-K |
-Macromolecule #5: DNA (145-mer)
| Macromolecule | Name: DNA (145-mer) / type: dna / ID: 5 / Number of copies: 1 / Classification: DNA |
|---|---|
| Source (natural) | Organism:  Homo sapiens (human) Homo sapiens (human) |
| Molecular weight | Theoretical: 46.105293 KDa |
| Sequence | String: (DG)(DG)(DG)(DT)(DT)(DA)(DG)(DG)(DG)(DT) (DT)(DA)(DG)(DG)(DG)(DT)(DT)(DA)(DG)(DG) (DG)(DT)(DT)(DA)(DG)(DG)(DG)(DT)(DT) (DA)(DG)(DG)(DG)(DT)(DT)(DA)(DG)(DG)(DG) (DT) (DT)(DA)(DG)(DG)(DG)(DT) ...String: (DG)(DG)(DG)(DT)(DT)(DA)(DG)(DG)(DG)(DT) (DT)(DA)(DG)(DG)(DG)(DT)(DT)(DA)(DG)(DG) (DG)(DT)(DT)(DA)(DG)(DG)(DG)(DT)(DT) (DA)(DG)(DG)(DG)(DT)(DT)(DA)(DG)(DG)(DG) (DT) (DT)(DA)(DG)(DG)(DG)(DT)(DT)(DA) (DG)(DG)(DG)(DT)(DT)(DA)(DG)(DG)(DG)(DT) (DT)(DA) (DG)(DG)(DG)(DT)(DT)(DA)(DG) (DG)(DG)(DT)(DT)(DA)(DG)(DG)(DG)(DT)(DT) (DA)(DG)(DG) (DG)(DT)(DT)(DA)(DG)(DG) (DG)(DT)(DT)(DA)(DG)(DG)(DG)(DT)(DT)(DA) (DG)(DG)(DG)(DT) (DT)(DA)(DG)(DG)(DG) (DT)(DT)(DA)(DG)(DG)(DG)(DT)(DT)(DA)(DG) (DG)(DG)(DT)(DT)(DA) (DG)(DG)(DG)(DT) (DT)(DA)(DG)(DG)(DG)(DT)(DT)(DA)(DG)(DG) (DG)(DT)(DT)(DA)(DG)(DG) (DG)(DT)(DT) (DA)(DG) |
-Macromolecule #6: DNA (145-mer)
| Macromolecule | Name: DNA (145-mer) / type: dna / ID: 6 / Number of copies: 1 / Classification: DNA |
|---|---|
| Source (natural) | Organism:  Homo sapiens (human) Homo sapiens (human) |
| Molecular weight | Theoretical: 43.399848 KDa |
| Sequence | String: (DC)(DT)(DA)(DA)(DC)(DC)(DC)(DT)(DA)(DA) (DC)(DC)(DC)(DT)(DA)(DA)(DC)(DC)(DC)(DT) (DA)(DA)(DC)(DC)(DC)(DT)(DA)(DA)(DC) (DC)(DC)(DT)(DA)(DA)(DC)(DC)(DC)(DT)(DA) (DA) (DC)(DC)(DC)(DT)(DA)(DA) ...String: (DC)(DT)(DA)(DA)(DC)(DC)(DC)(DT)(DA)(DA) (DC)(DC)(DC)(DT)(DA)(DA)(DC)(DC)(DC)(DT) (DA)(DA)(DC)(DC)(DC)(DT)(DA)(DA)(DC) (DC)(DC)(DT)(DA)(DA)(DC)(DC)(DC)(DT)(DA) (DA) (DC)(DC)(DC)(DT)(DA)(DA)(DC)(DC) (DC)(DT)(DA)(DA)(DC)(DC)(DC)(DT)(DA)(DA) (DC)(DC) (DC)(DT)(DA)(DA)(DC)(DC)(DC) (DT)(DA)(DA)(DC)(DC)(DC)(DT)(DA)(DA)(DC) (DC)(DC)(DT) (DA)(DA)(DC)(DC)(DC)(DT) (DA)(DA)(DC)(DC)(DC)(DT)(DA)(DA)(DC)(DC) (DC)(DT)(DA)(DA) (DC)(DC)(DC)(DT)(DA) (DA)(DC)(DC)(DC)(DT)(DA)(DA)(DC)(DC)(DC) (DT)(DA)(DA)(DC)(DC) (DC)(DT)(DA)(DA) (DC)(DC)(DC)(DT)(DA)(DA)(DC)(DC)(DC)(DT) (DA)(DA)(DC)(DC)(DC)(DT) (DA)(DA)(DC) (DC)(DC) |
-Experimental details
-Structure determination
| Method | cryo EM |
|---|---|
 Processing Processing | single particle reconstruction |
| Aggregation state | particle |
- Sample preparation
Sample preparation
| Concentration | 1 mg/mL |
|---|---|
| Buffer | pH: 6 |
| Grid | Model: Quantifoil R1.2/1.3 / Material: COPPER / Mesh: 400 / Support film - Material: CARBON / Support film - topology: HOLEY / Pretreatment - Type: GLOW DISCHARGE / Pretreatment - Time: 60 sec. |
| Vitrification | Cryogen name: ETHANE / Chamber humidity: 100 % |
- Electron microscopy
Electron microscopy
| Microscope | FEI TITAN KRIOS |
|---|---|
| Image recording | Film or detector model: GATAN K3 (6k x 4k) / Average electron dose: 50.0 e/Å2 |
| Electron beam | Acceleration voltage: 300 kV / Electron source:  FIELD EMISSION GUN FIELD EMISSION GUN |
| Electron optics | Illumination mode: OTHER / Imaging mode: BRIGHT FIELD |
| Experimental equipment |  Model: Titan Krios / Image courtesy: FEI Company |
 Movie
Movie Controller
Controller




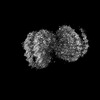


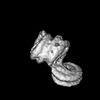
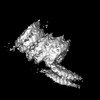












 Z (Sec.)
Z (Sec.) Y (Row.)
Y (Row.) X (Col.)
X (Col.)