[English] 日本語
 Yorodumi
Yorodumi- EMDB-2541: cryo-electron microscopy of microtubule-bound human kinesin-5 mot... -
+ Open data
Open data
- Basic information
Basic information
| Entry | Database: EMDB / ID: EMD-2541 | |||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
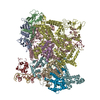
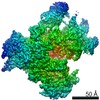
| Title | cryo-electron microscopy of microtubule-bound human kinesin-5 motor domain in the AMPPNP state (gold cluster in the N-terminus A9C). | |||||||||
 Map data Map data | Reconstruction of microtubule-bound human kinesin-5 motor domain in presence of AMPPNP and with a gold cluster covalently attached to the residue A9C | |||||||||
 Sample Sample |
| |||||||||
 Keywords Keywords | cryo-electron microscopy / kinesins / microtubules / mitosis / mechanochemistry | |||||||||
| Function / homology |  Function and homology information Function and homology informationspindle elongation / regulation of mitotic centrosome separation / plus-end-directed microtubule motor activity / Kinesins / mitotic centrosome separation / positive regulation of axon guidance / kinesin complex / microtubule motor activity / spindle organization / COPI-dependent Golgi-to-ER retrograde traffic ...spindle elongation / regulation of mitotic centrosome separation / plus-end-directed microtubule motor activity / Kinesins / mitotic centrosome separation / positive regulation of axon guidance / kinesin complex / microtubule motor activity / spindle organization / COPI-dependent Golgi-to-ER retrograde traffic / microtubule-based movement / mitotic spindle assembly / microtubule-based process / MHC class II antigen presentation / mitotic spindle organization / structural constituent of cytoskeleton / microtubule cytoskeleton organization / spindle / neuron migration / spindle pole / mitotic spindle / mitotic cell cycle / microtubule cytoskeleton / microtubule binding / Hydrolases; Acting on acid anhydrides; Acting on GTP to facilitate cellular and subcellular movement / microtubule / ciliary basal body / intracellular membrane-bounded organelle / protein heterodimerization activity / hydrolase activity / cell division / GTPase activity / protein kinase binding / GTP binding / protein-containing complex / ATP binding / metal ion binding / membrane / nucleus / cytoplasm / cytosol Similarity search - Function | |||||||||
| Biological species |   Homo sapiens (human) Homo sapiens (human) | |||||||||
| Method | single particle reconstruction / cryo EM / Resolution: 25.0 Å | |||||||||
 Authors Authors | GOULET A / MAJOR J / JUN Y / GROSS SP / ROSENFELD SR / MOORES CA | |||||||||
 Citation Citation |  Journal: Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A / Year: 2014 Journal: Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A / Year: 2014Title: Comprehensive structural model of the mechanochemical cycle of a mitotic motor highlights molecular adaptations in the kinesin family. Authors: Adeline Goulet / Jennifer Major / Yonggun Jun / Steven P Gross / Steven S Rosenfeld / Carolyn A Moores /  Abstract: Kinesins are responsible for a wide variety of microtubule-based, ATP-dependent functions. Their motor domain drives these activities, but the molecular adaptations that specify these diverse and ...Kinesins are responsible for a wide variety of microtubule-based, ATP-dependent functions. Their motor domain drives these activities, but the molecular adaptations that specify these diverse and essential cellular activities are poorly understood. It has been assumed that the first identified kinesin--the transport motor kinesin-1--is the mechanistic paradigm for the entire superfamily, but accumulating evidence suggests otherwise. To address the deficits in our understanding of the molecular basis of functional divergence within the kinesin superfamily, we studied kinesin-5s, which are essential mitotic motors whose inhibition blocks cell division. Using cryo-electron microscopy and determination of structure at subnanometer resolution, we have visualized conformations of microtubule-bound human kinesin-5 motor domain at successive steps in its ATPase cycle. After ATP hydrolysis, nucleotide-dependent conformational changes in the active site are allosterically propagated into rotations of the motor domain and uncurling of the drug-binding loop L5. In addition, the mechanical neck-linker element that is crucial for motor stepping undergoes discrete, ordered displacements. We also observed large reorientations of the motor N terminus that indicate its importance for kinesin-5 function through control of neck-linker conformation. A kinesin-5 mutant lacking this N terminus is enzymatically active, and ATP-dependent neck-linker movement and motility are defective, although not ablated. All these aspects of kinesin-5 mechanochemistry are distinct from kinesin-1. Our findings directly demonstrate the regulatory role of the kinesin-5 N terminus in collaboration with the motor's structured neck-linker and highlight the multiple adaptations within kinesin motor domains that tune their mechanochemistries according to distinct functional requirements. | |||||||||
| History |
|
- Structure visualization
Structure visualization
| Movie |
 Movie viewer Movie viewer |
|---|---|
| Structure viewer | EM map:  SurfView SurfView Molmil Molmil Jmol/JSmol Jmol/JSmol |
| Supplemental images |
- Downloads & links
Downloads & links
-EMDB archive
| Map data |  emd_2541.map.gz emd_2541.map.gz | 309.1 KB |  EMDB map data format EMDB map data format | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Header (meta data) |  emd-2541-v30.xml emd-2541-v30.xml emd-2541.xml emd-2541.xml | 11.2 KB 11.2 KB | Display Display |  EMDB header EMDB header |
| Images |  emd_2541.jpg emd_2541.jpg | 157 KB | ||
| Archive directory |  http://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/structures/EMD-2541 http://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/structures/EMD-2541 ftp://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/structures/EMD-2541 ftp://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/structures/EMD-2541 | HTTPS FTP |
-Related structure data
| Related structure data |  2533C  2534C  2535C  2536C  2537C  2538C  2539C  2540C  2542C  4ck5C  4ck6C  4ck7C C: citing same article ( |
|---|---|
| Similar structure data |
- Links
Links
| EMDB pages |  EMDB (EBI/PDBe) / EMDB (EBI/PDBe) /  EMDataResource EMDataResource |
|---|---|
| Related items in Molecule of the Month |
- Map
Map
| File |  Download / File: emd_2541.map.gz / Format: CCP4 / Size: 326.2 KB / Type: IMAGE STORED AS FLOATING POINT NUMBER (4 BYTES) Download / File: emd_2541.map.gz / Format: CCP4 / Size: 326.2 KB / Type: IMAGE STORED AS FLOATING POINT NUMBER (4 BYTES) | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Annotation | Reconstruction of microtubule-bound human kinesin-5 motor domain in presence of AMPPNP and with a gold cluster covalently attached to the residue A9C | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Projections & slices | Image control
Images are generated by Spider. | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Voxel size | X=Y=Z: 2.8 Å | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
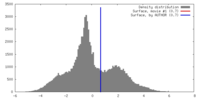
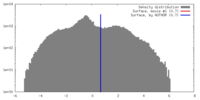
| Density |
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Symmetry | Space group: 1 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Details | EMDB XML:
CCP4 map header:
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
-Supplemental data
- Sample components
Sample components
-Entire : 13-protofilament microtubule-bound human kinesin-5 motor domain w...
| Entire | Name: 13-protofilament microtubule-bound human kinesin-5 motor domain with AMPPNP bound. A gold cluster is attached to the N-terminus (A9C). |
|---|---|
| Components |
|
-Supramolecule #1000: 13-protofilament microtubule-bound human kinesin-5 motor domain w...
| Supramolecule | Name: 13-protofilament microtubule-bound human kinesin-5 motor domain with AMPPNP bound. A gold cluster is attached to the N-terminus (A9C). type: sample / ID: 1000 Oligomeric state: 13-protofilament microtubule with one kinesin-5 motor domain bound every tubulin heterodimers Number unique components: 3 |
|---|
-Macromolecule #1: alpha tubulin
| Macromolecule | Name: alpha tubulin / type: protein_or_peptide / ID: 1 / Name.synonym: TUBULIN ALPHA-1D CHAIN / Recombinant expression: No |
|---|---|
| Source (natural) | Organism:  |
| Sequence | UniProtKB: Tubulin alpha-1D chain / InterPro: Alpha tubulin |
-Macromolecule #2: beta tubulin
| Macromolecule | Name: beta tubulin / type: protein_or_peptide / ID: 2 / Name.synonym: TUBULIN BETA-2B CHAIN / Recombinant expression: No |
|---|---|
| Source (natural) | Organism:  |
| Sequence | UniProtKB: Tubulin beta-2B chain / InterPro: Beta tubulin, autoregulation binding site |
-Macromolecule #3: Kinesin-5 motor domain
| Macromolecule | Name: Kinesin-5 motor domain / type: protein_or_peptide / ID: 3 / Name.synonym: KINESIN-LIKE PROTEIN KIF11 Details: cys-lite mutant containing the substitution A9C, undecagold cluster was attached to the specific cysteine residue in the N-terminus (A9C) Recombinant expression: Yes |
|---|---|
| Source (natural) | Organism:  Homo sapiens (human) / synonym: Human Homo sapiens (human) / synonym: Human |
| Recombinant expression | Organism:  |
| Sequence | UniProtKB: Kinesin-like protein KIF11 / InterPro: Kinesin motor domain, conserved site |
-Experimental details
-Structure determination
| Method | cryo EM |
|---|---|
 Processing Processing | single particle reconstruction |
| Aggregation state | particle |
- Sample preparation
Sample preparation
| Buffer | pH: 6.8 / Details: 80 mM PIPES, 5 mM MgCl2, 1 mM EGTA, 5 mM AMPPNP |
|---|---|
| Grid | Details: 400 mesh holey carbon grids |
| Vitrification | Cryogen name: ETHANE / Chamber humidity: 100 % / Instrument: FEI VITROBOT MARK I / Method: chamber at 24 degrees C, blot 3.5 sec |
- Electron microscopy
Electron microscopy
| Microscope | FEI TECNAI F20 |
|---|---|
| Temperature | Average: 90 K |
| Alignment procedure | Legacy - Astigmatism: Objective lens astigmatism was corrected at 150,000 times magnification |
| Date | Apr 5, 2013 |
| Image recording | Category: FILM / Film or detector model: KODAK SO-163 FILM / Digitization - Scanner: ZEISS SCAI / Digitization - Sampling interval: 7 µm / Number real images: 25 / Average electron dose: 18 e/Å2 / Bits/pixel: 8 |
| Electron beam | Acceleration voltage: 200 kV / Electron source:  FIELD EMISSION GUN FIELD EMISSION GUN |
| Electron optics | Illumination mode: FLOOD BEAM / Imaging mode: BRIGHT FIELD / Cs: 2.0 mm / Nominal defocus max: 2.6 µm / Nominal defocus min: 1.1 µm / Nominal magnification: 50000 |
| Sample stage | Specimen holder model: GATAN LIQUID NITROGEN |
| Experimental equipment |  Model: Tecnai F20 / Image courtesy: FEI Company |
- Image processing
Image processing
| Details | The particles were selected along individual microtubules. |
|---|---|
| CTF correction | Details: FREALIGN |
| Final reconstruction | Applied symmetry - Point group: C1 (asymmetric) / Resolution.type: BY AUTHOR / Resolution: 25.0 Å / Resolution method: OTHER / Software - Name: SPIDER, FREALIGN Details: Approximately 21,000 asymmetric units were averaged in the final reconstruction. Number images used: 1615 |
 Movie
Movie Controller
Controller



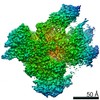

















 Z (Sec.)
Z (Sec.) Y (Row.)
Y (Row.) X (Col.)
X (Col.)