+Search query
-Structure paper
| Title | Comprehensive structural model of the mechanochemical cycle of a mitotic motor highlights molecular adaptations in the kinesin family. |
|---|---|
| Journal, issue, pages | Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A, Vol. 111, Issue 5, Page 1837-1842, Year 2014 |
| Publish date | Feb 4, 2014 |
 Authors Authors | Adeline Goulet / Jennifer Major / Yonggun Jun / Steven P Gross / Steven S Rosenfeld / Carolyn A Moores /  |
| PubMed Abstract | Kinesins are responsible for a wide variety of microtubule-based, ATP-dependent functions. Their motor domain drives these activities, but the molecular adaptations that specify these diverse and ...Kinesins are responsible for a wide variety of microtubule-based, ATP-dependent functions. Their motor domain drives these activities, but the molecular adaptations that specify these diverse and essential cellular activities are poorly understood. It has been assumed that the first identified kinesin--the transport motor kinesin-1--is the mechanistic paradigm for the entire superfamily, but accumulating evidence suggests otherwise. To address the deficits in our understanding of the molecular basis of functional divergence within the kinesin superfamily, we studied kinesin-5s, which are essential mitotic motors whose inhibition blocks cell division. Using cryo-electron microscopy and determination of structure at subnanometer resolution, we have visualized conformations of microtubule-bound human kinesin-5 motor domain at successive steps in its ATPase cycle. After ATP hydrolysis, nucleotide-dependent conformational changes in the active site are allosterically propagated into rotations of the motor domain and uncurling of the drug-binding loop L5. In addition, the mechanical neck-linker element that is crucial for motor stepping undergoes discrete, ordered displacements. We also observed large reorientations of the motor N terminus that indicate its importance for kinesin-5 function through control of neck-linker conformation. A kinesin-5 mutant lacking this N terminus is enzymatically active, and ATP-dependent neck-linker movement and motility are defective, although not ablated. All these aspects of kinesin-5 mechanochemistry are distinct from kinesin-1. Our findings directly demonstrate the regulatory role of the kinesin-5 N terminus in collaboration with the motor's structured neck-linker and highlight the multiple adaptations within kinesin motor domains that tune their mechanochemistries according to distinct functional requirements. |
 External links External links |  Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A / Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A /  PubMed:24449904 / PubMed:24449904 /  PubMed Central PubMed Central |
| Methods | EM (single particle) |
| Resolution | 9.2 - 25.0 Å |
| Structure data | EMDB-2533: Electron cryo-microscopy of microtubule-bound human kinesin-5 motor domain in the ADP.AlFx state.  EMDB-2534:  EMDB-2535:  EMDB-2536: EMDB-2537: cryo-electron microscopy of microtubule-bound human kinesin-5 motor domain in the ADP state  EMDB-2538:  EMDB-2539:  EMDB-2540:  EMDB-2541:  EMDB-2542: |
| Chemicals |  ChemComp-GTP:  ChemComp-GDP:  ChemComp-TA1:  ChemComp-MG:  ChemComp-ADP: 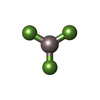 ChemComp-AF3: |
| Source |
|
 Keywords Keywords | MOTOR PROTEIN / KINESINS / MICROTUBULES / MITOSIS / MECHANOCHEMISTRY |
 Movie
Movie Controller
Controller Structure viewers
Structure viewers About Yorodumi Papers
About Yorodumi Papers





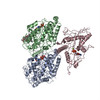

 homo sapiens (human)
homo sapiens (human)