[English] 日本語
 Yorodumi
Yorodumi- EMDB-23069: Structure of the S. cerevisiae phosphatidylcholine flippase Dnf1-... -
+ Open data
Open data
- Basic information
Basic information
| Entry | Database: EMDB / ID: EMD-23069 | |||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
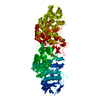
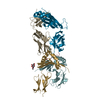
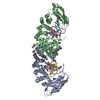
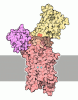
| Title | Structure of the S. cerevisiae phosphatidylcholine flippase Dnf1-Lem3 complex in the apo E1 state | |||||||||
 Map data Map data | Cryo-EM 3D map of the S. cerevisiae phosphatidylcholine flippase Dnf1-Lem3 complex in the apo E1 state | |||||||||
 Sample Sample |
| |||||||||
 Keywords Keywords | P4 ATPase / Phosphatidylcholine Flippases / TRANSLOCASE | |||||||||
| Function / homology |  Function and homology information Function and homology informationglycosylceramide flippase activity / mating projection tip membrane / phosphatidylcholine flippase activity / Ion transport by P-type ATPases / phosphatidylserine flippase activity / phospholipid-translocating ATPase complex / ceramide translocation / phosphatidylserine floppase activity / ATPase-coupled intramembrane lipid transporter activity / cell septum ...glycosylceramide flippase activity / mating projection tip membrane / phosphatidylcholine flippase activity / Ion transport by P-type ATPases / phosphatidylserine flippase activity / phospholipid-translocating ATPase complex / ceramide translocation / phosphatidylserine floppase activity / ATPase-coupled intramembrane lipid transporter activity / cell septum / phosphatidylethanolamine flippase activity / phosphatidylcholine floppase activity / cellular bud neck / P-type phospholipid transporter / phospholipid translocation / establishment or maintenance of cell polarity / membrane => GO:0016020 / Neutrophil degranulation / cell periphery / intracellular protein transport / endocytosis / endosome membrane / magnesium ion binding / endoplasmic reticulum / Golgi apparatus / ATP hydrolysis activity / mitochondrion / ATP binding / identical protein binding / plasma membrane Similarity search - Function | |||||||||
| Biological species |  | |||||||||
| Method | single particle reconstruction / cryo EM / Resolution: 3.1 Å | |||||||||
 Authors Authors | Bai L / You Q / Jain BK / Duan HD / Kovach A / Graham TR / Li H | |||||||||
| Funding support |  United States, 1 items United States, 1 items
| |||||||||
 Citation Citation |  Journal: Elife / Year: 2020 Journal: Elife / Year: 2020Title: Transport mechanism of P4 ATPase phosphatidylcholine flippases. Authors: Lin Bai / Qinglong You / Bhawik K Jain / H Diessel Duan / Amanda Kovach / Todd R Graham / Huilin Li /   Abstract: The P4 ATPases use ATP hydrolysis to transport large lipid substrates across lipid bilayers. The structures of the endosome- and Golgi-localized phosphatidylserine flippases-such as the yeast Drs2 ...The P4 ATPases use ATP hydrolysis to transport large lipid substrates across lipid bilayers. The structures of the endosome- and Golgi-localized phosphatidylserine flippases-such as the yeast Drs2 and human ATP8A1-have recently been reported. However, a substrate-binding site on the cytosolic side has not been found, and the transport mechanisms of P4 ATPases with other substrates are unknown. Here, we report structures of the Dnf1-Lem3 and Dnf2-Lem3 complexes. We captured substrate phosphatidylcholine molecules on both the exoplasmic and cytosolic sides and found that they have similar structures. Unexpectedly, Lem3 contributes to substrate binding. The conformational transitions of these phosphatidylcholine transporters match those of the phosphatidylserine transporters, suggesting a conserved mechanism among P4 ATPases. Dnf1/Dnf2 have a unique P domain helix-turn-helix insertion that is important for function. Therefore, P4 ATPases may have retained an overall transport mechanism while evolving distinct features for different lipid substrates. | |||||||||
| History |
|
- Structure visualization
Structure visualization
| Movie |
 Movie viewer Movie viewer |
|---|---|
| Structure viewer | EM map:  SurfView SurfView Molmil Molmil Jmol/JSmol Jmol/JSmol |
| Supplemental images |
- Downloads & links
Downloads & links
-EMDB archive
| Map data |  emd_23069.map.gz emd_23069.map.gz | 10.4 MB |  EMDB map data format EMDB map data format | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Header (meta data) |  emd-23069-v30.xml emd-23069-v30.xml emd-23069.xml emd-23069.xml | 16.7 KB 16.7 KB | Display Display |  EMDB header EMDB header |
| Images |  emd_23069.png emd_23069.png | 44 KB | ||
| Filedesc metadata |  emd-23069.cif.gz emd-23069.cif.gz | 7.3 KB | ||
| Archive directory |  http://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/structures/EMD-23069 http://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/structures/EMD-23069 ftp://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/structures/EMD-23069 ftp://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/structures/EMD-23069 | HTTPS FTP |
-Related structure data
| Related structure data |  7ky6MC  7ky5C  7ky7C  7ky8C  7ky9C  7kyaC  7kybC  7kycC C: citing same article ( M: atomic model generated by this map |
|---|---|
| Similar structure data |
- Links
Links
| EMDB pages |  EMDB (EBI/PDBe) / EMDB (EBI/PDBe) /  EMDataResource EMDataResource |
|---|---|
| Related items in Molecule of the Month |
- Map
Map
| File |  Download / File: emd_23069.map.gz / Format: CCP4 / Size: 83.7 MB / Type: IMAGE STORED AS FLOATING POINT NUMBER (4 BYTES) Download / File: emd_23069.map.gz / Format: CCP4 / Size: 83.7 MB / Type: IMAGE STORED AS FLOATING POINT NUMBER (4 BYTES) | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Annotation | Cryo-EM 3D map of the S. cerevisiae phosphatidylcholine flippase Dnf1-Lem3 complex in the apo E1 state | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Projections & slices | Image control
Images are generated by Spider. | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Voxel size | X=Y=Z: 0.826 Å | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Density |
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Symmetry | Space group: 1 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Details | EMDB XML:
CCP4 map header:
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
-Supplemental data
- Sample components
Sample components
-Entire : S. cerevisiae phosphatidylcholine flippase Dnf1-Lem3 complex in t...
| Entire | Name: S. cerevisiae phosphatidylcholine flippase Dnf1-Lem3 complex in the apo E1 state |
|---|---|
| Components |
|
-Supramolecule #1: S. cerevisiae phosphatidylcholine flippase Dnf1-Lem3 complex in t...
| Supramolecule | Name: S. cerevisiae phosphatidylcholine flippase Dnf1-Lem3 complex in the apo E1 state type: complex / ID: 1 / Parent: 0 / Macromolecule list: #1-#2 |
|---|---|
| Source (natural) | Organism:  Strain: ATCC 204508 / S288c |
-Macromolecule #1: Phospholipid-transporting ATPase DNF1
| Macromolecule | Name: Phospholipid-transporting ATPase DNF1 / type: protein_or_peptide / ID: 1 / Number of copies: 1 / Enantiomer: LEVO / EC number: P-type phospholipid transporter |
|---|---|
| Source (natural) | Organism:  Strain: ATCC 204508 / S288c |
| Molecular weight | Theoretical: 178.000172 KDa |
| Recombinant expression | Organism:  |
| Sequence | String: MSGTFHGDGH APMSPFEDTF QFEDNSSNED THIAPTHFDD GATSNKYSRP QVSFNDETPK NKREDAEEFT FNDDTEYDNH SFQPTPKLN NGSGTFDDVE LDNDSGEPHT NYDGMKRFRM GTKRNKKGNP IMGRSKTLKW ARKNIPNPFE DFTKDDIDPG A INRAQELR ...String: MSGTFHGDGH APMSPFEDTF QFEDNSSNED THIAPTHFDD GATSNKYSRP QVSFNDETPK NKREDAEEFT FNDDTEYDNH SFQPTPKLN NGSGTFDDVE LDNDSGEPHT NYDGMKRFRM GTKRNKKGNP IMGRSKTLKW ARKNIPNPFE DFTKDDIDPG A INRAQELR TVYYNMPLPK DMIDEEGNPI MQYPRNKIRT TKYTPLTFLP KNILFQFHNF ANVYFLVLII LGAFQIFGVT NP GLSAVPL VVIVIITAIK DAIEDSRRTV LDLEVNNTKT HILEGVENEN VSTDNISLWR RFKKANSRLL FKFIQYCKEH LTE EGKKKR MQRKRHELRV QKTVGTSGPR SSLDSIDSYR VSADYGRPSL DYDNLEQGAG EANIVDRSLP PRTDCKFAKN YWKG VKVGD IVRIHNNDEI PADIILLSTS DTDGACYVET KNLDGETNLK VRQSLKCTNT IRTSKDIART KFWIESEGPH SNLYT YQGN MKWRNLADGE IRNEPITINN VLLRGCTLRN TKWAMGVVMF TGGDTKIMLN SGITPTKKSR ISRELNFSVV INFVLL FIL CFVSGIANGV YYDKKGRSRF SYEFGTIAGS AATNGFVSFW VAVILYQSLV PISLYISVEI IKTAQAAFIY GDVLLYN AK LDYPCTPKSW NISDDLGQVE YIFSDKTGTL TQNVMEFKKC TINGVSYGRA YTEALAGLRK RQGIDVETEG RREKAEIA K DRDTMIDELR ALSGNSQFYP EEVTFVSKEF VRDLKGASGE VQQRCCEHFM LALALCHSVL VEANPDNPKK LDLKAQSPD EAALVATARD VGFSFVGKTK KGLIIEMQGI QKEFEILNIL EFNSSRKRMS CIVKIPGLNP GDEPRALLIC KGADSIIYSR LSRQSGSNS EAILEKTALH LEQYATEGLR TLCIAQRELS WSEYEKWNEK YDIAAASLAN REDELEVVAD SIERELILLG G TAIEDRLQ DGVPDCIELL AEAGIKLWVL TGDKVETAIN IGFSCNLLNN EMELLVIKTT GDDVKEFGSE PSEIVDALLS KY LKEYFNL TGSEEEIFEA KKDHEFPKGN YAIVIDGDAL KLALYGEDIR RKFLLLCKNC RAVLCCRVSP SQKAAVVKLV KDS LDVMTL AIGDGSNDVA MIQSADVGIG IAGEEGRQAV MCSDYAIGQF RYLARLVLVH GRWSYKRLAE MIPEFFYKNM IFAL ALFWY GIYNDFDGSY LYEYTYMMFY NLAFTSLPVI FLGILDQDVN DTISLVVPQL YRVGILRKEW NQRKFLWYML DGLYQ SIIC FFFPYLVYHK NMIVTSNGLG LDHRYFVGVY VTTIAVISCN TYVLLHQYRW DWFSGLFIAL SCLVVFAWTG IWSSAI ASR EFFKAAARIY GAPSFWAVFF VAVLFCLLPR FTYDSFQKFF YPTDVEIVRE MWQHGHFDHY PPGYDPTDPN RPKVTKA GQ HGEKIIEGIA LSDNLGGSNY SRDSVVTEEI PMTFMHGEDG SPSGYQKQET WMTSPKETQD LLQSPQFQQA QTFGRGPS T NVRSSLDRTR EQMIATNQLD NRYSVERART SLDLPGVTNA ASLIGTQQNN UniProtKB: Phospholipid-transporting ATPase DNF1 |
-Macromolecule #2: Alkylphosphocholine resistance protein LEM3
| Macromolecule | Name: Alkylphosphocholine resistance protein LEM3 / type: protein_or_peptide / ID: 2 / Number of copies: 1 / Enantiomer: LEVO |
|---|---|
| Source (natural) | Organism:  Strain: ATCC 204508 / S288c |
| Molecular weight | Theoretical: 47.490395 KDa |
| Recombinant expression | Organism:  |
| Sequence | String: MVNFDLGQVG EVFRRKDKGA IVSGDNPEEE EDVDASEFEE DEVKPVRTKN RRPKEDAFTQ QRLAAINPVL TPRTVLPLYL LIAVVFVIV GGCILAQNSK VDEVTIYYQD CMTNATSSWS DIPSEHWQFV FHKYKTYNTA PQWRFVDDES DDFTKQRGTC Q IRFTTPSD ...String: MVNFDLGQVG EVFRRKDKGA IVSGDNPEEE EDVDASEFEE DEVKPVRTKN RRPKEDAFTQ QRLAAINPVL TPRTVLPLYL LIAVVFVIV GGCILAQNSK VDEVTIYYQD CMTNATSSWS DIPSEHWQFV FHKYKTYNTA PQWRFVDDES DDFTKQRGTC Q IRFTTPSD MKNNVYLNYV LEKFAANHRR YVLSFSEDQI RGEDASYETV HDATGINCKP LSKNADGKIY YPCGLIANSM FN DTFPLQL TNVGDTSNNY SLTNKGINWE SDKKRYKKTK YNYTQIAPPP YWEKMYPDGY NETNIPDIQD WEEFQNWMRP GAF DKITKL IRINKNDTLP AGEYQLDIGL HWPVLEFNGK KGIYLTHGSH LGGRNPFLGI VYLIGGCICA AMALILLTFW LFGG RKIAD ASSLSWNMK UniProtKB: LEM3 isoform 1 |
-Macromolecule #5: MAGNESIUM ION
| Macromolecule | Name: MAGNESIUM ION / type: ligand / ID: 5 / Number of copies: 1 / Formula: MG |
|---|---|
| Molecular weight | Theoretical: 24.305 Da |
-Macromolecule #6: 2-acetamido-2-deoxy-beta-D-glucopyranose
| Macromolecule | Name: 2-acetamido-2-deoxy-beta-D-glucopyranose / type: ligand / ID: 6 / Number of copies: 2 / Formula: NAG |
|---|---|
| Molecular weight | Theoretical: 221.208 Da |
| Chemical component information |  ChemComp-NAG: |
-Experimental details
-Structure determination
| Method | cryo EM |
|---|---|
 Processing Processing | single particle reconstruction |
| Aggregation state | particle |
- Sample preparation
Sample preparation
| Concentration | 1.5 mg/mL |
|---|---|
| Buffer | pH: 7.4 |
| Grid | Model: Quantifoil R2/2 / Material: GOLD |
| Vitrification | Cryogen name: ETHANE |
- Electron microscopy
Electron microscopy
| Microscope | FEI TITAN KRIOS |
|---|---|
| Image recording | Film or detector model: GATAN K3 (6k x 4k) / Average electron dose: 64.0 e/Å2 |
| Electron beam | Acceleration voltage: 300 kV / Electron source:  FIELD EMISSION GUN FIELD EMISSION GUN |
| Electron optics | Illumination mode: OTHER / Imaging mode: BRIGHT FIELD |
| Experimental equipment |  Model: Titan Krios / Image courtesy: FEI Company |
 Movie
Movie Controller
Controller





























 Z (Sec.)
Z (Sec.) Y (Row.)
Y (Row.) X (Col.)
X (Col.)