[English] 日本語
 Yorodumi
Yorodumi- EMDB-22272: Structure of RAG1 (R848M/E649V)-RAG2-DNA Strand Transfer Complex ... -
+ Open data
Open data
- Basic information
Basic information
| Entry | Database: EMDB / ID: EMD-22272 | |||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
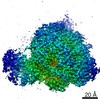
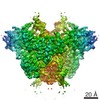
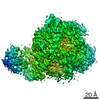
| Title | Structure of RAG1 (R848M/E649V)-RAG2-DNA Strand Transfer Complex (Dynamic-Form) | |||||||||
 Map data Map data | RAG1 (R848M/E649V)-RAG2-DNA Strand Transfer Complex (Dynamic-Form) | |||||||||
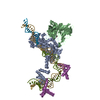
 Sample Sample |
| |||||||||
 Keywords Keywords | DNA Transposase / RECOMBINATION | |||||||||
| Function / homology |  Function and homology information Function and homology informationmature B cell differentiation involved in immune response / DNA recombinase complex / B cell homeostatic proliferation / endodeoxyribonuclease complex / negative regulation of T cell differentiation in thymus / DN2 thymocyte differentiation / pre-B cell allelic exclusion / positive regulation of organ growth / regulation of behavioral fear response / V(D)J recombination ...mature B cell differentiation involved in immune response / DNA recombinase complex / B cell homeostatic proliferation / endodeoxyribonuclease complex / negative regulation of T cell differentiation in thymus / DN2 thymocyte differentiation / pre-B cell allelic exclusion / positive regulation of organ growth / regulation of behavioral fear response / V(D)J recombination / negative regulation of T cell apoptotic process / phosphatidylinositol-3,4-bisphosphate binding / negative regulation of thymocyte apoptotic process / histone H3K4me3 reader activity / phosphatidylinositol-3,5-bisphosphate binding / regulation of T cell differentiation / organ growth / positive regulation of T cell differentiation / T cell lineage commitment / B cell lineage commitment / phosphatidylinositol-3,4,5-trisphosphate binding / T cell homeostasis / T cell differentiation / protein autoubiquitination / phosphatidylinositol-4,5-bisphosphate binding / phosphatidylinositol binding / B cell differentiation / thymus development / visual learning / RING-type E3 ubiquitin transferase / ubiquitin-protein transferase activity / ubiquitin protein ligase activity / T cell differentiation in thymus / chromatin organization / endonuclease activity / histone binding / DNA recombination / sequence-specific DNA binding / Hydrolases; Acting on ester bonds / adaptive immune response / defense response to bacterium / hydrolase activity / chromatin binding / protein homodimerization activity / DNA binding / zinc ion binding / nucleoplasm / metal ion binding / identical protein binding / nucleus Similarity search - Function | |||||||||
| Biological species |   Homo sapiens (human) Homo sapiens (human) | |||||||||
| Method | single particle reconstruction / cryo EM / Resolution: 2.7 Å | |||||||||
 Authors Authors | Zhang Y / Corbett E | |||||||||
| Funding support |  United States, 1 items United States, 1 items
| |||||||||
 Citation Citation |  Journal: EMBO J / Year: 2020 Journal: EMBO J / Year: 2020Title: Structural basis for the activation and suppression of transposition during evolution of the RAG recombinase. Authors: Yuhang Zhang / Elizabeth Corbett / Shenping Wu / David G Schatz /  Abstract: Jawed vertebrate adaptive immunity relies on the RAG1/RAG2 (RAG) recombinase, a domesticated transposase, for assembly of antigen receptor genes. Using an integration-activated form of RAG1 with ...Jawed vertebrate adaptive immunity relies on the RAG1/RAG2 (RAG) recombinase, a domesticated transposase, for assembly of antigen receptor genes. Using an integration-activated form of RAG1 with methionine at residue 848 and cryo-electron microscopy, we determined structures that capture RAG engaged with transposon ends and U-shaped target DNA prior to integration (the target capture complex) and two forms of the RAG strand transfer complex that differ based on whether target site DNA is annealed or dynamic. Target site DNA base unstacking, flipping, and melting by RAG1 methionine 848 explain how this residue activates transposition, how RAG can stabilize sharp bends in target DNA, and why replacement of residue 848 by arginine during RAG domestication led to suppression of transposition activity. RAG2 extends a jawed vertebrate-specific loop to interact with target site DNA, and functional assays demonstrate that this loop represents another evolutionary adaptation acquired during RAG domestication to inhibit transposition. Our findings identify mechanistic principles of the final step in cut-and-paste transposition and the molecular and structural logic underlying the transformation of RAG from transposase to recombinase. | |||||||||
| History |
|
- Structure visualization
Structure visualization
| Movie |
 Movie viewer Movie viewer |
|---|---|
| Structure viewer | EM map:  SurfView SurfView Molmil Molmil Jmol/JSmol Jmol/JSmol |
| Supplemental images |
- Downloads & links
Downloads & links
-EMDB archive
| Map data |  emd_22272.map.gz emd_22272.map.gz | 51.9 MB |  EMDB map data format EMDB map data format | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Header (meta data) |  emd-22272-v30.xml emd-22272-v30.xml emd-22272.xml emd-22272.xml | 21.4 KB 21.4 KB | Display Display |  EMDB header EMDB header |
| Images |  emd_22272.png emd_22272.png | 171.6 KB | ||
| Filedesc metadata |  emd-22272.cif.gz emd-22272.cif.gz | 7.1 KB | ||
| Archive directory |  http://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/structures/EMD-22272 http://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/structures/EMD-22272 ftp://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/structures/EMD-22272 ftp://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/structures/EMD-22272 | HTTPS FTP |
-Related structure data
| Related structure data |  6xnxMC  6xnyC  6xnzC M: atomic model generated by this map C: citing same article ( |
|---|---|
| Similar structure data |
- Links
Links
| EMDB pages |  EMDB (EBI/PDBe) / EMDB (EBI/PDBe) /  EMDataResource EMDataResource |
|---|---|
| Related items in Molecule of the Month |
- Map
Map
| File |  Download / File: emd_22272.map.gz / Format: CCP4 / Size: 55.4 MB / Type: IMAGE STORED AS FLOATING POINT NUMBER (4 BYTES) Download / File: emd_22272.map.gz / Format: CCP4 / Size: 55.4 MB / Type: IMAGE STORED AS FLOATING POINT NUMBER (4 BYTES) | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Annotation | RAG1 (R848M/E649V)-RAG2-DNA Strand Transfer Complex (Dynamic-Form) | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Projections & slices | Image control
Images are generated by Spider. | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Voxel size | X=Y=Z: 1.05 Å | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Density |
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Symmetry | Space group: 1 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Details | EMDB XML:
CCP4 map header:
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
-Supplemental data
- Sample components
Sample components
+Entire : RAG recombinase strand transfer complex
+Supramolecule #1: RAG recombinase strand transfer complex
+Supramolecule #2: V(D)J recombination-activating protein 1, V(D)J recombination-act...
+Supramolecule #3: DNA
+Macromolecule #1: V(D)J recombination-activating protein 1
+Macromolecule #2: V(D)J recombination-activating protein 2
+Macromolecule #3: 12RSS integration strand DNA (55-MER)
+Macromolecule #4: 23RSS integration strand DNA (66-MER)
+Macromolecule #5: Flanking DNA top strand DNA
+Macromolecule #6: 23RSS signal top strand DNA (45-MER)
+Macromolecule #7: 12RSS signal top strand DNA (34-MER)
+Macromolecule #8: MAGNESIUM ION
+Macromolecule #9: ZINC ION
-Experimental details
-Structure determination
| Method | cryo EM |
|---|---|
 Processing Processing | single particle reconstruction |
| Aggregation state | particle |
- Sample preparation
Sample preparation
| Concentration | 0.4 mg/mL |
|---|---|
| Buffer | pH: 7.6 Details: 20 mM HEPES pH7.6, 0.5 mM TCEP, 5 mM MgCl2 and 150 mM KCl |
| Grid | Model: C-flat-2/1 / Material: COPPER / Mesh: 400 / Pretreatment - Type: GLOW DISCHARGE / Pretreatment - Time: 30 sec. |
| Vitrification | Cryogen name: ETHANE / Chamber humidity: 100 % / Chamber temperature: 283 K / Instrument: FEI VITROBOT MARK IV |
- Electron microscopy
Electron microscopy
| Microscope | FEI TITAN KRIOS |
|---|---|
| Image recording | Film or detector model: GATAN K2 SUMMIT (4k x 4k) / Detector mode: SUPER-RESOLUTION / Number real images: 3527 / Average exposure time: 11.0 sec. / Average electron dose: 72.8 e/Å2 |
| Electron beam | Acceleration voltage: 300 kV / Electron source:  FIELD EMISSION GUN FIELD EMISSION GUN |
| Electron optics | C2 aperture diameter: 50.0 µm / Illumination mode: FLOOD BEAM / Imaging mode: BRIGHT FIELD / Cs: 2.7 mm / Nominal defocus max: 2.3000000000000003 µm / Nominal defocus min: 0.8 µm / Nominal magnification: 130000 |
| Sample stage | Specimen holder model: FEI TITAN KRIOS AUTOGRID HOLDER / Cooling holder cryogen: NITROGEN |
| Experimental equipment |  Model: Titan Krios / Image courtesy: FEI Company |
 Movie
Movie Controller
Controller



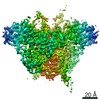


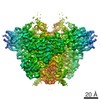
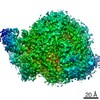
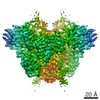









 Z (Sec.)
Z (Sec.) Y (Row.)
Y (Row.) X (Col.)
X (Col.)