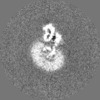
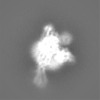
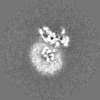
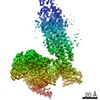
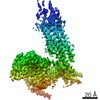
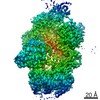
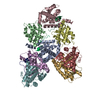
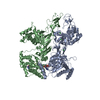
登録情報 データベース : EMDB / ID : EMD-22117タイトル Structure of human SMO-D384R complex with Gi Structure of human SMO-D384R complex with Gi 複合体 : SMO-GI COMPLEXタンパク質・ペプチド : Smoothened homologタンパク質・ペプチド : Guanine nucleotide-binding protein G(i) subunit alpha-1タンパク質・ペプチド : Guanine nucleotide-binding protein G(I)/G(S)/G(T) subunit beta-1タンパク質・ペプチド : Guanine nucleotide-binding protein G(I)/G(S)/G(O) subunit gamma-2タンパク質・ペプチド : scFv16リガンド : CHOLESTEROL / 機能・相同性 分子機能 ドメイン・相同性 構成要素
/ / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / 生物種 Homo sapiens (ヒト) / Mus musculus (ハツカネズミ)手法 / / 解像度 : 3.88 Å Qi X / Long T ジャーナル : Nat Chem Biol / 年 : 2020タイトル : Sterols in an intramolecular channel of Smoothened mediate Hedgehog signaling.著者 : Xiaofeng Qi / Lucas Friedberg / Ryan De Bose-Boyd / Tao Long / Xiaochun Li / 要旨 : Smoothened (SMO), a class Frizzled G protein-coupled receptor (class F GPCR), transduces the Hedgehog signal across the cell membrane. Sterols can bind to its extracellular cysteine-rich domain ... Smoothened (SMO), a class Frizzled G protein-coupled receptor (class F GPCR), transduces the Hedgehog signal across the cell membrane. Sterols can bind to its extracellular cysteine-rich domain (CRD) and to several sites in the seven transmembrane helices (7-TMs) of SMO. However, the mechanism by which sterols regulate SMO via multiple sites is unknown. Here we determined the structures of SMO-G complexes bound to the synthetic SMO agonist (SAG) and to 24(S),25-epoxycholesterol (24(S),25-EC). A novel sterol-binding site in the extracellular extension of TM6 was revealed to connect other sites in 7-TMs and CRD, forming an intramolecular sterol channel from the middle side of 7-TMs to CRD. Additional structures of two gain-of-function variants, SMO and SMO, showed that blocking the channel at its midpoints allows sterols to occupy the binding sites in 7-TMs, thereby activating SMO. These data indicate that sterol transport through the core of SMO is a major regulator of SMO-mediated signaling. 履歴 登録 2020年6月6日 - ヘッダ(付随情報) 公開 2020年9月30日 - マップ公開 2020年9月30日 - 更新 2024年10月23日 - 現状 2024年10月23日 処理サイト : RCSB / 状態 : 公開
すべて表示 表示を減らす
 データを開く
データを開く 基本情報
基本情報 マップデータ
マップデータ 試料
試料 キーワード
キーワード 機能・相同性情報
機能・相同性情報 Homo sapiens (ヒト) /
Homo sapiens (ヒト) / 
 データ登録者
データ登録者 引用
引用 ジャーナル: Nat Chem Biol / 年: 2020
ジャーナル: Nat Chem Biol / 年: 2020
 構造の表示
構造の表示 ムービービューア
ムービービューア SurfView
SurfView Molmil
Molmil Jmol/JSmol
Jmol/JSmol ダウンロードとリンク
ダウンロードとリンク emd_22117.map.gz
emd_22117.map.gz EMDBマップデータ形式
EMDBマップデータ形式 emd-22117-v30.xml
emd-22117-v30.xml emd-22117.xml
emd-22117.xml EMDBヘッダ
EMDBヘッダ emd_22117.png
emd_22117.png emd_22117_msk_1.map
emd_22117_msk_1.map マスクマップ
マスクマップ emd-22117.cif.gz
emd-22117.cif.gz emd_22117_half_map_1.map.gz
emd_22117_half_map_1.map.gz emd_22117_half_map_2.map.gz
emd_22117_half_map_2.map.gz http://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/structures/EMD-22117
http://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/structures/EMD-22117 ftp://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/structures/EMD-22117
ftp://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/structures/EMD-22117 emd_22117_validation.pdf.gz
emd_22117_validation.pdf.gz EMDB検証レポート
EMDB検証レポート emd_22117_full_validation.pdf.gz
emd_22117_full_validation.pdf.gz emd_22117_validation.xml.gz
emd_22117_validation.xml.gz emd_22117_validation.cif.gz
emd_22117_validation.cif.gz https://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/validation_reports/EMD-22117
https://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/validation_reports/EMD-22117 ftp://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/validation_reports/EMD-22117
ftp://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/validation_reports/EMD-22117 リンク
リンク EMDB (EBI/PDBe) /
EMDB (EBI/PDBe) /  EMDataResource
EMDataResource マップ
マップ ダウンロード / ファイル: emd_22117.map.gz / 形式: CCP4 / 大きさ: 83.7 MB / タイプ: IMAGE STORED AS FLOATING POINT NUMBER (4 BYTES)
ダウンロード / ファイル: emd_22117.map.gz / 形式: CCP4 / 大きさ: 83.7 MB / タイプ: IMAGE STORED AS FLOATING POINT NUMBER (4 BYTES) emd_22117_msk_1.map
emd_22117_msk_1.map 試料の構成要素
試料の構成要素 Homo sapiens (ヒト)
Homo sapiens (ヒト) Homo sapiens (ヒト)
Homo sapiens (ヒト) Homo sapiens (ヒト)
Homo sapiens (ヒト) Homo sapiens (ヒト)
Homo sapiens (ヒト) Trichoplusia ni (イラクサキンウワバ)
Trichoplusia ni (イラクサキンウワバ) Homo sapiens (ヒト)
Homo sapiens (ヒト) Trichoplusia ni (イラクサキンウワバ)
Trichoplusia ni (イラクサキンウワバ) Homo sapiens (ヒト)
Homo sapiens (ヒト) Trichoplusia ni (イラクサキンウワバ)
Trichoplusia ni (イラクサキンウワバ)
 Trichoplusia ni (イラクサキンウワバ)
Trichoplusia ni (イラクサキンウワバ)
 解析
解析 試料調製
試料調製 電子顕微鏡法
電子顕微鏡法 FIELD EMISSION GUN
FIELD EMISSION GUN
 画像解析
画像解析 ムービー
ムービー コントローラー
コントローラー






































 Z (Sec.)
Z (Sec.) Y (Row.)
Y (Row.) X (Col.)
X (Col.)