+ Open data
Open data
- Basic information
Basic information
| Entry | Database: EMDB / ID: EMD-22120 | |||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Title | Structure of human SMO-Gi complex with 24(S),25-EC | |||||||||
 Map data Map data | Structure of human SMO-Gi complex with 24(S),25-EC | |||||||||
 Sample Sample |
| |||||||||
 Keywords Keywords | GPCR / MEMBRANE PROTEIN | |||||||||
| Function / homology |  Function and homology information Function and homology informationventral midline determination / mesenchymal to epithelial transition involved in metanephric renal vesicle formation / response to inositol / regulation of heart morphogenesis / contact inhibition / negative regulation of hair follicle development / 9+0 non-motile cilium / regulation of somatic stem cell population maintenance / pancreas morphogenesis / epithelial-mesenchymal cell signaling ...ventral midline determination / mesenchymal to epithelial transition involved in metanephric renal vesicle formation / response to inositol / regulation of heart morphogenesis / contact inhibition / negative regulation of hair follicle development / 9+0 non-motile cilium / regulation of somatic stem cell population maintenance / pancreas morphogenesis / epithelial-mesenchymal cell signaling / myoblast migration / atrial septum morphogenesis / spinal cord dorsal/ventral patterning / determination of left/right asymmetry in lateral mesoderm / midgut development / left/right axis specification / negative regulation of DNA binding / patched binding / somite development / forebrain morphogenesis / type B pancreatic cell development / Activation of SMO / BBSome-mediated cargo-targeting to cilium / positive regulation of organ growth / smooth muscle tissue development / cerebellar cortex morphogenesis / mammary gland epithelial cell differentiation / cellular response to cholesterol / positive regulation of branching involved in ureteric bud morphogenesis / dentate gyrus development / commissural neuron axon guidance / pattern specification process / oxysterol binding / dopaminergic neuron differentiation / thalamus development / positive regulation of multicellular organism growth / positive regulation of smoothened signaling pathway / Class B/2 (Secretin family receptors) / cell fate specification / cAMP-dependent protein kinase inhibitor activity / central nervous system neuron differentiation / anterior/posterior pattern specification / neural crest cell migration / positive regulation of mesenchymal cell proliferation / dorsal/ventral neural tube patterning / hair follicle morphogenesis / ciliary membrane / smoothened signaling pathway / positive regulation of neuroblast proliferation / negative regulation of epithelial cell differentiation / endoplasmic reticulum-Golgi intermediate compartment / heart looping / ciliary tip / protein kinase A catalytic subunit binding / odontogenesis of dentin-containing tooth / negative regulation of protein phosphorylation / neuroblast proliferation / vasculogenesis / Hedgehog 'off' state / adenylate cyclase inhibitor activity / skeletal muscle fiber development / positive regulation of protein localization to cell cortex / T cell migration / Adenylate cyclase inhibitory pathway / D2 dopamine receptor binding / response to prostaglandin E / G protein-coupled serotonin receptor binding / adenylate cyclase regulator activity / adenylate cyclase-inhibiting serotonin receptor signaling pathway / astrocyte activation / centriole / homeostasis of number of cells within a tissue / protein sequestering activity / cellular response to forskolin / regulation of mitotic spindle organization / epithelial cell proliferation / central nervous system development / positive regulation of epithelial cell proliferation / Regulation of insulin secretion / positive regulation of cholesterol biosynthetic process / Hedgehog 'on' state / negative regulation of insulin secretion / G protein-coupled receptor binding / cerebral cortex development / positive regulation of protein import into nucleus / G protein-coupled receptor activity / adenylate cyclase-inhibiting G protein-coupled receptor signaling pathway / response to peptide hormone / multicellular organism growth / adenylate cyclase-modulating G protein-coupled receptor signaling pathway / centriolar satellite / G-protein beta/gamma-subunit complex binding / Olfactory Signaling Pathway / Activation of the phototransduction cascade / protein import into nucleus / G beta:gamma signalling through PLC beta / Presynaptic function of Kainate receptors / Thromboxane signalling through TP receptor / G protein-coupled acetylcholine receptor signaling pathway / Activation of G protein gated Potassium channels Similarity search - Function | |||||||||
| Biological species |  Homo sapiens (human) / Homo sapiens (human) /  | |||||||||
| Method | single particle reconstruction / cryo EM / Resolution: 3.14 Å | |||||||||
 Authors Authors | Qi X / Long T | |||||||||
 Citation Citation |  Journal: Nat Chem Biol / Year: 2020 Journal: Nat Chem Biol / Year: 2020Title: Sterols in an intramolecular channel of Smoothened mediate Hedgehog signaling. Authors: Xiaofeng Qi / Lucas Friedberg / Ryan De Bose-Boyd / Tao Long / Xiaochun Li /  Abstract: Smoothened (SMO), a class Frizzled G protein-coupled receptor (class F GPCR), transduces the Hedgehog signal across the cell membrane. Sterols can bind to its extracellular cysteine-rich domain ...Smoothened (SMO), a class Frizzled G protein-coupled receptor (class F GPCR), transduces the Hedgehog signal across the cell membrane. Sterols can bind to its extracellular cysteine-rich domain (CRD) and to several sites in the seven transmembrane helices (7-TMs) of SMO. However, the mechanism by which sterols regulate SMO via multiple sites is unknown. Here we determined the structures of SMO-G complexes bound to the synthetic SMO agonist (SAG) and to 24(S),25-epoxycholesterol (24(S),25-EC). A novel sterol-binding site in the extracellular extension of TM6 was revealed to connect other sites in 7-TMs and CRD, forming an intramolecular sterol channel from the middle side of 7-TMs to CRD. Additional structures of two gain-of-function variants, SMO and SMO, showed that blocking the channel at its midpoints allows sterols to occupy the binding sites in 7-TMs, thereby activating SMO. These data indicate that sterol transport through the core of SMO is a major regulator of SMO-mediated signaling. | |||||||||
| History |
|
- Structure visualization
Structure visualization
| Movie |
 Movie viewer Movie viewer |
|---|---|
| Structure viewer | EM map:  SurfView SurfView Molmil Molmil Jmol/JSmol Jmol/JSmol |
| Supplemental images |
- Downloads & links
Downloads & links
-EMDB archive
| Map data |  emd_22120.map.gz emd_22120.map.gz | 76.6 MB |  EMDB map data format EMDB map data format | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Header (meta data) |  emd-22120-v30.xml emd-22120-v30.xml emd-22120.xml emd-22120.xml | 18.8 KB 18.8 KB | Display Display |  EMDB header EMDB header |
| Images |  emd_22120.png emd_22120.png | 39.7 KB | ||
| Masks |  emd_22120_msk_1.map emd_22120_msk_1.map | 83.7 MB |  Mask map Mask map | |
| Filedesc metadata |  emd-22120.cif.gz emd-22120.cif.gz | 6.3 KB | ||
| Others |  emd_22120_half_map_1.map.gz emd_22120_half_map_1.map.gz emd_22120_half_map_2.map.gz emd_22120_half_map_2.map.gz | 65.3 MB 65.3 MB | ||
| Archive directory |  http://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/structures/EMD-22120 http://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/structures/EMD-22120 ftp://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/structures/EMD-22120 ftp://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/structures/EMD-22120 | HTTPS FTP |
-Related structure data
| Related structure data |  6xbmMC  6xbjC  6xbkC  6xblC M: atomic model generated by this map C: citing same article ( |
|---|---|
| Similar structure data |
- Links
Links
| EMDB pages |  EMDB (EBI/PDBe) / EMDB (EBI/PDBe) /  EMDataResource EMDataResource |
|---|---|
| Related items in Molecule of the Month |
- Map
Map
| File |  Download / File: emd_22120.map.gz / Format: CCP4 / Size: 83.7 MB / Type: IMAGE STORED AS FLOATING POINT NUMBER (4 BYTES) Download / File: emd_22120.map.gz / Format: CCP4 / Size: 83.7 MB / Type: IMAGE STORED AS FLOATING POINT NUMBER (4 BYTES) | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Annotation | Structure of human SMO-Gi complex with 24(S),25-EC | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Projections & slices | Image control
Images are generated by Spider. | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Voxel size | X=Y=Z: 0.832 Å | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
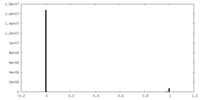
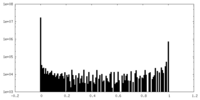
| Density |
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Symmetry | Space group: 1 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Details | EMDB XML:
CCP4 map header:
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
-Supplemental data
-Mask #1
| File |  emd_22120_msk_1.map emd_22120_msk_1.map | ||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Projections & Slices |
| ||||||||||||
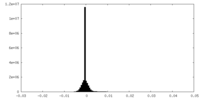
| Density Histograms |
-Half map: Structure of human SMO-Gi complex with 24(S),25-EC
| File | emd_22120_half_map_1.map | ||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Annotation | Structure of human SMO-Gi complex with 24(S),25-EC | ||||||||||||
| Projections & Slices |
| ||||||||||||
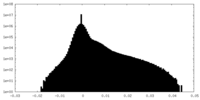
| Density Histograms |
-Half map: Structure of human SMO-Gi complex with 24(S),25-EC
| File | emd_22120_half_map_2.map | ||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Annotation | Structure of human SMO-Gi complex with 24(S),25-EC | ||||||||||||
| Projections & Slices |
| ||||||||||||
| Density Histograms |
- Sample components
Sample components
-Entire : SMO-GI COMPLEX
| Entire | Name: SMO-GI COMPLEX |
|---|---|
| Components |
|
-Supramolecule #1: SMO-GI COMPLEX
| Supramolecule | Name: SMO-GI COMPLEX / type: complex / ID: 1 / Parent: 0 / Macromolecule list: #1-#5 |
|---|---|
| Source (natural) | Organism:  Homo sapiens (human) Homo sapiens (human) |
-Macromolecule #1: Smoothened homolog
| Macromolecule | Name: Smoothened homolog / type: protein_or_peptide / ID: 1 / Number of copies: 1 / Enantiomer: LEVO |
|---|---|
| Source (natural) | Organism:  Homo sapiens (human) Homo sapiens (human) |
| Molecular weight | Theoretical: 71.786438 KDa |
| Recombinant expression | Organism:  Homo sapiens (human) Homo sapiens (human) |
| Sequence | String: MAAARPARGP ELPLLGLLLL LLLGDPGRGA ASSGNATGPG PRSAGGSARR SAAVTGPPPP LSHCGRAAPC EPLRYNVCLG SVLPYGATS TLLAGDSDSQ EEAHGKLVLW SGLRNAPRCW AVIQPLLCAV YMPKCENDRV ELPSRTLCQA TRGPCAIVER E RGWPDFLR ...String: MAAARPARGP ELPLLGLLLL LLLGDPGRGA ASSGNATGPG PRSAGGSARR SAAVTGPPPP LSHCGRAAPC EPLRYNVCLG SVLPYGATS TLLAGDSDSQ EEAHGKLVLW SGLRNAPRCW AVIQPLLCAV YMPKCENDRV ELPSRTLCQA TRGPCAIVER E RGWPDFLR CTPDRFPEGC TNEVQNIKFN SSGQCEVPLV RTDNPKSWYE DVEGCGIQCQ NPLFTEAEHQ DMHSYIAAFG AV TGLCTLF TLATFVADWR NSNRYPAVIL FYVNACFFVG SIGWLAQFMD GARREIVCRA DGTMRLGEPT SNETLSCVII FVI VYYALM AGVVWFVVLT YAWHTSFKAL GTTYQPLSGK TSYFHLLTWS LPFVLTVAIL AVAQVDGDSV SGICFVGYKN YRYR AGFVL APIGLVLIVG GYFLIRGVMT LFSIKSNHPG LLSEKAASKI NETMLRLGIF GFLAFGFVLI TFSCHFYDFF NQAEW ERSF RDYVLCQANV TIGLPTKQPI PDCEIKNRPS LLVEKINLFA MFGTGIAMST WVWTKATLLI WRRTWCRLTG QSDDEP KRI KKSKMIAKAF SKRHELLQNP GQELSFSMHT VSHDGPVAGL AFDLNEPSAD VSSAWAQHVT KMVARRGAIL PQDISVT PV ATDYKDDDDK UniProtKB: Protein smoothened |
-Macromolecule #2: Guanine nucleotide-binding protein G(i) subunit alpha-1
| Macromolecule | Name: Guanine nucleotide-binding protein G(i) subunit alpha-1 type: protein_or_peptide / ID: 2 / Number of copies: 1 / Enantiomer: LEVO |
|---|---|
| Source (natural) | Organism:  Homo sapiens (human) Homo sapiens (human) |
| Molecular weight | Theoretical: 40.415031 KDa |
| Recombinant expression | Organism:  Trichoplusia ni (cabbage looper) Trichoplusia ni (cabbage looper) |
| Sequence | String: MGCTLSAEDK AAVERSKMID RNLREDGEKA AREVKLLLLG AGESGKSTIV KQMKIIHEAG YSEEECKQYK AVVYSNTIQS IIAIIRAMG RLKIDFGDSA RADDARQLFV LAGAAEEGFM TAELAGVIKR LWKDSGVQAC FNRSREYQLN DSAAYYLNDL D RIAQPNYI ...String: MGCTLSAEDK AAVERSKMID RNLREDGEKA AREVKLLLLG AGESGKSTIV KQMKIIHEAG YSEEECKQYK AVVYSNTIQS IIAIIRAMG RLKIDFGDSA RADDARQLFV LAGAAEEGFM TAELAGVIKR LWKDSGVQAC FNRSREYQLN DSAAYYLNDL D RIAQPNYI PTQQDVLRTR VKTTGIVETH FTFKDLHFKM FDVGGQRSER KKWIHCFEGV TAIIFCVALS DYDLVLAEDE EM NRMHESM KLFDSICNNK WFTDTSIILF LNKKDLFEEK IKKSPLTICY PEYAGSNTYE EAAAYIQCQF EDLNKRKDTK EIY THFTCA TDTKNVQFVF DAVTDVIIKN NLKDCGLF UniProtKB: Guanine nucleotide-binding protein G(i) subunit alpha-1 |
-Macromolecule #3: Guanine nucleotide-binding protein G(I)/G(S)/G(T) subunit beta-1
| Macromolecule | Name: Guanine nucleotide-binding protein G(I)/G(S)/G(T) subunit beta-1 type: protein_or_peptide / ID: 3 / Number of copies: 1 / Enantiomer: LEVO |
|---|---|
| Source (natural) | Organism:  Homo sapiens (human) Homo sapiens (human) |
| Molecular weight | Theoretical: 37.671102 KDa |
| Recombinant expression | Organism:  Trichoplusia ni (cabbage looper) Trichoplusia ni (cabbage looper) |
| Sequence | String: PGSSGSELDQ LRQEAEQLKN QIRDARKACA DATLSQITNN IDPVGRIQMR TRRTLRGHLA KIYAMHWGTD SRLLVSASQD GKLIIWDSY TTNKVHAIPL RSSWVMTCAY APSGNYVACG GLDNICSIYN LKTREGNVRV SRELAGHTGY LSCCRFLDDN Q IVTSSGDT ...String: PGSSGSELDQ LRQEAEQLKN QIRDARKACA DATLSQITNN IDPVGRIQMR TRRTLRGHLA KIYAMHWGTD SRLLVSASQD GKLIIWDSY TTNKVHAIPL RSSWVMTCAY APSGNYVACG GLDNICSIYN LKTREGNVRV SRELAGHTGY LSCCRFLDDN Q IVTSSGDT TCALWDIETG QQTTTFTGHT GDVMSLSLAP DTRLFVSGAC DASAKLWDVR EGMCRQTFTG HESDINAICF FP NGNAFAT GSDDATCRLF DLRADQELMT YSHDNIICGI TSVSFSKSGR LLLAGYDDFN CNVWDALKAD RAGVLAGHDN RVS CLGVTD DGMAVATGSW DSFLKIWN UniProtKB: Guanine nucleotide-binding protein G(I)/G(S)/G(T) subunit beta-1 |
-Macromolecule #4: Guanine nucleotide-binding protein G(I)/G(S)/G(O) subunit gamma-2
| Macromolecule | Name: Guanine nucleotide-binding protein G(I)/G(S)/G(O) subunit gamma-2 type: protein_or_peptide / ID: 4 / Number of copies: 1 / Enantiomer: LEVO |
|---|---|
| Source (natural) | Organism:  Homo sapiens (human) Homo sapiens (human) |
| Molecular weight | Theoretical: 7.861143 KDa |
| Recombinant expression | Organism:  Trichoplusia ni (cabbage looper) Trichoplusia ni (cabbage looper) |
| Sequence | String: MASNNTASIA QARKLVEQLK MEANIDRIKV SKAAADLMAY CEAHAKEDPL LTPVPASENP FREKKFFCAI L UniProtKB: Guanine nucleotide-binding protein G(I)/G(S)/G(O) subunit gamma-2 |
-Macromolecule #5: scFv16
| Macromolecule | Name: scFv16 / type: protein_or_peptide / ID: 5 / Number of copies: 1 / Enantiomer: LEVO |
|---|---|
| Source (natural) | Organism:  |
| Molecular weight | Theoretical: 27.784896 KDa |
| Recombinant expression | Organism:  Trichoplusia ni (cabbage looper) Trichoplusia ni (cabbage looper) |
| Sequence | String: DVQLVESGGG LVQPGGSRKL SCSASGFAFS SFGMHWVRQA PEKGLEWVAY ISSGSGTIYY ADTVKGRFTI SRDDPKNTLF LQMTSLRSE DTAMYYCVRS IYYYGSSPFD FWGQGTTLTV SSGGGGSGGG GSGGGGSDIV MTQATSSVPV TPGESVSISC R SSKSLLHS ...String: DVQLVESGGG LVQPGGSRKL SCSASGFAFS SFGMHWVRQA PEKGLEWVAY ISSGSGTIYY ADTVKGRFTI SRDDPKNTLF LQMTSLRSE DTAMYYCVRS IYYYGSSPFD FWGQGTTLTV SSGGGGSGGG GSGGGGSDIV MTQATSSVPV TPGESVSISC R SSKSLLHS NGNTYLYWFL QRPGQSPQLL IYRMSNLASG VPDRFSGSGS GTAFTLTISR LEAEDVGVYY CMQHLEYPLT FG AGTKLEL KAAAHHHHHH HH |
-Macromolecule #6: 17-[3-(3,3-DIMETHYL-OXIRANYL)-1-METHYL-PROPYL]-10,13-DIMETHYL-2,3...
| Macromolecule | Name: 17-[3-(3,3-DIMETHYL-OXIRANYL)-1-METHYL-PROPYL]-10,13-DIMETHYL-2,3,4,7,8,9,10,11,12,13,14,15,16,17-TETRADECAHYDRO-1H-CYC LOPENTA[A]PHENANTHREN-3-OL type: ligand / ID: 6 / Number of copies: 2 / Formula: CO1 |
|---|---|
| Molecular weight | Theoretical: 400.637 Da |
-Experimental details
-Structure determination
| Method | cryo EM |
|---|---|
 Processing Processing | single particle reconstruction |
| Aggregation state | particle |
- Sample preparation
Sample preparation
| Buffer | pH: 7.5 |
|---|---|
| Vitrification | Cryogen name: ETHANE |
- Electron microscopy
Electron microscopy
| Microscope | FEI TITAN KRIOS |
|---|---|
| Image recording | Film or detector model: GATAN K3 (6k x 4k) / Average electron dose: 60.0 e/Å2 |
| Electron beam | Acceleration voltage: 300 kV / Electron source:  FIELD EMISSION GUN FIELD EMISSION GUN |
| Electron optics | Illumination mode: FLOOD BEAM / Imaging mode: DARK FIELD |
| Experimental equipment |  Model: Titan Krios / Image courtesy: FEI Company |
- Image processing
Image processing
| Startup model | Type of model: EMDB MAP |
|---|---|
| Final reconstruction | Resolution.type: BY AUTHOR / Resolution: 3.14 Å / Resolution method: FSC 0.143 CUT-OFF / Number images used: 443107 |
| Initial angle assignment | Type: ANGULAR RECONSTITUTION |
| Final angle assignment | Type: ANGULAR RECONSTITUTION |
 Movie
Movie Controller
Controller





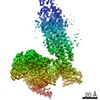
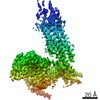
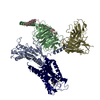


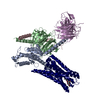
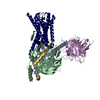






























 Z (Sec.)
Z (Sec.) Y (Row.)
Y (Row.) X (Col.)
X (Col.)