[English] 日本語
 Yorodumi
Yorodumi- EMDB-21989: Inward-facing state of the glutamate transporter homologue GltPh ... -
+ Open data
Open data
- Basic information
Basic information
| Entry | Database: EMDB / ID: EMD-21989 | |||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
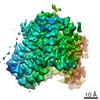
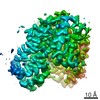
| Title | Inward-facing state of the glutamate transporter homologue GltPh in complex with L-aspartate and sodium ions | |||||||||
 Map data Map data | ||||||||||
 Sample Sample |
| |||||||||
 Keywords Keywords | sodium-coupled L-aspartate transporter / TRANSPORT PROTEIN | |||||||||
| Function / homology |  Function and homology information Function and homology informationL-aspartate transmembrane transport / L-aspartate transmembrane transporter activity / amino acid:sodium symporter activity / L-aspartate import across plasma membrane / chloride transmembrane transporter activity / protein homotrimerization / chloride transmembrane transport / metal ion binding / identical protein binding / plasma membrane Similarity search - Function | |||||||||
| Biological species |   Pyrococcus horikoshii (archaea) Pyrococcus horikoshii (archaea) | |||||||||
| Method | single particle reconstruction / cryo EM / Resolution: 3.05 Å | |||||||||
 Authors Authors | Wang X / Boudker O | |||||||||
| Funding support |  United States, 2 items United States, 2 items
| |||||||||
 Citation Citation |  Journal: Elife / Year: 2020 Journal: Elife / Year: 2020Title: Large domain movements through the lipid bilayer mediate substrate release and inhibition of glutamate transporters. Authors: Xiaoyu Wang / Olga Boudker /  Abstract: Glutamate transporters are essential players in glutamatergic neurotransmission in the brain, where they maintain extracellular glutamate below cytotoxic levels and allow for rounds of transmission. ...Glutamate transporters are essential players in glutamatergic neurotransmission in the brain, where they maintain extracellular glutamate below cytotoxic levels and allow for rounds of transmission. The structural bases of their function are well established, particularly within a model archaeal homolog, sodium, and aspartate symporter Glt. However, the mechanism of gating on the cytoplasmic side of the membrane remains ambiguous. We report Cryo-EM structures of Glt reconstituted into nanodiscs, including those structurally constrained in the cytoplasm-facing state and either apo, bound to sodium ions only, substrate, or blockers. The structures show that both substrate translocation and release involve movements of the bulky transport domain through the lipid bilayer. They further reveal a novel mode of inhibitor binding and show how solutes release is coupled to protein conformational changes. Finally, we describe how domain movements are associated with the displacement of bound lipids and significant membrane deformations, highlighting the potential regulatory role of the bilayer. | |||||||||
| History |
|
- Structure visualization
Structure visualization
| Movie |
 Movie viewer Movie viewer |
|---|---|
| Structure viewer | EM map:  SurfView SurfView Molmil Molmil Jmol/JSmol Jmol/JSmol |
| Supplemental images |
- Downloads & links
Downloads & links
-EMDB archive
| Map data |  emd_21989.map.gz emd_21989.map.gz | 59.9 MB |  EMDB map data format EMDB map data format | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Header (meta data) |  emd-21989-v30.xml emd-21989-v30.xml emd-21989.xml emd-21989.xml | 12.4 KB 12.4 KB | Display Display |  EMDB header EMDB header |
| Images |  emd_21989.png emd_21989.png | 84.1 KB | ||
| Filedesc metadata |  emd-21989.cif.gz emd-21989.cif.gz | 5.5 KB | ||
| Archive directory |  http://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/structures/EMD-21989 http://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/structures/EMD-21989 ftp://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/structures/EMD-21989 ftp://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/structures/EMD-21989 | HTTPS FTP |
-Related structure data
| Related structure data |  6x15MC  6x12C  6x13C  6x14C  6x16C  6x17C C: citing same article ( M: atomic model generated by this map |
|---|---|
| Similar structure data |
- Links
Links
| EMDB pages |  EMDB (EBI/PDBe) / EMDB (EBI/PDBe) /  EMDataResource EMDataResource |
|---|---|
| Related items in Molecule of the Month |
- Map
Map
| File |  Download / File: emd_21989.map.gz / Format: CCP4 / Size: 64 MB / Type: IMAGE STORED AS FLOATING POINT NUMBER (4 BYTES) Download / File: emd_21989.map.gz / Format: CCP4 / Size: 64 MB / Type: IMAGE STORED AS FLOATING POINT NUMBER (4 BYTES) | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Projections & slices | Image control
Images are generated by Spider. | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Voxel size | X=Y=Z: 1.0605 Å | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Density |
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Symmetry | Space group: 1 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Details | EMDB XML:
CCP4 map header:
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
-Supplemental data
- Sample components
Sample components
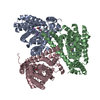
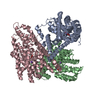
-Entire : Complex of inward-facing state of GltPh with L-aspartate and sodi...
| Entire | Name: Complex of inward-facing state of GltPh with L-aspartate and sodium ions in MSP1E3 nanodisc |
|---|---|
| Components |
|
-Supramolecule #1: Complex of inward-facing state of GltPh with L-aspartate and sodi...
| Supramolecule | Name: Complex of inward-facing state of GltPh with L-aspartate and sodium ions in MSP1E3 nanodisc type: complex / ID: 1 / Parent: 0 / Macromolecule list: #1 |
|---|---|
| Source (natural) | Organism:   Pyrococcus horikoshii (archaea) Pyrococcus horikoshii (archaea) |
| Molecular weight | Theoretical: 134 KDa |
-Macromolecule #1: Glutamate transporter homologue GltPh
| Macromolecule | Name: Glutamate transporter homologue GltPh / type: protein_or_peptide / ID: 1 / Number of copies: 3 / Enantiomer: LEVO |
|---|---|
| Source (natural) | Organism:   Pyrococcus horikoshii (archaea) Pyrococcus horikoshii (archaea) |
| Molecular weight | Theoretical: 44.643918 KDa |
| Recombinant expression | Organism:  |
| Sequence | String: (FME)GLYRKYIEY PVLQKILIGL ILGAIVGLIL GHYGYAHAVH TYVKPFGDLF VRLLCMLVMP IVFASLVVGA ASISPA RLG RVGVKIVVYY LLTSAFAVTL GIIMARLFNP GAGIHLAVGG QQFQPHQAPP LVHILLDIVP TNPFGALANG QVLPTIF FA IILGIAITYL ...String: (FME)GLYRKYIEY PVLQKILIGL ILGAIVGLIL GHYGYAHAVH TYVKPFGDLF VRLLCMLVMP IVFASLVVGA ASISPA RLG RVGVKIVVYY LLTSAFAVTL GIIMARLFNP GAGIHLAVGG QQFQPHQAPP LVHILLDIVP TNPFGALANG QVLPTIF FA IILGIAITYL MNSENEKVRK SAETLLDAIN GLAEAMYKIV NGVMQYAPIG VFALIAYVMA EQGVHVVGEL AKVTAAVY V GLTLQILLVY FVLLKIYGID PISFIKHAKD AMLTAFVTRS SSGTLPVTMR VAKEMGISEG IYSFTLPLGA TINMDGTAL YQGVATFFIA NALGSHLTVG QQLTIVLTAV LASIGTAGVP GAGAIMLCMV LHSVGLPLTD PNVAAAYAMI LGIDAILDMG RTMVNVTGD LTGTAIVAKT EGTLVPR |
-Macromolecule #2: SODIUM ION
| Macromolecule | Name: SODIUM ION / type: ligand / ID: 2 / Number of copies: 9 |
|---|---|
| Molecular weight | Theoretical: 22.99 Da |
-Macromolecule #3: ASPARTIC ACID
| Macromolecule | Name: ASPARTIC ACID / type: ligand / ID: 3 / Number of copies: 3 / Formula: ASP |
|---|---|
| Molecular weight | Theoretical: 133.103 Da |
| Chemical component information | 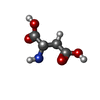 ChemComp-ASP: |
-Macromolecule #4: MERCURY (II) ION
| Macromolecule | Name: MERCURY (II) ION / type: ligand / ID: 4 / Number of copies: 3 / Formula: HG |
|---|---|
| Molecular weight | Theoretical: 200.59 Da |
-Macromolecule #5: [(2~{R})-1-[2-azanylethoxy(oxidanyl)phosphoryl]oxy-3-hexadecanoyl...
| Macromolecule | Name: [(2~{R})-1-[2-azanylethoxy(oxidanyl)phosphoryl]oxy-3-hexadecanoyloxy-propan-2-yl] (~{Z})-octadec-9-enoate type: ligand / ID: 5 / Number of copies: 39 / Formula: 6OU |
|---|---|
| Molecular weight | Theoretical: 717.996 Da |
| Chemical component information |  ChemComp-6OU: |
-Macromolecule #6: water
| Macromolecule | Name: water / type: ligand / ID: 6 / Number of copies: 9 / Formula: HOH |
|---|---|
| Molecular weight | Theoretical: 18.015 Da |
| Chemical component information |  ChemComp-HOH: |
-Experimental details
-Structure determination
| Method | cryo EM |
|---|---|
 Processing Processing | single particle reconstruction |
| Aggregation state | particle |
- Sample preparation
Sample preparation
| Buffer | pH: 7.4 |
|---|---|
| Sugar embedding | Material: ice |
| Grid | Details: unspecified |
| Vitrification | Cryogen name: ETHANE |
- Electron microscopy
Electron microscopy
| Microscope | FEI TITAN KRIOS |
|---|---|
| Image recording | Film or detector model: GATAN K3 (6k x 4k) / Average electron dose: 69.3 e/Å2 |
| Electron beam | Acceleration voltage: 300 kV / Electron source:  FIELD EMISSION GUN FIELD EMISSION GUN |
| Electron optics | Illumination mode: FLOOD BEAM / Imaging mode: BRIGHT FIELD |
| Experimental equipment |  Model: Titan Krios / Image courtesy: FEI Company |
- Image processing
Image processing
| Startup model | Type of model: PDB ENTRY |
|---|---|
| Final reconstruction | Applied symmetry - Point group: C3 (3 fold cyclic) / Resolution.type: BY AUTHOR / Resolution: 3.05 Å / Resolution method: FSC 0.143 CUT-OFF / Number images used: 74233 |
| Initial angle assignment | Type: ANGULAR RECONSTITUTION |
| Final angle assignment | Type: ANGULAR RECONSTITUTION |
 Movie
Movie Controller
Controller








 Z (Sec.)
Z (Sec.) Y (Row.)
Y (Row.) X (Col.)
X (Col.)





















