[English] 日本語
 Yorodumi
Yorodumi- PDB-6wzb: Crystal structure of the GltPh V216C-G388C mutant cross-linked wi... -
+ Open data
Open data
- Basic information
Basic information
| Entry | Database: PDB / ID: 6wzb | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
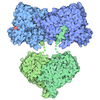
| Title | Crystal structure of the GltPh V216C-G388C mutant cross-linked with divalent mercury | ||||||
 Components Components | Glutamate transporter homolog | ||||||
 Keywords Keywords | TRANSPORT PROTEIN / Glutamate transporter homolog | ||||||
| Function / homology |  Function and homology information Function and homology informationL-aspartate transmembrane transport / L-aspartate transmembrane transporter activity / amino acid:sodium symporter activity / L-aspartate import across plasma membrane / chloride transmembrane transporter activity / protein homotrimerization / chloride transmembrane transport / metal ion binding / identical protein binding / plasma membrane Similarity search - Function | ||||||
| Biological species |   Pyrococcus horikoshii (archaea) Pyrococcus horikoshii (archaea) | ||||||
| Method |  X-RAY DIFFRACTION / X-RAY DIFFRACTION /  SYNCHROTRON / SYNCHROTRON /  MOLECULAR REPLACEMENT / Resolution: 3.45 Å MOLECULAR REPLACEMENT / Resolution: 3.45 Å | ||||||
 Authors Authors | Chen, I. / Font, J. / Ryan, R. | ||||||
| Funding support |  Australia, 1items Australia, 1items
| ||||||
 Citation Citation |  Journal: Nature / Year: 2021 Journal: Nature / Year: 2021Title: Glutamate transporters have a chloride channel with two hydrophobic gates. Authors: Ichia Chen / Shashank Pant / Qianyi Wu / Rosemary J Cater / Meghna Sobti / Robert J Vandenberg / Alastair G Stewart / Emad Tajkhorshid / Josep Font / Renae M Ryan /   Abstract: Glutamate is the most abundant excitatory neurotransmitter in the central nervous system, and its precise control is vital to maintain normal brain function and to prevent excitotoxicity. The removal ...Glutamate is the most abundant excitatory neurotransmitter in the central nervous system, and its precise control is vital to maintain normal brain function and to prevent excitotoxicity. The removal of extracellular glutamate is achieved by plasma-membrane-bound transporters, which couple glutamate transport to sodium, potassium and pH gradients using an elevator mechanism. Glutamate transporters also conduct chloride ions by means of a channel-like process that is thermodynamically uncoupled from transport. However, the molecular mechanisms that enable these dual-function transporters to carry out two seemingly contradictory roles are unknown. Here we report the cryo-electron microscopy structure of a glutamate transporter homologue in an open-channel state, which reveals an aqueous cavity that is formed during the glutamate transport cycle. The functional properties of this cavity, combined with molecular dynamics simulations, reveal it to be an aqueous-accessible chloride permeation pathway that is gated by two hydrophobic regions and is conserved across mammalian and archaeal glutamate transporters. Our findings provide insight into the mechanism by which glutamate transporters support their dual function, and add information that will assist in mapping the complete transport cycle shared by the solute carrier 1A transporter family. | ||||||
| History |
|
- Structure visualization
Structure visualization
| Structure viewer | Molecule:  Molmil Molmil Jmol/JSmol Jmol/JSmol |
|---|
- Downloads & links
Downloads & links
- Download
Download
| PDBx/mmCIF format |  6wzb.cif.gz 6wzb.cif.gz | 467.8 KB | Display |  PDBx/mmCIF format PDBx/mmCIF format |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| PDB format |  pdb6wzb.ent.gz pdb6wzb.ent.gz | 391.6 KB | Display |  PDB format PDB format |
| PDBx/mmJSON format |  6wzb.json.gz 6wzb.json.gz | Tree view |  PDBx/mmJSON format PDBx/mmJSON format | |
| Others |  Other downloads Other downloads |
-Validation report
| Arichive directory |  https://data.pdbj.org/pub/pdb/validation_reports/wz/6wzb https://data.pdbj.org/pub/pdb/validation_reports/wz/6wzb ftp://data.pdbj.org/pub/pdb/validation_reports/wz/6wzb ftp://data.pdbj.org/pub/pdb/validation_reports/wz/6wzb | HTTPS FTP |
|---|
-Related structure data
| Related structure data |  6wyjC  6wykC  6wylC  6x01C  3kbcS S: Starting model for refinement C: citing same article ( |
|---|---|
| Similar structure data |
- Links
Links
- Assembly
Assembly
| Deposited unit | 
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 |
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Unit cell |
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Noncrystallographic symmetry (NCS) | NCS domain:
NCS domain segments: Component-ID: 1 / Ens-ID: 1 / Beg auth comp-ID: LYS / Beg label comp-ID: LYS / End auth comp-ID: GLU / End label comp-ID: GLU / Auth seq-ID: 6 - 416 / Label seq-ID: 6 - 416
|
- Components
Components
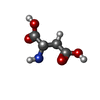
| #1: Protein | Mass: 44599.062 Da / Num. of mol.: 3 / Mutation: V216C, G388C, C321S Source method: isolated from a genetically manipulated source Source: (gene. exp.)   Pyrococcus horikoshii (strain ATCC 700860 / DSM 12428 / JCM 9974 / NBRC 100139 / OT-3) (archaea) Pyrococcus horikoshii (strain ATCC 700860 / DSM 12428 / JCM 9974 / NBRC 100139 / OT-3) (archaea)Strain: ATCC 700860 / DSM 12428 / JCM 9974 / NBRC 100139 / OT-3 Gene: PH1295 / Production host:  #2: Chemical | #3: Chemical | ChemComp-NA / #4: Chemical | Has ligand of interest | N | |
|---|
-Experimental details
-Experiment
| Experiment | Method:  X-RAY DIFFRACTION / Number of used crystals: 1 X-RAY DIFFRACTION / Number of used crystals: 1 |
|---|
- Sample preparation
Sample preparation
| Crystal | Density Matthews: 4.44 Å3/Da / Density % sol: 72.32 % |
|---|---|
| Crystal grow | Temperature: 293.15 K / Method: vapor diffusion, hanging drop Details: 30/35% PEG 400, 0.2M magnesium chloride, 0.1M potassium chloride, 0.025M sodium citrate PH range: 3.5 - 5.0 |
-Data collection
| Diffraction | Mean temperature: 100 K / Serial crystal experiment: N |
|---|---|
| Diffraction source | Source:  SYNCHROTRON / Site: SYNCHROTRON / Site:  Australian Synchrotron Australian Synchrotron  / Beamline: MX2 / Wavelength: 0.9537 Å / Beamline: MX2 / Wavelength: 0.9537 Å |
| Detector | Type: DECTRIS EIGER X 16M / Detector: PIXEL / Date: Jun 7, 2017 |
| Radiation | Protocol: SINGLE WAVELENGTH / Monochromatic (M) / Laue (L): M / Scattering type: x-ray |
| Radiation wavelength | Wavelength: 0.9537 Å / Relative weight: 1 |
| Reflection | Resolution: 3.45→49.311 Å / Num. obs: 31780 / % possible obs: 100 % / Redundancy: 13.8 % / CC1/2: 0.997 / Rmerge(I) obs: 0.155 / Net I/σ(I): 10.3 |
| Reflection shell | Resolution: 3.45→3.64 Å / Rmerge(I) obs: 1.518 / Mean I/σ(I) obs: 2.2 / Num. unique obs: 4587 / CC1/2: 0.782 |
- Processing
Processing
| Software |
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Refinement | Method to determine structure:  MOLECULAR REPLACEMENT MOLECULAR REPLACEMENTStarting model: 3KBC Resolution: 3.45→49.311 Å / SU ML: 0.38 / Cross valid method: THROUGHOUT / σ(F): 1.34 / Phase error: 29.49 / Stereochemistry target values: ML
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Solvent computation | Shrinkage radii: 0.9 Å / VDW probe radii: 1.11 Å / Solvent model: FLAT BULK SOLVENT MODEL | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Displacement parameters | Biso max: 217.04 Å2 / Biso mean: 111.4703 Å2 / Biso min: 55.36 Å2 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Refinement step | Cycle: final / Resolution: 3.45→49.311 Å
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Refine LS restraints NCS |
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| LS refinement shell | Refine-ID: X-RAY DIFFRACTION / Rfactor Rfree error: 0
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Refinement TLS params. | Method: refined / Refine-ID: X-RAY DIFFRACTION
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Refinement TLS group |
|
 Movie
Movie Controller
Controller




 PDBj
PDBj