[English] 日本語
 Yorodumi
Yorodumi- EMDB-21967: Cryo-EM structure of the GltPh L152C-G321C mutant in the intermed... -
+ Open data
Open data
- Basic information
Basic information
| Entry | Database: EMDB / ID: EMD-21967 | |||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
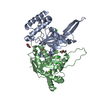
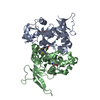
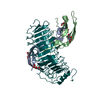
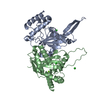
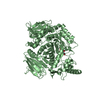
| Title | Cryo-EM structure of the GltPh L152C-G321C mutant in the intermediate chloride conducting state. | |||||||||
 Map data Map data | Cryo-EM structure of the GltPh L152C-G321C mutant in the intermediate chloride conducting state | |||||||||
 Sample Sample |
| |||||||||
 Keywords Keywords | Glutamate transporter homolog Gltph / TRANSPORT PROTEIN | |||||||||
| Function / homology |  Function and homology information Function and homology informationL-aspartate transmembrane transport / L-aspartate transmembrane transporter activity / amino acid:sodium symporter activity / L-aspartate import across plasma membrane / chloride transmembrane transporter activity / protein homotrimerization / chloride transmembrane transport / metal ion binding / identical protein binding / plasma membrane Similarity search - Function | |||||||||
| Biological species |   Pyrococcus horikoshii OT3 (archaea) / Pyrococcus horikoshii OT3 (archaea) /   Pyrococcus horikoshii (strain ATCC 700860 / DSM 12428 / JCM 9974 / NBRC 100139 / OT-3) (archaea) Pyrococcus horikoshii (strain ATCC 700860 / DSM 12428 / JCM 9974 / NBRC 100139 / OT-3) (archaea) | |||||||||
| Method | single particle reconstruction / cryo EM / Resolution: 4.0 Å | |||||||||
 Authors Authors | Font J / Chen I | |||||||||
| Funding support |  Australia, 1 items Australia, 1 items
| |||||||||
 Citation Citation |  Journal: Nature / Year: 2021 Journal: Nature / Year: 2021Title: Glutamate transporters have a chloride channel with two hydrophobic gates. Authors: Ichia Chen / Shashank Pant / Qianyi Wu / Rosemary J Cater / Meghna Sobti / Robert J Vandenberg / Alastair G Stewart / Emad Tajkhorshid / Josep Font / Renae M Ryan /   Abstract: Glutamate is the most abundant excitatory neurotransmitter in the central nervous system, and its precise control is vital to maintain normal brain function and to prevent excitotoxicity. The removal ...Glutamate is the most abundant excitatory neurotransmitter in the central nervous system, and its precise control is vital to maintain normal brain function and to prevent excitotoxicity. The removal of extracellular glutamate is achieved by plasma-membrane-bound transporters, which couple glutamate transport to sodium, potassium and pH gradients using an elevator mechanism. Glutamate transporters also conduct chloride ions by means of a channel-like process that is thermodynamically uncoupled from transport. However, the molecular mechanisms that enable these dual-function transporters to carry out two seemingly contradictory roles are unknown. Here we report the cryo-electron microscopy structure of a glutamate transporter homologue in an open-channel state, which reveals an aqueous cavity that is formed during the glutamate transport cycle. The functional properties of this cavity, combined with molecular dynamics simulations, reveal it to be an aqueous-accessible chloride permeation pathway that is gated by two hydrophobic regions and is conserved across mammalian and archaeal glutamate transporters. Our findings provide insight into the mechanism by which glutamate transporters support their dual function, and add information that will assist in mapping the complete transport cycle shared by the solute carrier 1A transporter family. | |||||||||
| History |
|
- Structure visualization
Structure visualization
| Movie |
 Movie viewer Movie viewer |
|---|---|
| Structure viewer | EM map:  SurfView SurfView Molmil Molmil Jmol/JSmol Jmol/JSmol |
| Supplemental images |
- Downloads & links
Downloads & links
-EMDB archive
| Map data |  emd_21967.map.gz emd_21967.map.gz | 3.1 MB |  EMDB map data format EMDB map data format | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Header (meta data) |  emd-21967-v30.xml emd-21967-v30.xml emd-21967.xml emd-21967.xml | 14.7 KB 14.7 KB | Display Display |  EMDB header EMDB header |
| Images |  emd_21967.png emd_21967.png | 21.7 KB | ||
| Filedesc metadata |  emd-21967.cif.gz emd-21967.cif.gz | 5.8 KB | ||
| Archive directory |  http://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/structures/EMD-21967 http://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/structures/EMD-21967 ftp://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/structures/EMD-21967 ftp://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/structures/EMD-21967 | HTTPS FTP |
-Related structure data
| Related structure data |  6wykMC  6wyjC  6wylC  6wzbC  6x01C M: atomic model generated by this map C: citing same article ( |
|---|---|
| Similar structure data |
- Links
Links
| EMDB pages |  EMDB (EBI/PDBe) / EMDB (EBI/PDBe) /  EMDataResource EMDataResource |
|---|---|
| Related items in Molecule of the Month |
- Map
Map
| File |  Download / File: emd_21967.map.gz / Format: CCP4 / Size: 64 MB / Type: IMAGE STORED AS FLOATING POINT NUMBER (4 BYTES) Download / File: emd_21967.map.gz / Format: CCP4 / Size: 64 MB / Type: IMAGE STORED AS FLOATING POINT NUMBER (4 BYTES) | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Annotation | Cryo-EM structure of the GltPh L152C-G321C mutant in the intermediate chloride conducting state | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Projections & slices | Image control
Images are generated by Spider. | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Voxel size | X=Y=Z: 0.986 Å | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Density |
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Symmetry | Space group: 1 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Details | EMDB XML:
CCP4 map header:
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
-Supplemental data
- Sample components
Sample components
-Entire : Glutamate transporter homolog GltPh monomer in intermediate chlor...
| Entire | Name: Glutamate transporter homolog GltPh monomer in intermediate chloride conducting configuration |
|---|---|
| Components |
|
-Supramolecule #1: Glutamate transporter homolog GltPh monomer in intermediate chlor...
| Supramolecule | Name: Glutamate transporter homolog GltPh monomer in intermediate chloride conducting configuration type: complex / ID: 1 / Parent: 0 / Macromolecule list: #1 |
|---|---|
| Source (natural) | Organism:   Pyrococcus horikoshii OT3 (archaea) Pyrococcus horikoshii OT3 (archaea) |
-Macromolecule #1: Glutamate transporter homolog
| Macromolecule | Name: Glutamate transporter homolog / type: protein_or_peptide / ID: 1 / Number of copies: 1 / Enantiomer: LEVO |
|---|---|
| Source (natural) | Organism:   Pyrococcus horikoshii (strain ATCC 700860 / DSM 12428 / JCM 9974 / NBRC 100139 / OT-3) (archaea) Pyrococcus horikoshii (strain ATCC 700860 / DSM 12428 / JCM 9974 / NBRC 100139 / OT-3) (archaea)Strain: ATCC 700860 / DSM 12428 / JCM 9974 / NBRC 100139 / OT-3 |
| Molecular weight | Theoretical: 44.585035 KDa |
| Recombinant expression | Organism:  |
| Sequence | String: MGLYRKYIEY PVLQKILIGL ILGAIVGLIL GHYGYADAVK TYVKPFGDLF VRLLKMLVMP IVFASLVVGA ASISPARLGR VGVKIVVYY LLTSAFAVTL GIIMARLFNP GAGIHLAVGG QQFQPKQAPP LVKILLDIVP TNPFGALANG QVCPTIFFAI I LGIAITYL ...String: MGLYRKYIEY PVLQKILIGL ILGAIVGLIL GHYGYADAVK TYVKPFGDLF VRLLKMLVMP IVFASLVVGA ASISPARLGR VGVKIVVYY LLTSAFAVTL GIIMARLFNP GAGIHLAVGG QQFQPKQAPP LVKILLDIVP TNPFGALANG QVCPTIFFAI I LGIAITYL MNSENEKVRK SAETLLDAIN GLAEAMYKIV NGVMQYAPIG VFALIAYVMA EQGVKVVGEL AKVTAAVYVG LT LQILLVY FVLLKIYGID PISFIKKAKD AMLTAFVTRS SSGTLPVTMR VAKEMGISEG IYSFTLPLGA TINMDGTALY QGV STFFIA NALGSHLTVG QQLTIVLTAV LASICTAGVP GAGAIMLAMV LESVGLPLTD PNVAAAYAMI LGIDAILDMG RTMV NVTGD LTGTAIVAKT EGTLVPR UniProtKB: Glutamate transporter homolog |
-Macromolecule #2: ASPARTIC ACID
| Macromolecule | Name: ASPARTIC ACID / type: ligand / ID: 2 / Number of copies: 1 / Formula: ASP |
|---|---|
| Molecular weight | Theoretical: 133.103 Da |
| Chemical component information | 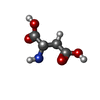 ChemComp-ASP: |
-Experimental details
-Structure determination
| Method | cryo EM |
|---|---|
 Processing Processing | single particle reconstruction |
| Aggregation state | particle |
- Sample preparation
Sample preparation
| Buffer | pH: 7.5 |
|---|---|
| Vitrification | Cryogen name: ETHANE |
- Electron microscopy
Electron microscopy
| Microscope | FEI TALOS ARCTICA |
|---|---|
| Image recording | Film or detector model: FEI FALCON III (4k x 4k) / Detector mode: COUNTING / Average electron dose: 40.0 e/Å2 |
| Electron beam | Acceleration voltage: 200 kV / Electron source:  FIELD EMISSION GUN FIELD EMISSION GUN |
| Electron optics | Illumination mode: FLOOD BEAM / Imaging mode: BRIGHT FIELD |
| Experimental equipment |  Model: Talos Arctica / Image courtesy: FEI Company |
 Movie
Movie Controller
Controller



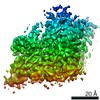
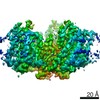

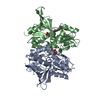




 Z (Sec.)
Z (Sec.) Y (Row.)
Y (Row.) X (Col.)
X (Col.)





















