[English] 日本語
 Yorodumi
Yorodumi- EMDB-21200: Doublet Tau Fibril from Corticobasal Degeneration Human Brain Tissue -
+ Open data
Open data
- Basic information
Basic information
| Entry | Database: EMDB / ID: EMD-21200 | |||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
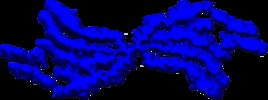
| Title | Doublet Tau Fibril from Corticobasal Degeneration Human Brain Tissue | |||||||||
 Map data Map data | Doublet Tau Fibril from Corticobasal Degeneration Human Brain Tissue | |||||||||
 Sample Sample |
| |||||||||
 Keywords Keywords | Pathological amyloid fibril / cross-beta fold / parallel beta-sheets / PROTEIN FIBRIL | |||||||||
| Function / homology |  Function and homology information Function and homology informationplus-end-directed organelle transport along microtubule / histone-dependent DNA binding / negative regulation of protein localization to mitochondrion / neurofibrillary tangle / microtubule lateral binding / axonal transport / tubulin complex / positive regulation of protein localization to synapse / phosphatidylinositol bisphosphate binding / generation of neurons ...plus-end-directed organelle transport along microtubule / histone-dependent DNA binding / negative regulation of protein localization to mitochondrion / neurofibrillary tangle / microtubule lateral binding / axonal transport / tubulin complex / positive regulation of protein localization to synapse / phosphatidylinositol bisphosphate binding / generation of neurons / rRNA metabolic process / axonal transport of mitochondrion / regulation of mitochondrial fission / axon development / regulation of microtubule-based movement / regulation of chromosome organization / central nervous system neuron development / intracellular distribution of mitochondria / minor groove of adenine-thymine-rich DNA binding / lipoprotein particle binding / microtubule polymerization / negative regulation of mitochondrial membrane potential / regulation of microtubule polymerization / dynactin binding / apolipoprotein binding / main axon / protein polymerization / axolemma / Caspase-mediated cleavage of cytoskeletal proteins / regulation of microtubule polymerization or depolymerization / negative regulation of mitochondrial fission / glial cell projection / neurofibrillary tangle assembly / positive regulation of axon extension / regulation of cellular response to heat / Activation of AMPK downstream of NMDARs / positive regulation of superoxide anion generation / positive regulation of protein localization / cellular response to brain-derived neurotrophic factor stimulus / supramolecular fiber organization / regulation of long-term synaptic depression / positive regulation of microtubule polymerization / synapse assembly / cytoplasmic microtubule organization / regulation of calcium-mediated signaling / somatodendritic compartment / axon cytoplasm / astrocyte activation / phosphatidylinositol binding / enzyme inhibitor activity / nuclear periphery / stress granule assembly / protein phosphatase 2A binding / regulation of microtubule cytoskeleton organization / cellular response to reactive oxygen species / microglial cell activation / Hsp90 protein binding / cellular response to nerve growth factor stimulus / PKR-mediated signaling / protein homooligomerization / synapse organization / regulation of synaptic plasticity / regulation of autophagy / SH3 domain binding / response to lead ion / microtubule cytoskeleton organization / memory / neuron projection development / cytoplasmic ribonucleoprotein granule / cell-cell signaling / single-stranded DNA binding / protein-folding chaperone binding / cellular response to heat / microtubule cytoskeleton / actin binding / growth cone / cell body / double-stranded DNA binding / protein-macromolecule adaptor activity / microtubule binding / sequence-specific DNA binding / dendritic spine / amyloid fibril formation / microtubule / learning or memory / neuron projection / membrane raft / negative regulation of gene expression / axon / neuronal cell body / DNA damage response / dendrite / protein kinase binding / enzyme binding / mitochondrion / DNA binding / RNA binding / extracellular region / identical protein binding / nucleus Similarity search - Function | |||||||||
| Biological species |  Homo sapiens (human) Homo sapiens (human) | |||||||||
| Method | helical reconstruction / cryo EM / Resolution: 3.8 Å | |||||||||
 Authors Authors | Arakhamia T / Lee CE | |||||||||
| Funding support |  United States, 2 items United States, 2 items
| |||||||||
 Citation Citation |  Journal: Cell / Year: 2020 Journal: Cell / Year: 2020Title: Posttranslational Modifications Mediate the Structural Diversity of Tauopathy Strains. Authors: Tamta Arakhamia / Christina E Lee / Yari Carlomagno / Duc M Duong / Sean R Kundinger / Kevin Wang / Dewight Williams / Michael DeTure / Dennis W Dickson / Casey N Cook / Nicholas T Seyfried ...Authors: Tamta Arakhamia / Christina E Lee / Yari Carlomagno / Duc M Duong / Sean R Kundinger / Kevin Wang / Dewight Williams / Michael DeTure / Dennis W Dickson / Casey N Cook / Nicholas T Seyfried / Leonard Petrucelli / Anthony W P Fitzpatrick /  Abstract: Tau aggregation into insoluble filaments is the defining pathological hallmark of tauopathies. However, it is not known what controls the formation and templated seeding of strain-specific structures ...Tau aggregation into insoluble filaments is the defining pathological hallmark of tauopathies. However, it is not known what controls the formation and templated seeding of strain-specific structures associated with individual tauopathies. Here, we use cryo-electron microscopy (cryo-EM) to determine the structures of tau filaments from corticobasal degeneration (CBD) human brain tissue. Cryo-EM and mass spectrometry of tau filaments from CBD reveal that this conformer is heavily decorated with posttranslational modifications (PTMs), enabling us to map PTMs directly onto the structures. By comparing the structures and PTMs of tau filaments from CBD and Alzheimer's disease, it is found that ubiquitination of tau can mediate inter-protofilament interfaces. We propose a structure-based model in which cross-talk between PTMs influences tau filament structure, contributing to the structural diversity of tauopathy strains. Our approach establishes a framework for further elucidating the relationship between the structures of polymorphic fibrils, including their PTMs, and neurodegenerative disease. | |||||||||
| History |
|
- Structure visualization
Structure visualization
| Movie |
 Movie viewer Movie viewer |
|---|---|
| Structure viewer | EM map:  SurfView SurfView Molmil Molmil Jmol/JSmol Jmol/JSmol |
| Supplemental images |
- Downloads & links
Downloads & links
-EMDB archive
| Map data |  emd_21200.map.gz emd_21200.map.gz | 1.1 MB |  EMDB map data format EMDB map data format | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Header (meta data) |  emd-21200-v30.xml emd-21200-v30.xml emd-21200.xml emd-21200.xml | 11.9 KB 11.9 KB | Display Display |  EMDB header EMDB header |
| Images |  emd_21200.png emd_21200.png | 266.1 KB | ||
| Filedesc metadata |  emd-21200.cif.gz emd-21200.cif.gz | 5.4 KB | ||
| Archive directory |  http://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/structures/EMD-21200 http://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/structures/EMD-21200 ftp://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/structures/EMD-21200 ftp://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/structures/EMD-21200 | HTTPS FTP |
-Related structure data
| Related structure data |  6vh7MC  6vhaC  6vhlC  6vi3C M: atomic model generated by this map C: citing same article ( |
|---|---|
| Similar structure data |
- Links
Links
| EMDB pages |  EMDB (EBI/PDBe) / EMDB (EBI/PDBe) /  EMDataResource EMDataResource |
|---|---|
| Related items in Molecule of the Month |
- Map
Map
| File |  Download / File: emd_21200.map.gz / Format: CCP4 / Size: 75.1 MB / Type: IMAGE STORED AS FLOATING POINT NUMBER (4 BYTES) Download / File: emd_21200.map.gz / Format: CCP4 / Size: 75.1 MB / Type: IMAGE STORED AS FLOATING POINT NUMBER (4 BYTES) | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Annotation | Doublet Tau Fibril from Corticobasal Degeneration Human Brain Tissue | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Projections & slices | Image control
Images are generated by Spider. | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Voxel size | X=Y=Z: 1.414 Å | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Density |
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Symmetry | Space group: 1 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Details | EMDB XML:
CCP4 map header:
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
-Supplemental data
- Sample components
Sample components
-Entire : Doublet Tau Fibril from Corticobasal Degeneration Human Brain Tissue
| Entire | Name: Doublet Tau Fibril from Corticobasal Degeneration Human Brain Tissue |
|---|---|
| Components |
|
-Supramolecule #1: Doublet Tau Fibril from Corticobasal Degeneration Human Brain Tissue
| Supramolecule | Name: Doublet Tau Fibril from Corticobasal Degeneration Human Brain Tissue type: tissue / ID: 1 / Parent: 0 / Macromolecule list: all |
|---|---|
| Source (natural) | Organism:  Homo sapiens (human) Homo sapiens (human) |
-Macromolecule #1: Microtubule-associated protein tau
| Macromolecule | Name: Microtubule-associated protein tau / type: protein_or_peptide / ID: 1 / Number of copies: 6 / Enantiomer: LEVO |
|---|---|
| Source (natural) | Organism:  Homo sapiens (human) Homo sapiens (human) |
| Molecular weight | Theoretical: 11.608375 KDa |
| Recombinant expression | Organism:  Homo sapiens (human) Homo sapiens (human) |
| Sequence | String: KVQIINKKLD LSNVQSKCGS KDNIKHVPGG GSVQIVYKPV DLSKVTSKCG SLGNIHHKPG GGQVEVKSEK LDFKDRVQSK IGSLDNITH VPGGGNKKIE THKLTFRE UniProtKB: Microtubule-associated protein tau |
-Experimental details
-Structure determination
| Method | cryo EM |
|---|---|
 Processing Processing | helical reconstruction |
| Aggregation state | filament |
- Sample preparation
Sample preparation
| Buffer | pH: 7.4 |
|---|---|
| Grid | Details: unspecified |
| Vitrification | Cryogen name: ETHANE |
- Electron microscopy
Electron microscopy
| Microscope | FEI TITAN KRIOS |
|---|---|
| Image recording | Film or detector model: GATAN K2 SUMMIT (4k x 4k) / Average electron dose: 60.0 e/Å2 |
| Electron beam | Acceleration voltage: 300 kV / Electron source:  FIELD EMISSION GUN FIELD EMISSION GUN |
| Electron optics | Illumination mode: FLOOD BEAM / Imaging mode: BRIGHT FIELD |
| Experimental equipment |  Model: Titan Krios / Image courtesy: FEI Company |
- Image processing
Image processing
| Final reconstruction | Applied symmetry - Helical parameters - Δz: 4.8 Å Applied symmetry - Helical parameters - Δ&Phi: -0.6 ° Applied symmetry - Helical parameters - Axial symmetry: C2 (2 fold cyclic) Resolution.type: BY AUTHOR / Resolution: 3.8 Å / Resolution method: FSC 0.143 CUT-OFF / Number images used: 7549 |
|---|---|
| CTF correction | Type: PHASE FLIPPING AND AMPLITUDE CORRECTION |
| Startup model | Type of model: NONE |
| Final angle assignment | Type: NOT APPLICABLE |
 Movie
Movie Controller
Controller

















 Z (Sec.)
Z (Sec.) Y (Row.)
Y (Row.) X (Col.)
X (Col.)





















