[English] 日本語
 Yorodumi
Yorodumi- EMDB-20959: Cryo-EM structure of the mechanosensitive channel MscS reconstitu... -
+ Open data
Open data
- Basic information
Basic information
| Entry | Database: EMDB / ID: EMD-20959 | |||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Title | Cryo-EM structure of the mechanosensitive channel MscS reconstituted into peptidiscs | |||||||||
 Map data Map data | mechanosensitive channel MscS reconstituted into peptidiscs | |||||||||
 Sample Sample |
| |||||||||
 Keywords Keywords | membrane protein / mechanosensitive channels / MscS / membrane mimetic / peptidisc / TRANSPORT PROTEIN | |||||||||
| Function / homology |  Function and homology information Function and homology informationintracellular water homeostasis / mechanosensitive monoatomic ion channel activity / membrane => GO:0016020 / protein homooligomerization / transmembrane transport / monoatomic ion transmembrane transport / identical protein binding / membrane / plasma membrane Similarity search - Function | |||||||||
| Biological species |  | |||||||||
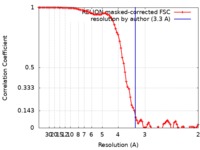
| Method | single particle reconstruction / cryo EM / Resolution: 3.3 Å | |||||||||
 Authors Authors | Angiulli G / Walz T | |||||||||
 Citation Citation |  Journal: Elife / Year: 2020 Journal: Elife / Year: 2020Title: New approach for membrane protein reconstitution into peptidiscs and basis for their adaptability to different proteins. Authors: Gabriella Angiulli / Harveer Singh Dhupar / Hiroshi Suzuki / Irvinder Singh Wason / Franck Duong Van Hoa / Thomas Walz /   Abstract: Previously we introduced peptidiscs as an alternative to detergents to stabilize membrane proteins in solution (Carlson et al., 2018). Here, we present 'on-gradient' reconstitution, a new gentle ...Previously we introduced peptidiscs as an alternative to detergents to stabilize membrane proteins in solution (Carlson et al., 2018). Here, we present 'on-gradient' reconstitution, a new gentle approach for the reconstitution of labile membrane-protein complexes, and used it to reconstitute reaction center complexes, demonstrating that peptidiscs can adapt to transmembrane domains of very different sizes and shapes. Using the conventional 'on-bead' approach, we reconstituted proteins MsbA and MscS and find that peptidiscs stabilize them in their native conformation and allow for high-resolution structure determination by cryo-electron microscopy. The structures reveal that peptidisc peptides can arrange around transmembrane proteins differently, thus revealing the structural basis for why peptidiscs can stabilize such a large variety of membrane proteins. Together, our results establish the gentle and easy-to-use peptidiscs as a potentially universal alternative to detergents as a means to stabilize membrane proteins in solution for structural and functional studies. | |||||||||
| History |
|
- Structure visualization
Structure visualization
| Movie |
 Movie viewer Movie viewer |
|---|---|
| Structure viewer | EM map:  SurfView SurfView Molmil Molmil Jmol/JSmol Jmol/JSmol |
| Supplemental images |
- Downloads & links
Downloads & links
-EMDB archive
| Map data |  emd_20959.map.gz emd_20959.map.gz | 49.2 MB |  EMDB map data format EMDB map data format | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Header (meta data) |  emd-20959-v30.xml emd-20959-v30.xml emd-20959.xml emd-20959.xml | 16 KB 16 KB | Display Display |  EMDB header EMDB header |
| FSC (resolution estimation) |  emd_20959_fsc.xml emd_20959_fsc.xml | 8.5 KB | Display |  FSC data file FSC data file |
| Images |  emd_20959.png emd_20959.png | 56.5 KB | ||
| Filedesc metadata |  emd-20959.cif.gz emd-20959.cif.gz | 6.1 KB | ||
| Archive directory |  http://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/structures/EMD-20959 http://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/structures/EMD-20959 ftp://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/structures/EMD-20959 ftp://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/structures/EMD-20959 | HTTPS FTP |
-Related structure data
| Related structure data |  6uzhMC  6uz2C  6uzlC C: citing same article ( M: atomic model generated by this map |
|---|---|
| Similar structure data |
- Links
Links
| EMDB pages |  EMDB (EBI/PDBe) / EMDB (EBI/PDBe) /  EMDataResource EMDataResource |
|---|---|
| Related items in Molecule of the Month |
- Map
Map
| File |  Download / File: emd_20959.map.gz / Format: CCP4 / Size: 52.7 MB / Type: IMAGE STORED AS FLOATING POINT NUMBER (4 BYTES) Download / File: emd_20959.map.gz / Format: CCP4 / Size: 52.7 MB / Type: IMAGE STORED AS FLOATING POINT NUMBER (4 BYTES) | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Annotation | mechanosensitive channel MscS reconstituted into peptidiscs | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Projections & slices | Image control
Images are generated by Spider. | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Voxel size | X=Y=Z: 1 Å | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
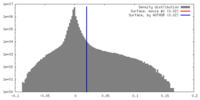
| Density |
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Symmetry | Space group: 1 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Details | EMDB XML:
CCP4 map header:
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
-Supplemental data
- Sample components
Sample components
-Entire : Small-conductance mechanosensitive channel MscS
| Entire | Name: Small-conductance mechanosensitive channel MscS |
|---|---|
| Components |
|
-Supramolecule #1: Small-conductance mechanosensitive channel MscS
| Supramolecule | Name: Small-conductance mechanosensitive channel MscS / type: complex / ID: 1 / Parent: 0 / Macromolecule list: all |
|---|---|
| Source (natural) | Organism:  |
-Macromolecule #1: Small-conductance mechanosensitive channel
| Macromolecule | Name: Small-conductance mechanosensitive channel / type: protein_or_peptide / ID: 1 / Number of copies: 7 / Enantiomer: LEVO |
|---|---|
| Source (natural) | Organism:  |
| Molecular weight | Theoretical: 33.094258 KDa |
| Recombinant expression | Organism:  |
| Sequence | String: MGSSHHHHHH SSGLVPRGSH MEDLNVVDSI NGAGSWLVAN QALLLSYAVN IVAALAIIIV GLIIARMISN AVNRLMISRK IDATVADFL SALVRYGIIA FTLIAALGRV GVQTASVIAV LGAAGLAVGL ALQGSLSNLA AGVLLVMFRP FRAGEYVDLG G VAGTVLSV ...String: MGSSHHHHHH SSGLVPRGSH MEDLNVVDSI NGAGSWLVAN QALLLSYAVN IVAALAIIIV GLIIARMISN AVNRLMISRK IDATVADFL SALVRYGIIA FTLIAALGRV GVQTASVIAV LGAAGLAVGL ALQGSLSNLA AGVLLVMFRP FRAGEYVDLG G VAGTVLSV QIFSTTMRTA DGKIIVIPNG KIIAGNIINF SREPVRRNEF IIGVAYDSDI DQVKQILTNI IQSEDRILKD RE MTVRLNE LGASSINFVV RVWSNSGDLQ NVYWDVLERI KREFDAAGIS FPYPQMDVNF KRVKEDKAA UniProtKB: Small-conductance mechanosensitive channel |
-Experimental details
-Structure determination
| Method | cryo EM |
|---|---|
 Processing Processing | single particle reconstruction |
| Aggregation state | particle |
- Sample preparation
Sample preparation
| Concentration | 0.1 mg/mL | |||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Buffer | pH: 7.9 Component:
| |||||||||
| Sugar embedding | Material: vitreous ice | |||||||||
| Grid | Model: Quantifoil R1.2/1.3 / Material: COPPER / Mesh: 400 / Support film - Material: CARBON / Support film - topology: HOLEY / Pretreatment - Type: GLOW DISCHARGE | |||||||||
| Vitrification | Cryogen name: ETHANE / Chamber humidity: 90 % / Chamber temperature: 277 K / Instrument: FEI VITROBOT MARK IV |
- Electron microscopy
Electron microscopy
| Microscope | FEI TITAN KRIOS |
|---|---|
| Image recording | Film or detector model: GATAN K2 SUMMIT (4k x 4k) / Detector mode: SUPER-RESOLUTION / Number grids imaged: 1 / Average exposure time: 10.0 sec. / Average electron dose: 80.0 e/Å2 |
| Electron beam | Acceleration voltage: 300 kV / Electron source:  FIELD EMISSION GUN FIELD EMISSION GUN |
| Electron optics | Illumination mode: FLOOD BEAM / Imaging mode: BRIGHT FIELD / Cs: 2.7 mm / Nominal defocus max: -3.5 µm / Nominal defocus min: -1.5 µm |
| Sample stage | Specimen holder model: FEI TITAN KRIOS AUTOGRID HOLDER / Cooling holder cryogen: NITROGEN |
| Experimental equipment |  Model: Titan Krios / Image courtesy: FEI Company |
 Movie
Movie Controller
Controller










 Z (Sec.)
Z (Sec.) Y (Row.)
Y (Row.) X (Col.)
X (Col.)