[English] 日本語
 Yorodumi
Yorodumi- EMDB-20657: Electron cryomicroscopy Structure of C. albicans FAS in the Apo state -
+ Open data
Open data
- Basic information
Basic information
| Entry | Database: EMDB / ID: EMD-20657 | |||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Title | Electron cryomicroscopy Structure of C. albicans FAS in the Apo state | |||||||||
 Map data Map data | ||||||||||
 Sample Sample |
| |||||||||
 Keywords Keywords | Fungal Fatty acid synthase / TRANSFERASE | |||||||||
| Function / homology |  Function and homology information Function and homology informationmitotic nuclear membrane biogenesis / palmitic acid biosynthetic process / fatty-acyl-CoA synthase system / fatty-acyl-CoA synthase activity / fatty acid synthase complex / palmitoyltransferase activity / [acyl-carrier-protein] S-acetyltransferase / [acyl-carrier-protein] S-acetyltransferase activity / holo-[acyl-carrier-protein] synthase activity / enoyl-[acyl-carrier-protein] reductase (NADPH) activity ...mitotic nuclear membrane biogenesis / palmitic acid biosynthetic process / fatty-acyl-CoA synthase system / fatty-acyl-CoA synthase activity / fatty acid synthase complex / palmitoyltransferase activity / [acyl-carrier-protein] S-acetyltransferase / [acyl-carrier-protein] S-acetyltransferase activity / holo-[acyl-carrier-protein] synthase activity / enoyl-[acyl-carrier-protein] reductase (NADPH) activity / [acyl-carrier-protein] S-malonyltransferase / [acyl-carrier-protein] S-malonyltransferase activity / 3-hydroxyacyl-[acyl-carrier-protein] dehydratase / (3R)-hydroxyacyl-[acyl-carrier-protein] dehydratase activity / beta-ketoacyl-[acyl-carrier-protein] synthase I / 3-oxoacyl-[acyl-carrier-protein] reductase (NADPH) activity / 3-oxoacyl-[acyl-carrier-protein] reductase / oleoyl-[acyl-carrier-protein] hydrolase / fatty acyl-[ACP] hydrolase activity / enoyl-[acyl-carrier-protein] reductase (NADH) / enoyl-[acyl-carrier-protein] reductase (NADH) activity / long-chain fatty acid biosynthetic process / fatty acid synthase activity / 3-oxoacyl-[acyl-carrier-protein] synthase activity / lipid droplet / magnesium ion binding / cytosol Similarity search - Function | |||||||||
| Biological species |  Candida albicans (yeast) Candida albicans (yeast) | |||||||||
| Method | single particle reconstruction / cryo EM / Resolution: 2.8 Å | |||||||||
 Authors Authors | Lou JW / Mazhab-Jafari MT | |||||||||
 Citation Citation |  Journal: Sci Rep / Year: 2019 Journal: Sci Rep / Year: 2019Title: Electron cryomicroscopy observation of acyl carrier protein translocation in type I fungal fatty acid synthase. Authors: Jennifer W Lou / Kali R Iyer / S M Naimul Hasan / Leah E Cowen / Mohammad T Mazhab-Jafari /  Abstract: During fatty acid biosynthesis, acyl carrier proteins (ACPs) from type I fungal fatty acid synthase (FAS) shuttle substrates and intermediates within a reaction chamber that hosts multiple spatially- ...During fatty acid biosynthesis, acyl carrier proteins (ACPs) from type I fungal fatty acid synthase (FAS) shuttle substrates and intermediates within a reaction chamber that hosts multiple spatially-fixed catalytic centers. A major challenge in understanding the mechanism of ACP-mediated substrate shuttling is experimental observation of its transient interaction landscape within the reaction chamber. Here, we have shown that ACP spatial distribution is sensitive to the presence of substrates in a catalytically inhibited state, which enables high-resolution investigation of the ACP-dependent conformational transitions within the enoyl reductase (ER) reaction site. In two fungal FASs with distinct ACP localization, the shuttling domain is targeted to the ketoacyl-synthase (KS) domain and away from other catalytic centers, such as acetyl-transferase (AT) and ER domains by steric blockage of the KS active site followed by addition of substrates. These studies strongly suggest that acylation of phosphopantetheine arm of ACP may be an integral part of the substrate shuttling mechanism in type I fungal FAS. | |||||||||
| History |
|
- Structure visualization
Structure visualization
| Movie |
 Movie viewer Movie viewer |
|---|---|
| Structure viewer | EM map:  SurfView SurfView Molmil Molmil Jmol/JSmol Jmol/JSmol |
| Supplemental images |
- Downloads & links
Downloads & links
-EMDB archive
| Map data |  emd_20657.map.gz emd_20657.map.gz | 83.3 MB |  EMDB map data format EMDB map data format | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Header (meta data) |  emd-20657-v30.xml emd-20657-v30.xml emd-20657.xml emd-20657.xml | 19.2 KB 19.2 KB | Display Display |  EMDB header EMDB header |
| Images |  emd_20657.png emd_20657.png | 290.9 KB | ||
| Filedesc metadata |  emd-20657.cif.gz emd-20657.cif.gz | 8.3 KB | ||
| Archive directory |  http://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/structures/EMD-20657 http://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/structures/EMD-20657 ftp://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/structures/EMD-20657 ftp://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/structures/EMD-20657 | HTTPS FTP |
-Related structure data
| Related structure data |  6u5vMC  6u5tC  6u5uC  6u5wC M: atomic model generated by this map C: citing same article ( |
|---|---|
| Similar structure data |
- Links
Links
| EMDB pages |  EMDB (EBI/PDBe) / EMDB (EBI/PDBe) /  EMDataResource EMDataResource |
|---|---|
| Related items in Molecule of the Month |
- Map
Map
| File |  Download / File: emd_20657.map.gz / Format: CCP4 / Size: 166.4 MB / Type: IMAGE STORED AS FLOATING POINT NUMBER (4 BYTES) Download / File: emd_20657.map.gz / Format: CCP4 / Size: 166.4 MB / Type: IMAGE STORED AS FLOATING POINT NUMBER (4 BYTES) | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Projections & slices | Image control
Images are generated by Spider. | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Voxel size | X=Y=Z: 1.06 Å | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Density |
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Symmetry | Space group: 1 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Details | EMDB XML:
CCP4 map header:
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
-Supplemental data
- Sample components
Sample components
-Entire : Fatty acid synthase
| Entire | Name: Fatty acid synthase |
|---|---|
| Components |
|
-Supramolecule #1: Fatty acid synthase
| Supramolecule | Name: Fatty acid synthase / type: complex / ID: 1 / Parent: 0 / Macromolecule list: #2 |
|---|---|
| Source (natural) | Organism:  Candida albicans (yeast) Candida albicans (yeast) |
| Molecular weight | Theoretical: 2.6 MDa |
-Macromolecule #1: Fatty acid synthase subunit alpha
| Macromolecule | Name: Fatty acid synthase subunit alpha / type: protein_or_peptide / ID: 1 / Number of copies: 1 / Enantiomer: LEVO / EC number: fatty-acyl-CoA synthase system |
|---|---|
| Source (natural) | Organism:  Candida albicans (yeast) Candida albicans (yeast) |
| Molecular weight | Theoretical: 207.703453 KDa |
| Sequence | String: MKPEIEQELS HTLLTELLAY QFASPVRWIE TQDVFLKQHN TERIIEIGPS PTLAGMANRT IKAKYESYDA ALSLQRQVLC YSKDAKEIY YKPDPADLAP KETPKQEEST PSAPAAATPT PAAAAAPTPA PAPASAGPVE SIPDEPVKAN LLIHVLVAQK L KKPLDAVP ...String: MKPEIEQELS HTLLTELLAY QFASPVRWIE TQDVFLKQHN TERIIEIGPS PTLAGMANRT IKAKYESYDA ALSLQRQVLC YSKDAKEIY YKPDPADLAP KETPKQEEST PSAPAAATPT PAAAAAPTPA PAPASAGPVE SIPDEPVKAN LLIHVLVAQK L KKPLDAVP MTKAIKDLVN GKSTVQNEIL GDLGKEFGST PEKPEDTPLE ELAEQFQDSF SGQLGKTSTS LIGRLMSSKM PG GFSITTA RKYLESRFGL GAGRQDSVLL MALTNEPANR LGSEADAKTF FDGIAQKYAS SAGISLSSGA GSGAGAANSG GAV VDSAAL DALTAENKKL AKQQLEVLAR YLQVDLNKGS AKSFIKEKEA SAVLQKELDL WEAEHGEFYA KGIQPTFSAL KSRT YDSYW NWARQDVLSM YFDIIFGKLT SVDRETINQC IQIMNRANPT LIKFMQYHID HCPEYKGETY KLAKRLGQQL IDNCK QVLT EDPVYKDVSR ITGPKTKVSA KGNIEYEETQ KDSVRKFEQY VYEMAQGGAM TKVSQPTIQE DLARVYKAIS KQASKD SKL ELQRVYEDLL KVVESSKEIE TEQLTKDILQ AATVPTTPTE EVDDPCTPSS DDEIASLPDK TSIIQPVSST IPSQTIP FL HIQKKTKDGW EYNKKLSSLY LDGLESAAIN GLTFKDKYVL VTGAGAGSIG AEILQGLISG GAKVIVTTSR FSKKVTEY Y QNMYARYGAA GSTLIVVPFN QGSKQDVDAL VQYIYDEPKK GGLGWDLDAI IPFAAIPENG NGLDNIDSKS EFAHRIMLT NLLRLLGAVK SKKTTDTRPA QCILPLSPNH GTFGFDGLYS ESKISLETLF NRWYSEDWGS KLTVCGAVIG WTRGTGLMSA NNIIAEGIE KLGVRTFSQK EMAFNILGLL TPEIVQLCQE EPVMADLNGG LQFIDNLKDF TSKLRTDLLE TADIRRAVSI E SAIEQKVV NGDNVDANYS KVMVEPRANM KFDFPTLKSY DEIKQIAPEL EGMLDLENVV VVTGFAEVGP WGNSRTRWEM EA YGEFSLE GAIEMAWIMG FIKYHNGNLK GKPYSGWVDA KTQTPIDEKD IKSKYEEEIL EHSGIRLIEP ELFNGYDPKK KQM IQEVVV QHDLEPFECS KETAEQYKHE HGEKCEIFEI EESGEYTVRI LKGATLYVPK ALRFDRLVAG QIPTGWDART YGIP EDTIS QVDPITLYVL VATVEALLSA GITDPYEFYK YVHVSEVGNC SGSGMGGVSA LRGMFKDRYA DKPVQNDILQ ESFIN TMSA WVNMLLLSSS GPIKTPVGAC ATAVESVDIG IETILSGKAK VVLVGGYDDF QEEGSYEFAN MNATSNSIEE FKHGRT PKE MSRPTTTTRN GFMEAQGSGI QVIMTADLAL KMGVPIHAVL AMTATATDKI GRSVPAPGKG ILTTAREHHG NLKYPSP LL NIEYRKRQLN KRLEQIKSWE ETELSYLQEE AELAKEEFGD EFSMHEFLKE RTEEVYRESK RQVSDAKKQW GNSFYKSD P RIAPLRGALA AFNLTIDDIG VASFHGTSTV ANDKNESATI NNMMKHLGRS EGNPVFGVFQ KYLTGHPKGA AGAWMLNGA IQILESGLVP GNRNADNVDK LLEQYEYVLY PSRSIQTDGI KAVSVTSFGF GQKGAQAVVV HPDYLFAVLD RSTYEEYATK VSARNKKTY RYMHNAITRN TMFVAKDKAP YSDELEQPVY LDPLARVEEN KKKLVFSDKT IQSSQSYVGE VAQKTAKALS T LNKSSKGV GVDVELLSAI NIDNETFIER NFTGNEVEYC LNTAHPQASF TGTWSAKEAV FKALGVESKG AGASLIDIEI TR DVNGAPK VILHGEAKKA AAKAGVKNVN ISISHDDFQA TAVALSEF UniProtKB: Fatty acid synthase subunit alpha |
-Macromolecule #2: Fatty acid synthase subunit beta
| Macromolecule | Name: Fatty acid synthase subunit beta / type: protein_or_peptide / ID: 2 / Number of copies: 1 / Enantiomer: LEVO / EC number: fatty-acyl-CoA synthase system |
|---|---|
| Source (natural) | Organism:  Candida albicans (yeast) Candida albicans (yeast) |
| Molecular weight | Theoretical: 228.177609 KDa |
| Sequence | String: MSTHRPFQLT HGSIEHTLLV PNDLFFNYSQ LKDEFIKTLP EPTEGFAGDD EPSSPAELYG KFIGFISNAQ FPQIVELSLK DFESRFLDN NNDNIHSFAV KLLDDETYPT TIAKVKENIV KNYYKAVKSI NKVESNLLYH CKHDAKLVAI FGGQGNTDDY F EELRELYT ...String: MSTHRPFQLT HGSIEHTLLV PNDLFFNYSQ LKDEFIKTLP EPTEGFAGDD EPSSPAELYG KFIGFISNAQ FPQIVELSLK DFESRFLDN NNDNIHSFAV KLLDDETYPT TIAKVKENIV KNYYKAVKSI NKVESNLLYH CKHDAKLVAI FGGQGNTDDY F EELRELYT LYQGLIEDLL VSIAEKLNQL HPSFDKIYTQ GLNILSWLKH PETTPDQDYL LSVPVSCPVI CVIQLCHYTI TC KVLGLTP GEFRNSLKWS TGHSQGLVTA VTIAASDSWD SFLKNSLTAV SLLLFIGSRC LSTYPRTSLP PTMLQDSLDN GEG RPSPML SVRDLSIKQV EKFIEQTNSH LPREKHIAIS LINGARNLVL SGPPESLYGF NLNLRNQKAP MGLDQSRVPF SERK LKCSN RFLPIFAPFH SHLLADATEL ILDDVKEHGL SFEGLKIPVY DTFDGSDFQA LKEPIIDRVV KLITELPVHW EEATN HKAT HILDFGPGGV SGLGVLTHRN KEGTGARIIL AGTLDSNPID DEYGFKHEIF QTSADKAIKW APDWLKELRP TLVKNS EGK IYVKTKFSQL LGRAPLMVAG MTPTTVNTDI VSASLNAGYH IELAGGGYFS PVMMTRAIDD IVSRIKPGYG LGINLIY VN PFMLQWGIPL IKDLREKGYP IQSLTIGAGV PSIEVATEYI EDLGLTHLGL KPGSVDAISQ VIAIAKAHPT FPIVLQWT G GRGGGHHSFE DFHQPIIQMY SKIRRCSNIV LVAGSGFGSD EDTYPYLSGY WSEKFNYPPM PFDGVLFGSR VMTSKESHT SLAAKKLIVE CKGVPDQQWE QTYKKPTGGI ITVRSEMGEP IHKIATRGVM FWKELDDTIF NLPKNKLLDA LNKKRDHIIK KLNNDFQKP WFGKNANGVC DLQEMTYKEV ANRLVELMYV KKSHRWIDVS LRNMYGDFLR RVEERFTSSA GTVSLLQNFN Q LNEPEQFT ADFFEKFPQA GKQLISEEDC DYFLMLAARP GQKPVPFVPV LDERFEFFFK KDSLWQSEDL ESVVDEDVQR TC ILHGPVA SQYTSKVDEP IGDILNSIHE GHIARLIKEE YAGDESKIPV VEYFGGKKPA SVSATSVNII DGNQVVYEID SEL PNKQEW LDLLAGTELN WLQAFISTDR IVQGSKHVSN PLHDILTPAK HSKVTIDKKT KKLTAFENIK GDLLPVVEIE LVKP NTIQL SLIEHRTADT NPVALPFLYK YNPADGFAPI LEIMEDRNER IKEFYWKLWF GSSVPYSNDI NVEKAILGDE ITISS QTIS EFTHAIGNKC DAFVDRPGKA TLAPMDFAIV IGWKAIIKAI FPKSVDGDLL KLVHLSNGYK MITGAAPLKK GDVVST KAE IKAVLNQPSG KLVEVVGTIY REGKPVMEVT SQFLYRGEYN DYCNTFQKVT ETPVQVAFKS AKDLAVLRSK EWFHLEK DV QFDVLTFRCE STYKFKSANV YSSIKTTGQV LLELPTKEVI QVGSVDYEAG TSYGNPVTDY LSRNGKTIEE SVIFENAI P LSSGEELTSK APGTNEPYAI VSGDYNPIHV SRVFAAYAKL PGTITHGMYS SASIRALVEE WAANNVAARV RAFKCDFVG MVLPNDTLQT TMEHVGMING RKIIKVETRN VETELPVLIG EAEIEQPTTT YVFTGQGSQE QGMGMELYNS SEVAREVWDK ADRHFVNNY GFSILDIVQN NPNELTIHFG GAKGRAIRDN YIGMMFETIG EDGALKSEKI FKDIDETTTS YTFVSPTGLL S ATQFTQPA LTLMEKAAYE DIKSKGLIPS DIMFAGHSLG EYSALSSLAN VMPIESLVDV VFYRGMTMQV AVPRDELGRS NY GMVAVNP SRVSATFDDS ALRFVVDEVA NKTKWLLEIV NYNVENQQYV AAGDLRALDT LTNVLNVLKI NKIDIVKLQE QMS IEKVKE HLYEIVDEVA AKSLAKPQPI DLERGFAVIP LKGISVPFHS SYLMSGVKPF QRFLCKKIPK SSVKPQDLIG KYIP NLTAK PFELTKEYFQ SVYDLTKSEK IKSILDNWEQ YE UniProtKB: Fatty acid synthase subunit beta |
-Macromolecule #3: 4'-PHOSPHOPANTETHEINE
| Macromolecule | Name: 4'-PHOSPHOPANTETHEINE / type: ligand / ID: 3 / Number of copies: 1 / Formula: PNS |
|---|---|
| Molecular weight | Theoretical: 358.348 Da |
| Chemical component information | 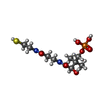 ChemComp-PNS: |
-Macromolecule #4: FLAVIN MONONUCLEOTIDE
| Macromolecule | Name: FLAVIN MONONUCLEOTIDE / type: ligand / ID: 4 / Number of copies: 1 / Formula: FMN |
|---|---|
| Molecular weight | Theoretical: 456.344 Da |
| Chemical component information | 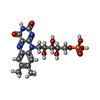 ChemComp-FMN: |
-Experimental details
-Structure determination
| Method | cryo EM |
|---|---|
 Processing Processing | single particle reconstruction |
| Aggregation state | particle |
- Sample preparation
Sample preparation
| Buffer | pH: 7.4 |
|---|---|
| Vitrification | Cryogen name: ETHANE / Chamber humidity: 100 % / Chamber temperature: 277.15 K / Instrument: FEI VITROBOT MARK IV |
- Electron microscopy
Electron microscopy
| Microscope | FEI TITAN KRIOS |
|---|---|
| Image recording | Film or detector model: FEI FALCON III (4k x 4k) / Average electron dose: 43.0 e/Å2 |
| Electron beam | Acceleration voltage: 300 kV / Electron source:  FIELD EMISSION GUN FIELD EMISSION GUN |
| Electron optics | Illumination mode: FLOOD BEAM / Imaging mode: BRIGHT FIELD |
| Experimental equipment |  Model: Titan Krios / Image courtesy: FEI Company |
- Image processing
Image processing
| Startup model | Type of model: PDB ENTRY PDB model - PDB ID: |
|---|---|
| Final reconstruction | Number classes used: 1 / Applied symmetry - Point group: D3 (2x3 fold dihedral) / Resolution.type: BY AUTHOR / Resolution: 2.8 Å / Resolution method: FSC 0.143 CUT-OFF / Software - Name: cryoSPARC (ver. 2) / Number images used: 92958 |
| Initial angle assignment | Type: OTHER / Software - Name: cryoSPARC (ver. 2) / Details: cryoSPARC2 |
| Final angle assignment | Type: MAXIMUM LIKELIHOOD / Software - Name: cryoSPARC (ver. 2) |
 Movie
Movie Controller
Controller







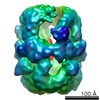
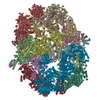


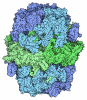

 Z (Sec.)
Z (Sec.) Y (Row.)
Y (Row.) X (Col.)
X (Col.)






















