[English] 日本語
 Yorodumi
Yorodumi- EMDB-20656: Electron cryomicroscopy Structure of S. cerevisiae FAS in the KS-... -
+ Open data
Open data
- Basic information
Basic information
| Entry | Database: EMDB / ID: EMD-20656 | |||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Title | Electron cryomicroscopy Structure of S. cerevisiae FAS in the KS-stalled state | |||||||||
 Map data Map data | primary map | |||||||||
 Sample Sample |
| |||||||||
 Keywords Keywords | Fungal Fatty acid synthase / TRANSFERASE | |||||||||
| Function / homology |  Function and homology information Function and homology informationfatty-acyl-CoA synthase system / fatty-acyl-CoA synthase activity / fatty acid synthase complex / palmitoyltransferase activity / [acyl-carrier-protein] S-acetyltransferase / [acyl-carrier-protein] S-acetyltransferase activity / holo-[acyl-carrier-protein] synthase activity / [acyl-carrier-protein] S-malonyltransferase / [acyl-carrier-protein] S-malonyltransferase activity / enoyl-[acyl-carrier-protein] reductase (NADPH) activity ...fatty-acyl-CoA synthase system / fatty-acyl-CoA synthase activity / fatty acid synthase complex / palmitoyltransferase activity / [acyl-carrier-protein] S-acetyltransferase / [acyl-carrier-protein] S-acetyltransferase activity / holo-[acyl-carrier-protein] synthase activity / [acyl-carrier-protein] S-malonyltransferase / [acyl-carrier-protein] S-malonyltransferase activity / enoyl-[acyl-carrier-protein] reductase (NADPH) activity / 3-hydroxyacyl-[acyl-carrier-protein] dehydratase / (3R)-hydroxyacyl-[acyl-carrier-protein] dehydratase activity / beta-ketoacyl-[acyl-carrier-protein] synthase I / 3-oxoacyl-[acyl-carrier-protein] reductase / 3-oxoacyl-[acyl-carrier-protein] reductase (NADPH) activity / oleoyl-[acyl-carrier-protein] hydrolase / fatty acyl-[ACP] hydrolase activity / enoyl-[acyl-carrier-protein] reductase (NADH) / enoyl-[acyl-carrier-protein] reductase (NADH) activity / long-chain fatty acid biosynthetic process / fatty acid synthase activity / 3-oxoacyl-[acyl-carrier-protein] synthase activity / lipid droplet / magnesium ion binding / mitochondrion / cytoplasm / cytosol Similarity search - Function | |||||||||
| Biological species |  | |||||||||
| Method | single particle reconstruction / cryo EM / Resolution: 2.8 Å | |||||||||
 Authors Authors | Lou JW / Mazhab-Jafari MT | |||||||||
 Citation Citation |  Journal: Sci Rep / Year: 2019 Journal: Sci Rep / Year: 2019Title: Electron cryomicroscopy observation of acyl carrier protein translocation in type I fungal fatty acid synthase. Authors: Jennifer W Lou / Kali R Iyer / S M Naimul Hasan / Leah E Cowen / Mohammad T Mazhab-Jafari /  Abstract: During fatty acid biosynthesis, acyl carrier proteins (ACPs) from type I fungal fatty acid synthase (FAS) shuttle substrates and intermediates within a reaction chamber that hosts multiple spatially- ...During fatty acid biosynthesis, acyl carrier proteins (ACPs) from type I fungal fatty acid synthase (FAS) shuttle substrates and intermediates within a reaction chamber that hosts multiple spatially-fixed catalytic centers. A major challenge in understanding the mechanism of ACP-mediated substrate shuttling is experimental observation of its transient interaction landscape within the reaction chamber. Here, we have shown that ACP spatial distribution is sensitive to the presence of substrates in a catalytically inhibited state, which enables high-resolution investigation of the ACP-dependent conformational transitions within the enoyl reductase (ER) reaction site. In two fungal FASs with distinct ACP localization, the shuttling domain is targeted to the ketoacyl-synthase (KS) domain and away from other catalytic centers, such as acetyl-transferase (AT) and ER domains by steric blockage of the KS active site followed by addition of substrates. These studies strongly suggest that acylation of phosphopantetheine arm of ACP may be an integral part of the substrate shuttling mechanism in type I fungal FAS. | |||||||||
| History |
|
- Structure visualization
Structure visualization
| Movie |
 Movie viewer Movie viewer |
|---|---|
| Structure viewer | EM map:  SurfView SurfView Molmil Molmil Jmol/JSmol Jmol/JSmol |
| Supplemental images |
- Downloads & links
Downloads & links
-EMDB archive
| Map data |  emd_20656.map.gz emd_20656.map.gz | 82.1 MB |  EMDB map data format EMDB map data format | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Header (meta data) |  emd-20656-v30.xml emd-20656-v30.xml emd-20656.xml emd-20656.xml | 20.2 KB 20.2 KB | Display Display |  EMDB header EMDB header |
| Images |  emd_20656.png emd_20656.png | 284.3 KB | ||
| Filedesc metadata |  emd-20656.cif.gz emd-20656.cif.gz | 8.5 KB | ||
| Archive directory |  http://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/structures/EMD-20656 http://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/structures/EMD-20656 ftp://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/structures/EMD-20656 ftp://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/structures/EMD-20656 | HTTPS FTP |
-Related structure data
| Related structure data |  6u5uMC  6u5tC  6u5vC  6u5wC M: atomic model generated by this map C: citing same article ( |
|---|---|
| Similar structure data |
- Links
Links
| EMDB pages |  EMDB (EBI/PDBe) / EMDB (EBI/PDBe) /  EMDataResource EMDataResource |
|---|---|
| Related items in Molecule of the Month |
- Map
Map
| File |  Download / File: emd_20656.map.gz / Format: CCP4 / Size: 166.4 MB / Type: IMAGE STORED AS FLOATING POINT NUMBER (4 BYTES) Download / File: emd_20656.map.gz / Format: CCP4 / Size: 166.4 MB / Type: IMAGE STORED AS FLOATING POINT NUMBER (4 BYTES) | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Annotation | primary map | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Projections & slices | Image control
Images are generated by Spider. | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Voxel size | X=Y=Z: 1.06 Å | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
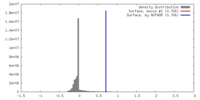
| Density |
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Symmetry | Space group: 1 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Details | EMDB XML:
CCP4 map header:
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
-Supplemental data
- Sample components
Sample components
-Entire : Fatty acid synthase
| Entire | Name: Fatty acid synthase |
|---|---|
| Components |
|
-Supramolecule #1: Fatty acid synthase
| Supramolecule | Name: Fatty acid synthase / type: complex / ID: 1 / Parent: 0 / Macromolecule list: #1-#2 |
|---|---|
| Source (natural) | Organism:  |
| Molecular weight | Theoretical: 2.6 MDa |
-Macromolecule #1: Fatty acid synthase subunit alpha
| Macromolecule | Name: Fatty acid synthase subunit alpha / type: protein_or_peptide / ID: 1 / Number of copies: 1 / Enantiomer: LEVO / EC number: fatty-acyl-CoA synthase system |
|---|---|
| Source (natural) | Organism:  |
| Molecular weight | Theoretical: 207.211453 KDa |
| Sequence | String: MKPEVEQELA HILLTELLAY QFASPVRWIE TQDVFLKDFN TERVVEIGPS PTLAGMAQRT LKNKYESYDA ALSLHREILC YSKDAKEIY YTPDPSELAA KEEPAKEEAP APTPAANAPA PAAAAPAPVA AAAPAAAAAE IADEPVKASL LLHVLVAHKL K KSLDSIPM ...String: MKPEVEQELA HILLTELLAY QFASPVRWIE TQDVFLKDFN TERVVEIGPS PTLAGMAQRT LKNKYESYDA ALSLHREILC YSKDAKEIY YTPDPSELAA KEEPAKEEAP APTPAANAPA PAAAAPAPVA AAAPAAAAAE IADEPVKASL LLHVLVAHKL K KSLDSIPM SKTIKDLVGG KSTVQNEILG DLGKEFGTTP EKPEETPLEE LAETFQDTFS GALGKQSSSL LSRLISSKMP GG FTITVAR KYLQTRWGLP SGRQDGVLLV ALSNEPAARL GSEADAKAFL DSMAQKYASI VGVDLSSAAS ASGAAGAGAA AGA AMIDAG ALEEITKDHK VLARQQLQVL ARYLKMDLDN GERKFLKEKD TVAELQAQLD YLNAELGEFF VNGVATSFSR KKAR TFDSS WNWAKQSLLS LYFEIIHGVL KNVDREVVSE AINIMNRSND ALIKFMEYHI SNTDETKGEN YQLVKTLGEQ LIENC KQVL DVDPVYKDVA KPTGPKTAID KNGNITYSEE PREKVRKLSQ YVQEMALGGP ITKESQPTIE EDLTRVYKAI SAQADK QDI SSSTRVEFEK LYSDLMKFLE SSKEIDPSQT TQLAGMDVED ALDKDSTKEV ASLPNKSTIS KTVSSTIPRE TIPFLHL RK KTPAGDWKYD RQLSSLFLDG LEKAAFNGVT FKDKYVLITG AGKGSIGAEV LQGLLQGGAK VVVTTSRFSK QVTDYYQS I YAKYGAKGST LIVVPFNQGS KQDVEALIEF IYDTEKNGGL GWDLDAIIPF AAIPEQGIEL EHIDSKSEFA HRIMLTNIL RMMGCVKKQK SARGIETRPA QVILPMSPNH GTFGGDGMYS ESKLSLETLF NRWHSESWAN QLTVCGAIIG WTRGTGLMSA NNIIAEGIE KMGVRTFSQK EMAFNLLGLL TPEVVELCQK SPVMADLNGG LQFVPELKEF TAKLRKELVE TSEVRKAVSI E TALEHKVV NGNSADAAYA QVEIQPRANI QLDFPELKPY KQVKQIAPAE LEGLLDLERV IVVTGFAEVG PWGSARTRWE ME AFGEFSL EGCVEMAWIM GFISYHNGNL KGRPYTGWVD SKTKEPVDDK DVKAKYETSI LEHSGIRLIE PELFNGYNPE KKE MIQEVI VEEDLEPFEA SKETAEQFKH QHGDKVDIFE IPETGEYSVK LLKGATLYIP KALRFDRLVA GQIPTGWNAK TYGI SDDII SQVDPITLFV LVSVVEAFIA SGITDPYEMY KYVHVSEVGN CSGSGMGGVS ALRGMFKDRF KDEPVQNDIL QESFI NTMS AWVNMLLISS SGPIKTPVGA CATSVESVDI GVETILSGKA RICIVGGYDD FQEEGSFEFG NMKATSNTLE EFEHGR TPA EMSRPATTTR NGFMEAQGAG IQIIMQADLA LKMGVPIYGI VAMAATATDK IGRSVPAPGK GILTTAREHH SSVKYAS PN LNMKYRKRQL VTREAQIKDW VENELEALKL EAEEIPSEDQ NEFLLERTRE IHNEAESQLR AAQQQWGNDF YKRDPRIA P LRGALATYGL TIDDLGVASF HGTSTKANDK NESATINEMM KHLGRSEGNP VIGVFQKFLT GHPKGAAGAW MMNGALQIL NSGIIPGNRN ADNVDKILEQ FEYVLYPSKT LKTDGVRAVS ITSFGFGQKG GQAIVVHPDY LYGAITEDRY NEYVAKVSAR EKSAYKFFH NGMIYNKLFV SKEHAPYTDE LEEDVYLDPL ARVSKDKKSG SLTFNSKNIQ SKDSYINANT IETAKMIENM T KEKVSNGG VGVDVELITS INVENDTFIE RNFTPQEIEY CSAQPSVQSS FAGTWSAKEA VFKSLGVKSL GGGAALKDIE IV RVNKNAP AVELHGNAKK AAEEAGVTDV KVSISHDDLQ AVAVAVSTKK UniProtKB: Fatty acid synthase subunit alpha |
-Macromolecule #2: Fatty acid synthase subunit beta
| Macromolecule | Name: Fatty acid synthase subunit beta / type: protein_or_peptide / ID: 2 / Number of copies: 1 / Enantiomer: LEVO / EC number: fatty-acyl-CoA synthase system |
|---|---|
| Source (natural) | Organism:  |
| Molecular weight | Theoretical: 231.658938 KDa |
| Sequence | String: MDAYSTRPLT LSHGSLEHVL LVPTASFFIA SQLQEQFNKI LPEPTEGFAA DDEPTTPAEL VGKFLGYVSS LVEPSKVGQF DQVLNLCLT EFENCYLEGN DIHALAAKLL QENDTTLVKT KELIKNYITA RIMAKRPFDK KSNSALFRAV GEGNAQLVAI F GGQGNTDD ...String: MDAYSTRPLT LSHGSLEHVL LVPTASFFIA SQLQEQFNKI LPEPTEGFAA DDEPTTPAEL VGKFLGYVSS LVEPSKVGQF DQVLNLCLT EFENCYLEGN DIHALAAKLL QENDTTLVKT KELIKNYITA RIMAKRPFDK KSNSALFRAV GEGNAQLVAI F GGQGNTDD YFEELRDLYQ TYHVLVGDLI KFSAETLSEL IRTTLDAEKV FTQGLNILEW LENPSNTPDK DYLLSIPISC PL IGVIQLA HYVVTAKLLG FTPGELRSYL KGATGHSQGL VTAVAIAETD SWESFFVSVR KAITVLFFIG VRCYEAYPNT SLP PSILED SLENNEGVPS PMLSISNLTQ EQVQDYVNKT NSHLPAGKQV EISLVNGAKN LVVSGPPQSL YGLNLTLRKA KAPS GLDQS RIPFSERKLK FSNRFLPVAS PFHSHLLVPA SDLINKDLVK NNVSFNAKDI QIPVYDTFDG SDLRVLSGSI SERIV DCII RLPVKWETTT QFKATHILDF GPGGASGLGV LTHRNKDGTG VRVIVAGTLD INPDDDYGFK QEIFDVTSNG LKKNPN WLE EYHPKLIKNK SGKIFVETKF SKLIGRPPLL VPGMTPCTVS PDFVAATTNA GYTIELAGGG YFSAAGMTAA IDSVVSQ IE KGSTFGINLI YVNPFMLQWG IPLIKELRSK GYPIQFLTIG AGVPSLEVAS EYIETLGLKY LGLKPGSIDA ISQVINIA K AHPNFPIALQ WTGGRGGGHH SFEDAHTPML QMYSKIRRHP NIMLIFGSGF GSADDTYPYL TGEWSTKFDY PPMPFDGFL FGSRVMIAKE VKTSPDAKKC IAACTGVPDD KWEQTYKKPT GGIVTVRSEM GEPIHKIATR GVMLWKEFDE TIFNLPKNKL VPTLEAKRD YIISRLNADF QKPWFATVNG QARDLATMTY EEVAKRLVEL MFIRSTNSWF DVTWRTFTGD FLRRVEERFT K SKTLSLIQ SYSLLDKPDE AIEKVFNAYP AAREQFLNAQ DIDHFLSMCQ NPMQKPVPFV PVLDRRFEIF FKKDSLWQSE HL EAVVDQD VQRTCILHGP VAAQFTKVID EPIKSIMDGI HDGHIKKLLH QYYGDDESKI PAVEYFGGES PVDVQSQVDS SSV SEDSAV FKATSSTDEE SWFKALAGSE INWRHASFLC SFITQDKMFV SNPIRKVFKP SQGMVVEISN GNTSSKTVVT LSEP VQGEL KPTVILKLLK ENIIQMEMIE NRTMDGKPVS LPLLYNFNPD NGFAPISEVM EDRNQRIKEM YWKLWIDEPF NLDFD PRDV IKGKDFEITA KEVYDFTHAV GNNCEDFVSR PDRTMLAPMD FAIVVGWRAI IKAIFPNTVD GDLLKLVHLS NGYKMI PGA KPLQVGDVVS TTAVIESVVN QPTGKIVDVV GTLSRNGKPV MEVTSSFFYR GNYTDFENTF QKTVEPVYQM HIKTSKD IA VLRSKEWFQL DDEDFDLLNK TLTFETETEV TFKNANIFSS VKCFGPIKVE LPTKETVEIG IVDYEAGASH GNPVVDFL K RNGSTLEQKV NLENPIPIAV LDSYTPSTNE PYARVSGDLN PIHVSRHFAS YANLPGTITH GMFSSASVRA LIENWAADS VSSRVRGYTC QFVDMVLPNT ALKTSIQHVG MINGRKLIKF ETRNEDDVVV LTGEAEIEQP VTTFVFTGQG SQEQGMGMDL YKTSKAAQD VWNRADNHFK DTYGFSILDI VINNPVNLTI HFGGEKGKRI RENYSAMIFE TIVDGKLKTE KIFKEINEHS T SYTFRSEK GLLSATQFTQ PALTLMEKAA FEDLKSKGLI PADATFAGHS LGEYAALASL ADVMSIESLV EVVFYRGMTM QV AVPRDEL GRSNYGMIAI NPGRVAASFS QEALQYVVER VGKRTGWLVE IVNYNVENQQ YVAAGDLRAL DTVTNVLNFI KLQ KIDIIE LQKSLSLEEV EGHLFEIIDE ASKKSAVKPR PLKLERGFAC IPLVGISVPF HSTYLMNGVK PFKSFLKKNI IKEN VKVAR LAGKYIPNLT AKPFQVTKEY FQDVYDLTGS EPIKEIIDNW EKYEQSDYKD HDGDYKDHDI DYKDDDDK UniProtKB: Fatty acid synthase subunit beta |
-Macromolecule #3: NADP NICOTINAMIDE-ADENINE-DINUCLEOTIDE PHOSPHATE
| Macromolecule | Name: NADP NICOTINAMIDE-ADENINE-DINUCLEOTIDE PHOSPHATE / type: ligand / ID: 3 / Number of copies: 2 / Formula: NAP |
|---|---|
| Molecular weight | Theoretical: 743.405 Da |
| Chemical component information | 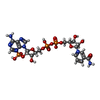 ChemComp-NAP: |
-Macromolecule #4: 4'-PHOSPHOPANTETHEINE
| Macromolecule | Name: 4'-PHOSPHOPANTETHEINE / type: ligand / ID: 4 / Number of copies: 1 / Formula: PNS |
|---|---|
| Molecular weight | Theoretical: 358.348 Da |
| Chemical component information | 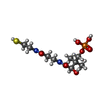 ChemComp-PNS: |
-Macromolecule #5: FLAVIN MONONUCLEOTIDE
| Macromolecule | Name: FLAVIN MONONUCLEOTIDE / type: ligand / ID: 5 / Number of copies: 1 / Formula: FMN |
|---|---|
| Molecular weight | Theoretical: 456.344 Da |
| Chemical component information | 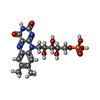 ChemComp-FMN: |
-Experimental details
-Structure determination
| Method | cryo EM |
|---|---|
 Processing Processing | single particle reconstruction |
| Aggregation state | particle |
- Sample preparation
Sample preparation
| Buffer | pH: 7.4 |
|---|---|
| Grid | Model: Quantifoil R2/2 / Material: COPPER/RHODIUM / Mesh: 400 / Pretreatment - Type: GLOW DISCHARGE / Pretreatment - Time: 25 sec. / Pretreatment - Atmosphere: AIR |
| Vitrification | Cryogen name: ETHANE / Chamber humidity: 100 % / Chamber temperature: 277.15 K / Instrument: FEI VITROBOT MARK IV |
- Electron microscopy
Electron microscopy
| Microscope | FEI TITAN KRIOS |
|---|---|
| Image recording | Film or detector model: FEI FALCON III (4k x 4k) / Average electron dose: 43.0 e/Å2 |
| Electron beam | Acceleration voltage: 300 kV / Electron source:  FIELD EMISSION GUN FIELD EMISSION GUN |
| Electron optics | Illumination mode: FLOOD BEAM / Imaging mode: BRIGHT FIELD |
| Experimental equipment |  Model: Titan Krios / Image courtesy: FEI Company |
- Image processing
Image processing
| Startup model | Type of model: PDB ENTRY PDB model - PDB ID: |
|---|---|
| Final reconstruction | Applied symmetry - Point group: D3 (2x3 fold dihedral) / Resolution.type: BY AUTHOR / Resolution: 2.8 Å / Resolution method: FSC 0.143 CUT-OFF / Software - Name: cryoSPARC (ver. 2) / Number images used: 594818 |
| Initial angle assignment | Type: OTHER / Software - Name: cryoSPARC (ver. 2) / Details: cryoSPARC2 |
| Final angle assignment | Type: MAXIMUM LIKELIHOOD / Software - Name: cryoSPARC (ver. 2) |
 Movie
Movie Controller
Controller



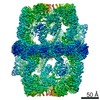






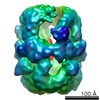
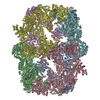
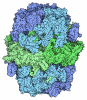

 Z (Sec.)
Z (Sec.) Y (Row.)
Y (Row.) X (Col.)
X (Col.)