+ Open data
Open data
- Basic information
Basic information
| Entry |  | ||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Title | Structure of the human CCAN CENP-A alpha-satellite complex | ||||||||||||
 Map data Map data | |||||||||||||
 Sample Sample |
| ||||||||||||
 Keywords Keywords | Chromosome / kinetochore / cell division / centromere / CELL CYCLE | ||||||||||||
| Function / homology |  Function and homology information Function and homology informationspindle attachment to meiosis I kinetochore / CENP-A containing chromatin assembly / centromeric DNA binding / protein localization to chromosome, centromeric region / kinetochore assembly / condensed chromosome, centromeric region / attachment of mitotic spindle microtubules to kinetochore / inner kinetochore / mitotic cytokinesis / establishment of mitotic spindle orientation ...spindle attachment to meiosis I kinetochore / CENP-A containing chromatin assembly / centromeric DNA binding / protein localization to chromosome, centromeric region / kinetochore assembly / condensed chromosome, centromeric region / attachment of mitotic spindle microtubules to kinetochore / inner kinetochore / mitotic cytokinesis / establishment of mitotic spindle orientation / chromosome, centromeric region / pericentric heterochromatin / negative regulation of megakaryocyte differentiation / protein localization to CENP-A containing chromatin / Replacement of protamines by nucleosomes in the male pronucleus / CENP-A containing nucleosome / Packaging Of Telomere Ends / Amplification of signal from unattached kinetochores via a MAD2 inhibitory signal / Recognition and association of DNA glycosylase with site containing an affected purine / Cleavage of the damaged purine / Deposition of new CENPA-containing nucleosomes at the centromere / Mitotic Prometaphase / EML4 and NUDC in mitotic spindle formation / telomere organization / Recognition and association of DNA glycosylase with site containing an affected pyrimidine / Cleavage of the damaged pyrimidine / RNA Polymerase I Promoter Opening / Inhibition of DNA recombination at telomere / Assembly of the ORC complex at the origin of replication / Meiotic synapsis / Resolution of Sister Chromatid Cohesion / SUMOylation of chromatin organization proteins / Regulation of endogenous retroelements by the Human Silencing Hub (HUSH) complex / DNA methylation / Condensation of Prophase Chromosomes / Chromatin modifications during the maternal to zygotic transition (MZT) / SIRT1 negatively regulates rRNA expression / HCMV Late Events / ERCC6 (CSB) and EHMT2 (G9a) positively regulate rRNA expression / PRC2 methylates histones and DNA / innate immune response in mucosa / Regulation of endogenous retroelements by KRAB-ZFP proteins / Defective pyroptosis / Negative Regulation of CDH1 Gene Transcription / HDACs deacetylate histones / chromosome segregation / Regulation of endogenous retroelements by Piwi-interacting RNAs (piRNAs) / Nonhomologous End-Joining (NHEJ) / RNA Polymerase I Promoter Escape / Transcriptional regulation by small RNAs / RHO GTPases Activate Formins / Formation of the beta-catenin:TCF transactivating complex / Activated PKN1 stimulates transcription of AR (androgen receptor) regulated genes KLK2 and KLK3 / HDMs demethylate histones / RUNX1 regulates genes involved in megakaryocyte differentiation and platelet function / G2/M DNA damage checkpoint / NoRC negatively regulates rRNA expression / kinetochore / B-WICH complex positively regulates rRNA expression / PKMTs methylate histone lysines / DNA Damage/Telomere Stress Induced Senescence / Pre-NOTCH Transcription and Translation / Meiotic recombination / Activation of anterior HOX genes in hindbrain development during early embryogenesis / Metalloprotease DUBs / Transcriptional regulation of granulopoiesis / RMTs methylate histone arginines / HCMV Early Events / structural constituent of chromatin / Separation of Sister Chromatids / UCH proteinases / heterochromatin formation / nucleosome / antimicrobial humoral immune response mediated by antimicrobial peptide / mitotic cell cycle / nucleosome assembly / E3 ubiquitin ligases ubiquitinate target proteins / antibacterial humoral response / Recruitment and ATM-mediated phosphorylation of repair and signaling proteins at DNA double strand breaks / HATs acetylate histones / RUNX1 regulates transcription of genes involved in differentiation of HSCs / MLL4 and MLL3 complexes regulate expression of PPARG target genes in adipogenesis and hepatic steatosis / chromatin organization / Processing of DNA double-strand break ends / Senescence-Associated Secretory Phenotype (SASP) / midbody / Oxidative Stress Induced Senescence / Estrogen-dependent gene expression / chromosome, telomeric region / Ub-specific processing proteases / nuclear body / defense response to Gram-positive bacterium / protein heterodimerization activity / Amyloid fiber formation / negative regulation of cell population proliferation / cell division / chromatin binding / protein-containing complex / extracellular space / DNA binding Similarity search - Function | ||||||||||||
| Biological species |  Homo sapiens (human) Homo sapiens (human) | ||||||||||||
| Method | single particle reconstruction / cryo EM / Resolution: 2.44 Å | ||||||||||||
 Authors Authors | Yatskevich S / Muir KW | ||||||||||||
| Funding support |  United Kingdom, United Kingdom,  Germany, 3 items Germany, 3 items
| ||||||||||||
 Citation Citation |  Journal: Science / Year: 2022 Journal: Science / Year: 2022Title: Structure of the human inner kinetochore bound to a centromeric CENP-A nucleosome. Authors: Stanislau Yatskevich / Kyle W Muir / Dom Bellini / Ziguo Zhang / Jing Yang / Thomas Tischer / Masa Predin / Tom Dendooven / Stephen H McLaughlin / David Barford /  Abstract: Kinetochores assemble onto specialized centromeric CENP-A (centromere protein A) nucleosomes (CENP-A) to mediate attachments between chromosomes and the mitotic spindle. We describe cryo-electron ...Kinetochores assemble onto specialized centromeric CENP-A (centromere protein A) nucleosomes (CENP-A) to mediate attachments between chromosomes and the mitotic spindle. We describe cryo-electron microscopy structures of the human inner kinetochore constitutive centromere associated network (CCAN) complex bound to CENP-A reconstituted onto α-satellite DNA. CCAN forms edge-on contacts with CENP-A, and a linker DNA segment of the α-satellite repeat emerges from the fully wrapped end of the nucleosome to thread through the central CENP-LN channel that tightly grips the DNA. The CENP-TWSX histone-fold module further augments DNA binding and partially wraps the linker DNA in a manner reminiscent of canonical nucleosomes. Our study suggests that the topological entrapment of the linker DNA by CCAN provides a robust mechanism by which kinetochores withstand both pushing and pulling forces exerted by the mitotic spindle. | ||||||||||||
| History |
|
- Structure visualization
Structure visualization
| Supplemental images |
|---|
- Downloads & links
Downloads & links
-EMDB archive
| Map data |  emd_14334.map.gz emd_14334.map.gz | 91.8 MB |  EMDB map data format EMDB map data format | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Header (meta data) |  emd-14334-v30.xml emd-14334-v30.xml emd-14334.xml emd-14334.xml | 17.1 KB 17.1 KB | Display Display |  EMDB header EMDB header |
| FSC (resolution estimation) |  emd_14334_fsc.xml emd_14334_fsc.xml | 12.5 KB | Display |  FSC data file FSC data file |
| Images |  emd_14334.png emd_14334.png | 56.4 KB | ||
| Filedesc metadata |  emd-14334.cif.gz emd-14334.cif.gz | 6.3 KB | ||
| Archive directory |  http://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/structures/EMD-14334 http://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/structures/EMD-14334 ftp://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/structures/EMD-14334 ftp://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/structures/EMD-14334 | HTTPS FTP |
-Related structure data
| Related structure data |  7r5rMC  7pb4C  7pb8C  7piiC  7pknC  7r5sC  7r5vC  7ywxC  7yyhC M: atomic model generated by this map C: citing same article ( |
|---|---|
| Similar structure data | Similarity search - Function & homology  F&H Search F&H Search |
- Links
Links
| EMDB pages |  EMDB (EBI/PDBe) / EMDB (EBI/PDBe) /  EMDataResource EMDataResource |
|---|---|
| Related items in Molecule of the Month |
- Map
Map
| File |  Download / File: emd_14334.map.gz / Format: CCP4 / Size: 178 MB / Type: IMAGE STORED AS FLOATING POINT NUMBER (4 BYTES) Download / File: emd_14334.map.gz / Format: CCP4 / Size: 178 MB / Type: IMAGE STORED AS FLOATING POINT NUMBER (4 BYTES) | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Projections & slices | Image control
Images are generated by Spider. | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Voxel size | X=Y=Z: 0.853 Å | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
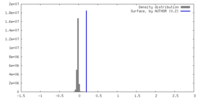
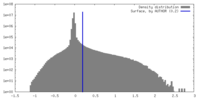
| Density |
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Symmetry | Space group: 1 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Details | EMDB XML:
|
-Supplemental data
- Sample components
Sample components
-Entire : Human CCAN complex with bound alpha-satellite DNA
| Entire | Name: Human CCAN complex with bound alpha-satellite DNA |
|---|---|
| Components |
|
-Supramolecule #1: Human CCAN complex with bound alpha-satellite DNA
| Supramolecule | Name: Human CCAN complex with bound alpha-satellite DNA / type: complex / ID: 1 / Parent: 0 / Macromolecule list: #1-#7 |
|---|
-Macromolecule #1: Histone H3-like centromeric protein A
| Macromolecule | Name: Histone H3-like centromeric protein A / type: protein_or_peptide / ID: 1 / Number of copies: 2 / Enantiomer: LEVO |
|---|---|
| Source (natural) | Organism:  Homo sapiens (human) Homo sapiens (human) |
| Molecular weight | Theoretical: 16.02363 KDa |
| Recombinant expression | Organism:  |
| Sequence | String: MGPRRRSRKP EAPRRRSPSP TPTPGPSRRG PSLGASSHQH SRRRQGWLKE IRKLQKSTHL LIRKLPFSRL AREICVKFTR GVDFNWQAQ ALLALQEAAE AFLVHLFEDA YLLTLHAGRV TLFPKDVQLA RRIRGLEEGL G UniProtKB: Histone H3-like centromeric protein A |
-Macromolecule #2: Histone H4
| Macromolecule | Name: Histone H4 / type: protein_or_peptide / ID: 2 / Number of copies: 2 / Enantiomer: LEVO |
|---|---|
| Source (natural) | Organism:  Homo sapiens (human) Homo sapiens (human) |
| Molecular weight | Theoretical: 11.394426 KDa |
| Recombinant expression | Organism:  |
| Sequence | String: MSGRGKGGKG LGKGGAKRHR KVLRDNIQGI TKPAIRRLAR RGGVKRISGL IYEETRGVLK VFLENVIRDA VTYTEHAKRK TVTAMDVVY ALKRQGRTLY GFGG UniProtKB: Histone H4 |
-Macromolecule #3: Histone H2A type 1-C
| Macromolecule | Name: Histone H2A type 1-C / type: protein_or_peptide / ID: 3 / Number of copies: 2 / Enantiomer: LEVO |
|---|---|
| Source (natural) | Organism:  Homo sapiens (human) Homo sapiens (human) |
| Molecular weight | Theoretical: 14.135523 KDa |
| Recombinant expression | Organism:  |
| Sequence | String: MSGRGKQGGK ARAKAKSRSS RAGLQFPVGR VHRLLRKGNY AERVGAGAPV YLAAVLEYLT AEILELAGNA ARDNKKTRII PRHLQLAIR NDEELNKLLG RVTIAQGGVL PNIQAVLLPK KTESHHKAKG K UniProtKB: Histone H2A type 1-C |
-Macromolecule #4: Histone H2B type 1-C/E/F/G/I
| Macromolecule | Name: Histone H2B type 1-C/E/F/G/I / type: protein_or_peptide / ID: 4 / Number of copies: 2 / Enantiomer: LEVO |
|---|---|
| Source (natural) | Organism:  Homo sapiens (human) Homo sapiens (human) |
| Molecular weight | Theoretical: 13.937213 KDa |
| Recombinant expression | Organism:  |
| Sequence | String: MPEPAKSAPA PKKGSKKAVT KAQKKDGKKR KRSRKESYSV YVYKVLKQVH PDTGISSKAM GIMNSFVNDI FERIAGEASR LAHYNKRST ITSREIQTAV RLLLPGELAK HAVSEGTKAV TKYTSSK UniProtKB: Histone H2B type 1-C/E/F/G/I |
-Macromolecule #7: Centromere protein C
| Macromolecule | Name: Centromere protein C / type: protein_or_peptide / ID: 7 / Number of copies: 2 / Enantiomer: LEVO |
|---|---|
| Source (natural) | Organism:  Homo sapiens (human) Homo sapiens (human) |
| Molecular weight | Theoretical: 61.724816 KDa |
| Recombinant expression | Organism:  Trichoplusia ni (cabbage looper) Trichoplusia ni (cabbage looper) |
| Sequence | String: AASGLDHLKN GYRRRFCRPS RARDINTEQG QNVLEILQDC FEEKSLANDF STNSTKSVPN STRKIKDTCI QSPSKECQKS HPKSVPVSS KKKEASLQFV VEPSEATNRS VQAHEVHQKI LATDVSSKNT PDSKKISSRN INDHHSEADE EFYLSVGSPS V LLDAKTSV ...String: AASGLDHLKN GYRRRFCRPS RARDINTEQG QNVLEILQDC FEEKSLANDF STNSTKSVPN STRKIKDTCI QSPSKECQKS HPKSVPVSS KKKEASLQFV VEPSEATNRS VQAHEVHQKI LATDVSSKNT PDSKKISSRN INDHHSEADE EFYLSVGSPS V LLDAKTSV SQNVIPSSAQ KRETYTFENS VNMLPSSTEV SVKTKKRLNF DDKVMLKKIE IDNKVSDEED KTSEGQERKP SG SSQNRIR DSEYEIQRQA KKSFSTLFLE TVKRKSESSP IVRHAATAPP HSCPPDDTKL IEDEFIIDES DQSFASRSWI TIP RKAGSL KQRTISPAES TALLQGRKSR EKHHNILPKT LANDKHSHKP HPVETSQPSD KTVLDTSYAL IGETVNNYRS TKYE MYSKN AEKPSRSKRT IKQKQRRKFM AKPAEEQLDV GQSKDENIHT SHITQDEFQR NSDRNMEEHE EMGNDCVSKK QMPPV GSKK SSTRKDKEES KKKRFSSESK NKLVPEEVTS TVTKSRRISR RPSDWWVVKS EESPVYSNS UniProtKB: Centromere protein C |
-Macromolecule #5: DNA (171-MER)
| Macromolecule | Name: DNA (171-MER) / type: dna / ID: 5 / Number of copies: 1 / Classification: DNA |
|---|---|
| Source (natural) | Organism:  Homo sapiens (human) Homo sapiens (human) |
| Molecular weight | Theoretical: 52.725812 KDa |
| Sequence | String: (DT)(DC)(DC)(DA)(DA)(DA)(DT)(DG)(DT)(DC) (DC)(DA)(DA)(DT)(DT)(DC)(DC)(DA)(DG)(DA) (DT)(DA)(DC)(DT)(DA)(DC)(DA)(DA)(DA) (DA)(DA)(DG)(DA)(DG)(DT)(DG)(DT)(DT)(DT) (DC) (DA)(DA)(DA)(DA)(DC)(DT) ...String: (DT)(DC)(DC)(DA)(DA)(DA)(DT)(DG)(DT)(DC) (DC)(DA)(DA)(DT)(DT)(DC)(DC)(DA)(DG)(DA) (DT)(DA)(DC)(DT)(DA)(DC)(DA)(DA)(DA) (DA)(DA)(DG)(DA)(DG)(DT)(DG)(DT)(DT)(DT) (DC) (DA)(DA)(DA)(DA)(DC)(DT)(DG)(DC) (DT)(DC)(DT)(DA)(DT)(DG)(DA)(DA)(DA)(DA) (DG)(DG) (DA)(DA)(DT)(DG)(DT)(DT)(DC) (DA)(DA)(DC)(DT)(DC)(DT)(DA)(DT)(DG)(DA) (DG)(DT)(DT) (DG)(DA)(DA)(DT)(DG)(DC) (DA)(DA)(DA)(DC)(DA)(DT)(DC)(DA)(DC)(DA) (DT)(DA)(DG)(DA) (DA)(DG)(DT)(DT)(DT) (DC)(DT)(DG)(DA)(DG)(DA)(DA)(DT)(DG)(DC) (DT)(DT)(DC)(DT)(DG) (DT)(DC)(DT)(DA) (DG)(DT)(DT)(DT)(DT)(DT)(DA)(DT)(DG)(DT) (DG)(DA)(DA)(DC)(DA)(DT) (DA)(DT)(DT) (DC)(DC)(DC)(DG)(DT)(DT)(DT)(DC)(DC)(DA) (DA)(DC)(DG)(DA)(DA)(DG)(DG) (DC)(DC) (DT)(DC)(DA)(DA)(DA)(DG)(DC)(DG)(DG) |
-Macromolecule #6: DNA (171-MER)
| Macromolecule | Name: DNA (171-MER) / type: dna / ID: 6 / Number of copies: 1 / Classification: DNA |
|---|---|
| Source (natural) | Organism:  Homo sapiens (human) Homo sapiens (human) |
| Molecular weight | Theoretical: 52.822809 KDa |
| Sequence | String: (DC)(DC)(DG)(DC)(DT)(DT)(DT)(DG)(DA)(DG) (DG)(DC)(DC)(DT)(DT)(DC)(DG)(DT)(DT)(DG) (DG)(DA)(DA)(DA)(DC)(DG)(DG)(DG)(DA) (DA)(DT)(DA)(DT)(DG)(DT)(DT)(DC)(DA)(DC) (DA) (DT)(DA)(DA)(DA)(DA)(DA) ...String: (DC)(DC)(DG)(DC)(DT)(DT)(DT)(DG)(DA)(DG) (DG)(DC)(DC)(DT)(DT)(DC)(DG)(DT)(DT)(DG) (DG)(DA)(DA)(DA)(DC)(DG)(DG)(DG)(DA) (DA)(DT)(DA)(DT)(DG)(DT)(DT)(DC)(DA)(DC) (DA) (DT)(DA)(DA)(DA)(DA)(DA)(DC)(DT) (DA)(DG)(DA)(DC)(DA)(DG)(DA)(DA)(DG)(DC) (DA)(DT) (DT)(DC)(DT)(DC)(DA)(DG)(DA) (DA)(DA)(DC)(DT)(DT)(DC)(DT)(DA)(DT)(DG) (DT)(DG)(DA) (DT)(DG)(DT)(DT)(DT)(DG) (DC)(DA)(DT)(DT)(DC)(DA)(DA)(DC)(DT)(DC) (DA)(DT)(DA)(DG) (DA)(DG)(DT)(DT)(DG) (DA)(DA)(DC)(DA)(DT)(DT)(DC)(DC)(DT)(DT) (DT)(DT)(DC)(DA)(DT) (DA)(DG)(DA)(DG) (DC)(DA)(DG)(DT)(DT)(DT)(DT)(DG)(DA)(DA) (DA)(DC)(DA)(DC)(DT)(DC) (DT)(DT)(DT) (DT)(DT)(DG)(DT)(DA)(DG)(DT)(DA)(DT)(DC) (DT)(DG)(DG)(DA)(DA)(DT)(DT) (DG)(DG) (DA)(DC)(DA)(DT)(DT)(DT)(DG)(DG)(DA) |
-Experimental details
-Structure determination
| Method | cryo EM |
|---|---|
 Processing Processing | single particle reconstruction |
| Aggregation state | particle |
- Sample preparation
Sample preparation
| Buffer | pH: 7.8 |
|---|---|
| Vitrification | Cryogen name: ETHANE |
- Electron microscopy
Electron microscopy
| Microscope | FEI TITAN KRIOS |
|---|---|
| Image recording | Film or detector model: GATAN K3 (6k x 4k) / Average electron dose: 40.0 e/Å2 |
| Electron beam | Acceleration voltage: 300 kV / Electron source:  FIELD EMISSION GUN FIELD EMISSION GUN |
| Electron optics | Illumination mode: FLOOD BEAM / Imaging mode: BRIGHT FIELD / Nominal defocus max: 3.0 µm / Nominal defocus min: 1.5 µm |
| Experimental equipment |  Model: Titan Krios / Image courtesy: FEI Company |
 Movie
Movie Controller
Controller






















 Z (Sec.)
Z (Sec.) Y (Row.)
Y (Row.) X (Col.)
X (Col.)