+ Open data
Open data
- Basic information
Basic information
| Entry | Database: EMDB / ID: EMD-13547 | |||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
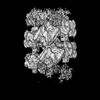
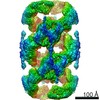
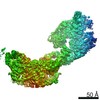
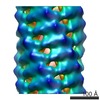
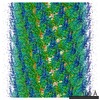
| Title | VWF Tubules of D1D2D'D3 domains | |||||||||
 Map data Map data | ||||||||||
 Sample Sample |
| |||||||||
 Keywords Keywords | VWF / BLOOD CLOTTING | |||||||||
| Function / homology |  Function and homology information Function and homology informationDefective VWF binding to collagen type I / Enhanced cleavage of VWF variant by ADAMTS13 / Defective VWF cleavage by ADAMTS13 variant / Defective F8 binding to von Willebrand factor / Enhanced binding of GP1BA variant to VWF multimer:collagen / Defective binding of VWF variant to GPIb:IX:V / Weibel-Palade body / hemostasis / platelet alpha granule / Platelet Adhesion to exposed collagen ...Defective VWF binding to collagen type I / Enhanced cleavage of VWF variant by ADAMTS13 / Defective VWF cleavage by ADAMTS13 variant / Defective F8 binding to von Willebrand factor / Enhanced binding of GP1BA variant to VWF multimer:collagen / Defective binding of VWF variant to GPIb:IX:V / Weibel-Palade body / hemostasis / platelet alpha granule / Platelet Adhesion to exposed collagen / GP1b-IX-V activation signalling / p130Cas linkage to MAPK signaling for integrins / cell-substrate adhesion / Defective F8 cleavage by thrombin / Platelet Aggregation (Plug Formation) / GRB2:SOS provides linkage to MAPK signaling for Integrins / positive regulation of intracellular signal transduction / immunoglobulin binding / Integrin cell surface interactions / collagen binding / Intrinsic Pathway of Fibrin Clot Formation / Integrin signaling / extracellular matrix / platelet alpha granule lumen / Signaling by high-kinase activity BRAF mutants / MAP2K and MAPK activation / platelet activation / response to wounding / integrin binding / blood coagulation / Signaling by RAF1 mutants / Signaling by moderate kinase activity BRAF mutants / Paradoxical activation of RAF signaling by kinase inactive BRAF / Signaling downstream of RAS mutants / Signaling by BRAF and RAF1 fusions / Platelet degranulation / protein-folding chaperone binding / : / protease binding / cell adhesion / endoplasmic reticulum / extracellular space / extracellular exosome / extracellular region / identical protein binding Similarity search - Function | |||||||||
| Biological species |  Homo sapiens (human) Homo sapiens (human) | |||||||||
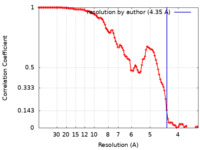
| Method | helical reconstruction / cryo EM / Resolution: 4.35 Å | |||||||||
 Authors Authors | Javitt G / Fass D | |||||||||
| Funding support | 1 items
| |||||||||
 Citation Citation |  Journal: Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A / Year: 2022 Journal: Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A / Year: 2022Title: Helical self-assembly of a mucin segment suggests an evolutionary origin for von Willebrand factor tubules. Authors: Gabriel Javitt / Deborah Fass /  Abstract: The glycoprotein von Willebrand factor (VWF) contributes to hemostasis by stanching injuries in blood vessel walls. A distinctive feature of VWF is its assembly into long, helical tubules in ...The glycoprotein von Willebrand factor (VWF) contributes to hemostasis by stanching injuries in blood vessel walls. A distinctive feature of VWF is its assembly into long, helical tubules in endothelial cells prior to secretion. When VWF is released into the bloodstream, these tubules unfurl to release linear polymers that bind subendothelial collagen at wound sites, recruit platelets, and initiate the clotting cascade. VWF evolved from gel-forming mucins, the polymeric glycoproteins that coat and protect exposed epithelia. Despite the divergent function of VWF in blood vessel repair, sequence conservation and shared domain organization imply that VWF retained key aspects of the mucin bioassembly mechanism. Here, we show using cryo-electron microscopy that the ability to form tubules, a property hitherto thought to have arisen as a VWF adaptation to the vasculature, is a feature of the amino-terminal region of mucin. This segment of the human intestinal gel-forming mucin (MUC2) was found to self-assemble into tubules with a striking resemblance to those of VWF itself. To facilitate a comparison, we determined the residue-resolution structure of tubules formed by the homologous segment of VWF. The structures of the MUC2 and VWF tubules revealed the flexible joints and the intermolecular interactions required for tubule formation. Steric constraints in full-length MUC2 suggest that linear filaments, a previously observed supramolecular assembly form, are more likely than tubules to be the physiological mucin storage intermediate. Nevertheless, MUC2 tubules indicate a possible evolutionary origin for VWF tubules and elucidate design principles present in mucins and VWF. | |||||||||
| History |
|
- Structure visualization
Structure visualization
| Movie |
 Movie viewer Movie viewer |
|---|---|
| Structure viewer | EM map:  SurfView SurfView Molmil Molmil Jmol/JSmol Jmol/JSmol |
| Supplemental images |
- Downloads & links
Downloads & links
-EMDB archive
| Map data |  emd_13547.map.gz emd_13547.map.gz | 51.5 MB |  EMDB map data format EMDB map data format | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Header (meta data) |  emd-13547-v30.xml emd-13547-v30.xml emd-13547.xml emd-13547.xml | 10.4 KB 10.4 KB | Display Display |  EMDB header EMDB header |
| FSC (resolution estimation) |  emd_13547_fsc.xml emd_13547_fsc.xml | 10.4 KB | Display |  FSC data file FSC data file |
| Images |  emd_13547.png emd_13547.png | 116.1 KB | ||
| Filedesc metadata |  emd-13547.cif.gz emd-13547.cif.gz | 5.9 KB | ||
| Archive directory |  http://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/structures/EMD-13547 http://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/structures/EMD-13547 ftp://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/structures/EMD-13547 ftp://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/structures/EMD-13547 | HTTPS FTP |
-Validation report
| Summary document |  emd_13547_validation.pdf.gz emd_13547_validation.pdf.gz | 540.7 KB | Display |  EMDB validaton report EMDB validaton report |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Full document |  emd_13547_full_validation.pdf.gz emd_13547_full_validation.pdf.gz | 540.2 KB | Display | |
| Data in XML |  emd_13547_validation.xml.gz emd_13547_validation.xml.gz | 12 KB | Display | |
| Data in CIF |  emd_13547_validation.cif.gz emd_13547_validation.cif.gz | 16 KB | Display | |
| Arichive directory |  https://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/validation_reports/EMD-13547 https://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/validation_reports/EMD-13547 ftp://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/validation_reports/EMD-13547 ftp://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/validation_reports/EMD-13547 | HTTPS FTP |
-Related structure data
| Related structure data |  7pnfMC  7pmvC  7povC  7pp6C M: atomic model generated by this map C: citing same article ( |
|---|---|
| Similar structure data |
- Links
Links
| EMDB pages |  EMDB (EBI/PDBe) / EMDB (EBI/PDBe) /  EMDataResource EMDataResource |
|---|---|
| Related items in Molecule of the Month |
- Map
Map
| File |  Download / File: emd_13547.map.gz / Format: CCP4 / Size: 103 MB / Type: IMAGE STORED AS FLOATING POINT NUMBER (4 BYTES) Download / File: emd_13547.map.gz / Format: CCP4 / Size: 103 MB / Type: IMAGE STORED AS FLOATING POINT NUMBER (4 BYTES) | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Projections & slices | Image control
Images are generated by Spider. | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Voxel size | X=Y=Z: 1.72 Å | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Density |
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Symmetry | Space group: 1 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Details | EMDB XML:
CCP4 map header:
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
-Supplemental data
- Sample components
Sample components
-Entire : VWF tubule of domains D1D2D'D3
| Entire | Name: VWF tubule of domains D1D2D'D3 |
|---|---|
| Components |
|
-Supramolecule #1: VWF tubule of domains D1D2D'D3
| Supramolecule | Name: VWF tubule of domains D1D2D'D3 / type: complex / ID: 1 / Parent: 0 / Macromolecule list: #1 |
|---|---|
| Source (natural) | Organism:  Homo sapiens (human) Homo sapiens (human) |
-Macromolecule #1: von Willebrand factor
| Macromolecule | Name: von Willebrand factor / type: protein_or_peptide / ID: 1 / Number of copies: 2 / Enantiomer: LEVO |
|---|---|
| Source (natural) | Organism:  Homo sapiens (human) Homo sapiens (human) |
| Molecular weight | Theoretical: 137.345641 KDa |
| Recombinant expression | Organism:  Homo sapiens (human) Homo sapiens (human) |
| Sequence | String: MIPARFAGVL LALALILPGT LCAEGTRGRS STARCSLFGS DFVNTFDGSM YSFAGYCSYL LAGGCQKRSF SIIGDFQNGK RVSLSVYLG EFFDIHLFVN GTVTQGDQRV SMPYASKGLY LETEAGYYKL SGEAYGFVAR IDGSGNFQVL LSDRYFNKTC G LCGNFNIF ...String: MIPARFAGVL LALALILPGT LCAEGTRGRS STARCSLFGS DFVNTFDGSM YSFAGYCSYL LAGGCQKRSF SIIGDFQNGK RVSLSVYLG EFFDIHLFVN GTVTQGDQRV SMPYASKGLY LETEAGYYKL SGEAYGFVAR IDGSGNFQVL LSDRYFNKTC G LCGNFNIF AEDDFMTQEG TLTSDPYDFA NSWALSSGEQ WCERASPPSS SCNISSGEMQ KGLWEQCQLL KSTSVFARCH PL VDPEPFV ALCEKTLCEC AGGLECACPA LLEYARTCAQ EGMVLYGWTD HSACSPVCPA GMEYRQCVSP CARTCQSLHI NEM CQERCV DGCSCPEGQL LDEGLCVEST ECPCVHSGKR YPPGTSLSRD CNTCICRNSQ WICSNEECPG ECLVTGQSHF KSFD NRYFT FSGICQYLLA RDCQDHSFSI VIETVQCADD RDAVCTRSVT VRLPGLHNSL VKLKHGAGVA MDGQDVQLPL LKGDL RIQH TVTASVRLSY GEDLQMDWDG RGRLLVKLSP VYAGKTCGLC GNYNGNQGDD FLTPSGLAEP RVEDFGNAWK LHGDCQ DLQ KQHSDPCALN PRMTRFSEEA CAVLTSPTFE ACHRAVSPLP YLRNCRYDVC SCSDGRECLC GALASYAAAC AGRGVRV AW REPGRCELNC PKGQVYLQCG TPCNLTCRSL SYPDEECNEA CLEGCFCPPG LYMDERGDCV PKAQCPCYYD GEIFQPED I FSDHHTMCYC EDGFMHCTMS GVPGSLLPDA VLSSPLSHRS KRSLSCRPPM VKLVCPADNL RAEGLECTKT CQNYDLECM SMGCVSGCLC PPGMVRHENR CVALERCPCF HQGKEYAPGE TVKIGCNTCV CRDRKWNCTD HVCDATCSTI GMAHYLTFDG LKYLFPGEC QYVLVQDYCG SNPGTFRILV GNKGCSHPSV KCKKRVTILV EGGEIELFDG EVNVKRPMKD ETHFEVVESG R YIILLLGK ALSVVWDRHL SISVVLKQTY QEKVCGLCGN FDGIQNNDLT SSNLQVEEDP VDFGNSWKVS SQCADTRKVP LD SSPATCH NNIMKQTMVD SSCRILTSDV FQDCNKLVDP EPYLDVCIYD TCSCESIGDC ACFCDTIAAY AHVCAQHGKV VTW RTATLC PQSCEERNLR ENGYECEWRY NSCAPACQVT CQHPEPLACP VQCVEGCHAH CPPGKILDEL LQTCVDPEDC PVCE VAGRR FASGKKVTLN PSDPEHCQIC HCDVVNLTCE ACQEPGHHHH HH UniProtKB: von Willebrand factor |
-Macromolecule #3: 2-acetamido-2-deoxy-beta-D-glucopyranose
| Macromolecule | Name: 2-acetamido-2-deoxy-beta-D-glucopyranose / type: ligand / ID: 3 / Number of copies: 8 / Formula: NAG |
|---|---|
| Molecular weight | Theoretical: 221.208 Da |
| Chemical component information |  ChemComp-NAG: |
-Macromolecule #4: CALCIUM ION
| Macromolecule | Name: CALCIUM ION / type: ligand / ID: 4 / Number of copies: 6 / Formula: CA |
|---|---|
| Molecular weight | Theoretical: 40.078 Da |
-Experimental details
-Structure determination
| Method | cryo EM |
|---|---|
 Processing Processing | helical reconstruction |
| Aggregation state | helical array |
- Sample preparation
Sample preparation
| Buffer | pH: 6 |
|---|---|
| Vitrification | Cryogen name: ETHANE |
- Electron microscopy
Electron microscopy
| Microscope | FEI TITAN KRIOS |
|---|---|
| Image recording | Film or detector model: GATAN K3 BIOQUANTUM (6k x 4k) / Average electron dose: 48.0 e/Å2 |
| Electron beam | Acceleration voltage: 300 kV / Electron source:  FIELD EMISSION GUN FIELD EMISSION GUN |
| Electron optics | Illumination mode: FLOOD BEAM / Imaging mode: BRIGHT FIELD |
| Experimental equipment |  Model: Titan Krios / Image courtesy: FEI Company |
 Movie
Movie Controller
Controller





















 Z (Sec.)
Z (Sec.) Y (Row.)
Y (Row.) X (Col.)
X (Col.)