+ Open data
Open data
- Basic information
Basic information
| Entry | Database: PDB / ID: 7pp6 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
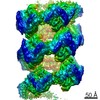
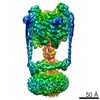
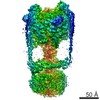
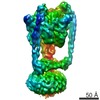
| Title | MUC2 Tubules of D1D2D3 domains | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
 Components Components | Mucin-2 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
 Keywords Keywords | ANTIMICROBIAL PROTEIN / MUC2 / Mucin / Tubule / 2-start / helix | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Function / homology |  Function and homology information Function and homology information | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Biological species |  Homo sapiens (human) Homo sapiens (human) | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Method | ELECTRON MICROSCOPY / helical reconstruction / cryo EM / Resolution: 3.4 Å | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
 Authors Authors | Javitt, G. / Fass, D. | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Funding support | 1items
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
 Citation Citation |  Journal: Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A / Year: 2022 Journal: Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A / Year: 2022Title: Helical self-assembly of a mucin segment suggests an evolutionary origin for von Willebrand factor tubules. Authors: Gabriel Javitt / Deborah Fass /  Abstract: The glycoprotein von Willebrand factor (VWF) contributes to hemostasis by stanching injuries in blood vessel walls. A distinctive feature of VWF is its assembly into long, helical tubules in ...The glycoprotein von Willebrand factor (VWF) contributes to hemostasis by stanching injuries in blood vessel walls. A distinctive feature of VWF is its assembly into long, helical tubules in endothelial cells prior to secretion. When VWF is released into the bloodstream, these tubules unfurl to release linear polymers that bind subendothelial collagen at wound sites, recruit platelets, and initiate the clotting cascade. VWF evolved from gel-forming mucins, the polymeric glycoproteins that coat and protect exposed epithelia. Despite the divergent function of VWF in blood vessel repair, sequence conservation and shared domain organization imply that VWF retained key aspects of the mucin bioassembly mechanism. Here, we show using cryo-electron microscopy that the ability to form tubules, a property hitherto thought to have arisen as a VWF adaptation to the vasculature, is a feature of the amino-terminal region of mucin. This segment of the human intestinal gel-forming mucin (MUC2) was found to self-assemble into tubules with a striking resemblance to those of VWF itself. To facilitate a comparison, we determined the residue-resolution structure of tubules formed by the homologous segment of VWF. The structures of the MUC2 and VWF tubules revealed the flexible joints and the intermolecular interactions required for tubule formation. Steric constraints in full-length MUC2 suggest that linear filaments, a previously observed supramolecular assembly form, are more likely than tubules to be the physiological mucin storage intermediate. Nevertheless, MUC2 tubules indicate a possible evolutionary origin for VWF tubules and elucidate design principles present in mucins and VWF. | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| History |
|
- Structure visualization
Structure visualization
| Movie |
 Movie viewer Movie viewer |
|---|---|
| Structure viewer | Molecule:  Molmil Molmil Jmol/JSmol Jmol/JSmol |
- Downloads & links
Downloads & links
- Download
Download
| PDBx/mmCIF format |  7pp6.cif.gz 7pp6.cif.gz | 1.4 MB | Display |  PDBx/mmCIF format PDBx/mmCIF format |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| PDB format |  pdb7pp6.ent.gz pdb7pp6.ent.gz | 1.1 MB | Display |  PDB format PDB format |
| PDBx/mmJSON format |  7pp6.json.gz 7pp6.json.gz | Tree view |  PDBx/mmJSON format PDBx/mmJSON format | |
| Others |  Other downloads Other downloads |
-Validation report
| Arichive directory |  https://data.pdbj.org/pub/pdb/validation_reports/pp/7pp6 https://data.pdbj.org/pub/pdb/validation_reports/pp/7pp6 ftp://data.pdbj.org/pub/pdb/validation_reports/pp/7pp6 ftp://data.pdbj.org/pub/pdb/validation_reports/pp/7pp6 | HTTPS FTP |
|---|
-Related structure data
| Related structure data | 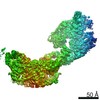 13580MC  7pmvC  7pnfC  7povC C: citing same article ( M: map data used to model this data |
|---|---|
| Similar structure data |
- Links
Links
- Assembly
Assembly
| Deposited unit | 
|
|---|---|
| 1 |
|
- Components
Components
| #1: Protein | Mass: 137642.609 Da / Num. of mol.: 6 Source method: isolated from a genetically manipulated source Source: (gene. exp.)  Homo sapiens (human) / Gene: MUC2 / Production host: Homo sapiens (human) / Gene: MUC2 / Production host:  Homo sapiens (human) / References: UniProt: A0A0G2JR65 Homo sapiens (human) / References: UniProt: A0A0G2JR65#2: Polysaccharide | 2-acetamido-2-deoxy-beta-D-glucopyranose-(1-4)-2-acetamido-2-deoxy-beta-D-glucopyranose Source method: isolated from a genetically manipulated source #3: Chemical | ChemComp-CA / #4: Sugar | ChemComp-NAG / #5: Water | ChemComp-HOH / | Has ligand of interest | N | Has protein modification | Y | |
|---|
-Experimental details
-Experiment
| Experiment | Method: ELECTRON MICROSCOPY |
|---|---|
| EM experiment | Aggregation state: HELICAL ARRAY / 3D reconstruction method: helical reconstruction |
- Sample preparation
Sample preparation
| Component | Name: MUC2 local refinement of 2 beads from D1D2D3 domain tubules Type: COMPLEX / Entity ID: #1 / Source: RECOMBINANT |
|---|---|
| Molecular weight | Experimental value: NO |
| Source (natural) | Organism:  Homo sapiens (human) Homo sapiens (human) |
| Source (recombinant) | Organism:  Homo sapiens (human) / Strain: HEK 293F / Plasmid: pCDNA3.1 Homo sapiens (human) / Strain: HEK 293F / Plasmid: pCDNA3.1 |
| Buffer solution | pH: 5.4 |
| Specimen | Embedding applied: NO / Shadowing applied: NO / Staining applied: NO / Vitrification applied: YES |
| Vitrification | Cryogen name: ETHANE |
- Electron microscopy imaging
Electron microscopy imaging
| Experimental equipment |  Model: Titan Krios / Image courtesy: FEI Company |
|---|---|
| Microscopy | Model: FEI TITAN KRIOS |
| Electron gun | Electron source:  FIELD EMISSION GUN / Accelerating voltage: 300 kV / Illumination mode: FLOOD BEAM FIELD EMISSION GUN / Accelerating voltage: 300 kV / Illumination mode: FLOOD BEAM |
| Electron lens | Mode: BRIGHT FIELD |
| Image recording | Electron dose: 48 e/Å2 / Film or detector model: GATAN K3 BIOQUANTUM (6k x 4k) |
- Processing
Processing
| Software |
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| EM software | Name: PHENIX / Category: model refinement | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
| CTF correction | Type: PHASE FLIPPING AND AMPLITUDE CORRECTION | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Helical symmerty | Angular rotation/subunit: 83.2 ° / Axial rise/subunit: 69.5 Å / Axial symmetry: D2 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 3D reconstruction | Resolution: 3.4 Å / Resolution method: FSC 0.143 CUT-OFF / Num. of particles: 515422 / Symmetry type: HELICAL | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Refinement | Cross valid method: NONE Stereochemistry target values: GeoStd + Monomer Library + CDL v1.2 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Displacement parameters | Biso mean: 142.21 Å2 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Refine LS restraints |
|
 Movie
Movie Controller
Controller








 PDBj
PDBj




