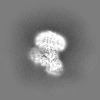
+ Open data
Open data
- Basic information
Basic information
| Entry | Database: EMDB / ID: EMD-13011 | |||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Title | Cryo-EM structure of P5B-ATPase E2PiAlF/SPM | |||||||||||||||
 Map data Map data | ||||||||||||||||
 Sample Sample |
| |||||||||||||||
 Keywords Keywords | SPM transporter / TRANSPORT PROTEIN | |||||||||||||||
| Function / homology |  Function and homology information Function and homology informationTranslocases; Catalysing the translocation of inorganic cations; Linked to the hydrolysis of a nucleoside triphosphate / P-type ion transporter activity / ATPase-coupled monoatomic cation transmembrane transporter activity / intracellular calcium ion homeostasis / ATP hydrolysis activity / ATP binding / metal ion binding / membrane Similarity search - Function | |||||||||||||||
| Biological species |  Chaetomium thermophilum var. thermophilum DSM 1495 (fungus) Chaetomium thermophilum var. thermophilum DSM 1495 (fungus) | |||||||||||||||
| Method | single particle reconstruction / cryo EM / Resolution: 3.7 Å | |||||||||||||||
 Authors Authors | Li P / Gourdon P | |||||||||||||||
| Funding support |  Sweden, Sweden,  Denmark, 4 items Denmark, 4 items
| |||||||||||||||
 Citation Citation |  Journal: Nat Commun / Year: 2021 Journal: Nat Commun / Year: 2021Title: Structure and transport mechanism of P5B-ATPases. Authors: Ping Li / Kaituo Wang / Nina Salustros / Christina Grønberg / Pontus Gourdon /   Abstract: In human cells, P5B-ATPases execute the active export of physiologically important polyamines such as spermine from lysosomes to the cytosol, a function linked to a palette of disorders. Yet, the ...In human cells, P5B-ATPases execute the active export of physiologically important polyamines such as spermine from lysosomes to the cytosol, a function linked to a palette of disorders. Yet, the overall shape of P5B-ATPases and the mechanisms of polyamine recognition, uptake and transport remain elusive. Here we describe a series of cryo-electron microscopy structures of a yeast homolog of human ATP13A2-5, Ypk9, determined at resolutions reaching 3.4 Å, and depicting three separate transport cycle intermediates, including spermine-bound conformations. Surprisingly, in the absence of cargo, Ypk9 rests in a phosphorylated conformation auto-inhibited by the N-terminus. Spermine uptake is accomplished through an electronegative cleft lined by transmembrane segments 2, 4 and 6. Despite the dramatically different nature of the transported cargo, these findings pinpoint shared principles of transport and regulation among the evolutionary related P4-, P5A- and P5B-ATPases. The data also provide a framework for analysis of associated maladies, such as Parkinson's disease. | |||||||||||||||
| History |
|
- Structure visualization
Structure visualization
| Movie |
 Movie viewer Movie viewer |
|---|---|
| Structure viewer | EM map:  SurfView SurfView Molmil Molmil Jmol/JSmol Jmol/JSmol |
| Supplemental images |
- Downloads & links
Downloads & links
-EMDB archive
| Map data |  emd_13011.map.gz emd_13011.map.gz | 64.3 MB |  EMDB map data format EMDB map data format | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Header (meta data) |  emd-13011-v30.xml emd-13011-v30.xml emd-13011.xml emd-13011.xml | 11.6 KB 11.6 KB | Display Display |  EMDB header EMDB header |
| Images |  emd_13011.png emd_13011.png | 31.3 KB | ||
| Filedesc metadata |  emd-13011.cif.gz emd-13011.cif.gz | 6 KB | ||
| Archive directory |  http://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/structures/EMD-13011 http://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/structures/EMD-13011 ftp://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/structures/EMD-13011 ftp://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/structures/EMD-13011 | HTTPS FTP |
-Related structure data
| Related structure data |  7op1MC  7op3C 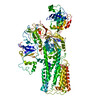 7op5C  7op8C M: atomic model generated by this map C: citing same article ( |
|---|---|
| Similar structure data |
- Links
Links
| EMDB pages |  EMDB (EBI/PDBe) / EMDB (EBI/PDBe) /  EMDataResource EMDataResource |
|---|---|
| Related items in Molecule of the Month |
- Map
Map
| File |  Download / File: emd_13011.map.gz / Format: CCP4 / Size: 125 MB / Type: IMAGE STORED AS FLOATING POINT NUMBER (4 BYTES) Download / File: emd_13011.map.gz / Format: CCP4 / Size: 125 MB / Type: IMAGE STORED AS FLOATING POINT NUMBER (4 BYTES) | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
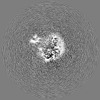
| Projections & slices | Image control
Images are generated by Spider. | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Voxel size | X=Y=Z: 0.8617 Å | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Density |
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Symmetry | Space group: 1 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Details | EMDB XML:
CCP4 map header:
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
-Supplemental data
- Sample components
Sample components
-Entire : P5B-ATPase
| Entire | Name: P5B-ATPase |
|---|---|
| Components |
|
-Supramolecule #1: P5B-ATPase
| Supramolecule | Name: P5B-ATPase / type: cell / ID: 1 / Parent: 0 / Macromolecule list: #1 |
|---|---|
| Source (natural) | Organism:  Chaetomium thermophilum var. thermophilum DSM 1495 (fungus) Chaetomium thermophilum var. thermophilum DSM 1495 (fungus) |
-Macromolecule #1: Cation-transporting ATPase
| Macromolecule | Name: Cation-transporting ATPase / type: protein_or_peptide / ID: 1 / Number of copies: 1 / Enantiomer: LEVO EC number: Translocases; Catalysing the translocation of inorganic cations; Linked to the hydrolysis of a nucleoside triphosphate |
|---|---|
| Source (natural) | Organism:  Chaetomium thermophilum var. thermophilum DSM 1495 (fungus) Chaetomium thermophilum var. thermophilum DSM 1495 (fungus) |
| Molecular weight | Theoretical: 156.013906 KDa |
| Recombinant expression | Organism:  |
| Sequence | String: MDGSRGTAPG GDDLRGDRRD SYQGEDREDS HLLGALEDGN HQQSQGHGGG SGFYHHNVNS SSASVLEGVE MAHDELFAGP VAESVPTSV SAFSHRHGRA ESVASFSFYH EQDDQREELE APPGSLGARL SIDDLDELPF EEEGLSESEM PEQLDTFGID L EWGSMNNG ...String: MDGSRGTAPG GDDLRGDRRD SYQGEDREDS HLLGALEDGN HQQSQGHGGG SGFYHHNVNS SSASVLEGVE MAHDELFAGP VAESVPTSV SAFSHRHGRA ESVASFSFYH EQDDQREELE APPGSLGARL SIDDLDELPF EEEGLSESEM PEQLDTFGID L EWGSMNNG YPLIRRSSTH SQFSAHHRLL RRESGVSAAS GYTGGRSSQK MRLDNDDLTI AISGFITNRI GFAIYIVLCV LT GGIAWLF LRWYPKYYVK LVGCATPFRD CQWVVIEDHF NKMTILSIRV KPYNRPLSTV FGTPSRATSW PLAQDPDPVL REL RSITYC YYKFYYHPVL DKFFCCNGWK DPQWNSMQNA RSGLHGDEKA HREAVFGPNS IDVDEQSILQ LLVSEILTPF YAFQ VFSLI LWLCDEYYYY AAAILLISAG SIITSLLETK ETRRRLREMS RFECEVRVFR GGFWRTFPSS DLVPGDVYEV SDPSL TQIP ADSLLLTGDC IVNESMLTGE SVAVSKTPAT NETLAKLNPA ASTFSHDVDK HFLYCGTKLI RARQRLADTD EAAAVA LVV RTGFNTTRGA LVRSMLVPKP SKFKFYEDSF RYLKVMGCLA GLAFIVSLVN FIRLKLHWTL ILLRALDLLT IVVPPAL PA TLTIGTSFAV QRLKGKKIFC TSPQRVNVGG KIDLMCFDKT GTLTEEGLDV LGIRVASRVS NRFTELLTNV DDLTWSCD S VSNGDEVKPA DHVDGSSLKK DKTKPLDPYR AALYVMASCH SLRIVDGVAV GDPLEVKMFE FTGWSYEEGF IAGEVISTE GRGDISPSIA RPPRYMTSQE MSIGEAPPAV GVLRAFDFNP LLRRSSVIAR VVGNSGGYAL VKGSPECMPE ICRPETLPSD FDELLSYYT HAGYRVIACA TKRIPKLNLV SVNRMTRDEV ESGLDFVGFI IFENKLKPTT TSVIKELLSS NIGTVMITGD N IRTAVSVA RQCGIIEEHA HCYMPRFIEG NADDCNAKLR WESINNPALE LDPWTLLPMP VPPQTDASLP YDVSNIRNYA IA VTGDVFR WIVDHAPTDV LHRMLVLGKV YARMSPDEKQ ELVKKFQSID YSCGFCGDGA NDCAALKAAD VGISLSEAEA SVA APFTSQ IFDIRCVPEV IREGRASLVT SFSCFKYMSL YSFIQFTSVS FLYVSASNLG DFQFLYIDLM LILPIAVFMS WAGP HSKLC AKRPVSDLVS RKVLVPLLSH VFVCVMIQAL AWVAVRQQPW YIPPIVDTEK SNIENSENTT LFFASCFEYI LSGVV LNAG RPFRQSPLET WPFLSAVAVT LIATLLMLLV PPYWLFEFMQ LTWMSWTFKI TLIAFGFVYF LIAWTGEHYL FLWLAR FLG RMRQRLFKQP KQRKLYKIVK EKLVFENLYF UniProtKB: Cation-transporting ATPase |
-Macromolecule #2: MAGNESIUM ION
| Macromolecule | Name: MAGNESIUM ION / type: ligand / ID: 2 / Number of copies: 1 / Formula: MG |
|---|---|
| Molecular weight | Theoretical: 24.305 Da |
-Macromolecule #3: TETRAFLUOROALUMINATE ION
| Macromolecule | Name: TETRAFLUOROALUMINATE ION / type: ligand / ID: 3 / Number of copies: 1 / Formula: ALF |
|---|---|
| Molecular weight | Theoretical: 102.975 Da |
| Chemical component information | 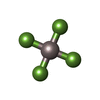 ChemComp-ALF: |
-Macromolecule #4: SPERMINE
| Macromolecule | Name: SPERMINE / type: ligand / ID: 4 / Number of copies: 1 / Formula: SPM |
|---|---|
| Molecular weight | Theoretical: 202.34 Da |
| Chemical component information | 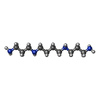 ChemComp-SPM: |
-Experimental details
-Structure determination
| Method | cryo EM |
|---|---|
 Processing Processing | single particle reconstruction |
| Aggregation state | particle |
- Sample preparation
Sample preparation
| Buffer | pH: 7.5 |
|---|---|
| Vitrification | Cryogen name: ETHANE |
- Electron microscopy
Electron microscopy
| Microscope | FEI TITAN KRIOS |
|---|---|
| Image recording | Film or detector model: GATAN K3 (6k x 4k) / Average electron dose: 50.0 e/Å2 |
| Electron beam | Acceleration voltage: 300 kV / Electron source:  FIELD EMISSION GUN FIELD EMISSION GUN |
| Electron optics | Illumination mode: FLOOD BEAM / Imaging mode: BRIGHT FIELD |
| Experimental equipment |  Model: Titan Krios / Image courtesy: FEI Company |
- Image processing
Image processing
| Startup model | Type of model: PDB ENTRY PDB model - PDB ID: |
|---|---|
| Final reconstruction | Resolution.type: BY AUTHOR / Resolution: 3.7 Å / Resolution method: FSC 0.5 CUT-OFF / Number images used: 59345 |
| Initial angle assignment | Type: NOT APPLICABLE |
| Final angle assignment | Type: NOT APPLICABLE |
 Movie
Movie Controller
Controller





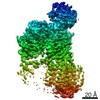
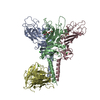

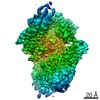

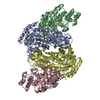


 Z (Sec.)
Z (Sec.) Y (Row.)
Y (Row.) X (Col.)
X (Col.)