[English] 日本語
 Yorodumi
Yorodumi- EMDB-12802: Resting state full-length GluA1/A2 heterotertramer in complex wit... -
+ Open data
Open data
- Basic information
Basic information
| Entry | Database: EMDB / ID: EMD-12802 | |||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
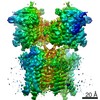
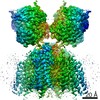
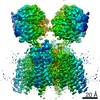
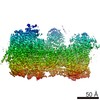
| Title | Resting state full-length GluA1/A2 heterotertramer in complex with TARP gamma 8 and CNIH2 | |||||||||
 Map data Map data | Composite map of full-length GluA1/A2 heteromer in complex with TARP gamma 8 and CNIH2 at resting state | |||||||||
 Sample Sample |
| |||||||||
 Keywords Keywords | AMPAR / ion channels / neurotransmission / MEMBRANE PROTEIN | |||||||||
| Function / homology |  Function and homology information Function and homology informationnegative regulation of receptor localization to synapse / negative regulation of anterograde synaptic vesicle transport / Phase 0 - rapid depolarisation / Phase 2 - plateau phase / Cargo concentration in the ER / axonal spine / positive regulation of locomotion involved in locomotory behavior / positive regulation of membrane potential / localization within membrane / COPII-mediated vesicle transport ...negative regulation of receptor localization to synapse / negative regulation of anterograde synaptic vesicle transport / Phase 0 - rapid depolarisation / Phase 2 - plateau phase / Cargo concentration in the ER / axonal spine / positive regulation of locomotion involved in locomotory behavior / positive regulation of membrane potential / localization within membrane / COPII-mediated vesicle transport / cellular response to ammonium ion / response to sucrose / L-type voltage-gated calcium channel complex / neuron spine / myosin V binding / postsynaptic neurotransmitter receptor diffusion trapping / proximal dendrite / regulation of monoatomic ion transmembrane transport / regulation of AMPA receptor activity / channel regulator activity / Trafficking of AMPA receptors / protein phosphatase 2B binding / LGI-ADAM interactions / response to arsenic-containing substance / regulation of NMDA receptor activity / cellular response to L-glutamate / cellular response to dsRNA / dendritic spine membrane / long-term synaptic depression / beta-2 adrenergic receptor binding / Synaptic adhesion-like molecules / cellular response to peptide hormone stimulus / response to morphine / neuronal cell body membrane / spine synapse / dendritic spine neck / protein kinase A binding / dendritic spine head / peptide hormone receptor binding / cellular response to amine stimulus / response to psychosocial stress / spinal cord development / perisynaptic space / Activation of AMPA receptors / ligand-gated monoatomic cation channel activity / AMPA glutamate receptor activity / transmission of nerve impulse / response to lithium ion / Trafficking of GluR2-containing AMPA receptors / behavioral response to pain / kainate selective glutamate receptor activity / cellular response to glycine / AMPA glutamate receptor complex / adenylate cyclase binding / extracellularly glutamate-gated ion channel activity / immunoglobulin binding / asymmetric synapse / ionotropic glutamate receptor complex / excitatory synapse / conditioned place preference / response to electrical stimulus / regulation of receptor recycling / G-protein alpha-subunit binding / glutamate receptor binding / positive regulation of excitatory postsynaptic potential / Unblocking of NMDA receptors, glutamate binding and activation / long-term memory / positive regulation of synaptic transmission / positive regulation of synaptic transmission, glutamatergic / postsynaptic density, intracellular component / regulation of postsynaptic membrane neurotransmitter receptor levels / regulation of synaptic transmission, glutamatergic / neuronal action potential / voltage-gated calcium channel activity / response to fungicide / cytoskeletal protein binding / glutamate-gated receptor activity / synapse assembly / vesicle-mediated transport / regulation of long-term synaptic depression / extracellular ligand-gated monoatomic ion channel activity / cellular response to brain-derived neurotrophic factor stimulus / glutamate-gated calcium ion channel activity / presynaptic active zone membrane / somatodendritic compartment / dendrite membrane / ionotropic glutamate receptor binding / ligand-gated monoatomic ion channel activity involved in regulation of presynaptic membrane potential / ionotropic glutamate receptor signaling pathway / dendrite cytoplasm / synaptic membrane / dendritic shaft / SNARE binding / regulation of membrane potential / response to cocaine / calcium channel regulator activity / transmitter-gated monoatomic ion channel activity involved in regulation of postsynaptic membrane potential / synaptic transmission, glutamatergic / protein tetramerization / PDZ domain binding Similarity search - Function | |||||||||
| Biological species |  | |||||||||
| Method | single particle reconstruction / cryo EM / Resolution: 3.4 Å | |||||||||
 Authors Authors | Zhang D / Watson JF / Matthews PM / Cais O / Greger IH | |||||||||
| Funding support | 2 items
| |||||||||
 Citation Citation |  Journal: Nature / Year: 2021 Journal: Nature / Year: 2021Title: Gating and modulation of a hetero-octameric AMPA glutamate receptor. Authors: Danyang Zhang / Jake F Watson / Peter M Matthews / Ondrej Cais / Ingo H Greger /   Abstract: AMPA receptors (AMPARs) mediate the majority of excitatory transmission in the brain and enable the synaptic plasticity that underlies learning. A diverse array of AMPAR signalling complexes are ...AMPA receptors (AMPARs) mediate the majority of excitatory transmission in the brain and enable the synaptic plasticity that underlies learning. A diverse array of AMPAR signalling complexes are established by receptor auxiliary subunits, which associate with the AMPAR in various combinations to modulate trafficking, gating and synaptic strength. However, their mechanisms of action are poorly understood. Here we determine cryo-electron microscopy structures of the heteromeric GluA1-GluA2 receptor assembled with both TARP-γ8 and CNIH2, the predominant AMPAR complex in the forebrain, in both resting and active states. Two TARP-γ8 and two CNIH2 subunits insert at distinct sites beneath the ligand-binding domains of the receptor, with site-specific lipids shaping each interaction and affecting the gating regulation of the AMPARs. Activation of the receptor leads to asymmetry between GluA1 and GluA2 along the ion conduction path and an outward expansion of the channel triggers counter-rotations of both auxiliary subunit pairs, promoting the active-state conformation. In addition, both TARP-γ8 and CNIH2 pivot towards the pore exit upon activation, extending their reach for cytoplasmic receptor elements. CNIH2 achieves this through its uniquely extended M2 helix, which has transformed this endoplasmic reticulum-export factor into a powerful AMPAR modulator that is capable of providing hippocampal pyramidal neurons with their integrative synaptic properties. | |||||||||
| History |
|
- Structure visualization
Structure visualization
| Movie |
 Movie viewer Movie viewer |
|---|---|
| Structure viewer | EM map:  SurfView SurfView Molmil Molmil Jmol/JSmol Jmol/JSmol |
| Supplemental images |
- Downloads & links
Downloads & links
-EMDB archive
| Map data |  emd_12802.map.gz emd_12802.map.gz | 14.5 MB |  EMDB map data format EMDB map data format | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Header (meta data) |  emd-12802-v30.xml emd-12802-v30.xml emd-12802.xml emd-12802.xml | 16.1 KB 16.1 KB | Display Display |  EMDB header EMDB header |
| Images |  emd_12802.png emd_12802.png | 100.1 KB | ||
| Filedesc metadata |  emd-12802.cif.gz emd-12802.cif.gz | 7 KB | ||
| Archive directory |  http://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/structures/EMD-12802 http://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/structures/EMD-12802 ftp://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/structures/EMD-12802 ftp://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/structures/EMD-12802 | HTTPS FTP |
-Validation report
| Summary document |  emd_12802_validation.pdf.gz emd_12802_validation.pdf.gz | 423 KB | Display |  EMDB validaton report EMDB validaton report |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Full document |  emd_12802_full_validation.pdf.gz emd_12802_full_validation.pdf.gz | 422.6 KB | Display | |
| Data in XML |  emd_12802_validation.xml.gz emd_12802_validation.xml.gz | 6.5 KB | Display | |
| Data in CIF |  emd_12802_validation.cif.gz emd_12802_validation.cif.gz | 7.5 KB | Display | |
| Arichive directory |  https://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/validation_reports/EMD-12802 https://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/validation_reports/EMD-12802 ftp://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/validation_reports/EMD-12802 ftp://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/validation_reports/EMD-12802 | HTTPS FTP |
-Related structure data
| Related structure data |  7ocaMC  7occC  7ocdC  7oceC  7ocfC M: atomic model generated by this map C: citing same article ( |
|---|---|
| Similar structure data |
- Links
Links
| EMDB pages |  EMDB (EBI/PDBe) / EMDB (EBI/PDBe) /  EMDataResource EMDataResource |
|---|---|
| Related items in Molecule of the Month |
- Map
Map
| File |  Download / File: emd_12802.map.gz / Format: CCP4 / Size: 125 MB / Type: IMAGE STORED AS FLOATING POINT NUMBER (4 BYTES) Download / File: emd_12802.map.gz / Format: CCP4 / Size: 125 MB / Type: IMAGE STORED AS FLOATING POINT NUMBER (4 BYTES) | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
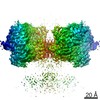
| Annotation | Composite map of full-length GluA1/A2 heteromer in complex with TARP gamma 8 and CNIH2 at resting state | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Projections & slices | Image control
Images are generated by Spider. | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Voxel size | X=Y=Z: 1.07 Å | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Density |
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Symmetry | Space group: 1 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Details | EMDB XML:
CCP4 map header:
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
-Supplemental data
- Sample components
Sample components
-Entire : GluA1/A2 heterotertramer in complex with auxiliary subunits TARP ...
| Entire | Name: GluA1/A2 heterotertramer in complex with auxiliary subunits TARP gamma 8 and CNIH2 |
|---|---|
| Components |
|
-Supramolecule #1: GluA1/A2 heterotertramer in complex with auxiliary subunits TARP ...
| Supramolecule | Name: GluA1/A2 heterotertramer in complex with auxiliary subunits TARP gamma 8 and CNIH2 type: complex / ID: 1 / Parent: 0 / Macromolecule list: #1-#4 |
|---|---|
| Source (natural) | Organism:  |
| Molecular weight | Theoretical: 527 KDa |
-Macromolecule #1: Glutamate receptor 1
| Macromolecule | Name: Glutamate receptor 1 / type: protein_or_peptide / ID: 1 / Number of copies: 2 / Enantiomer: LEVO |
|---|---|
| Source (natural) | Organism:  |
| Molecular weight | Theoretical: 102.66193 KDa |
| Recombinant expression | Organism:  Homo sapiens (human) Homo sapiens (human) |
| Sequence | String: MPYIFAFFCT GFLGAVVGAD YKDDDDKNFP NNIQIGGLFP NQQSQEHAAF RFALSQLTEP PKLLPQIDIV NISDSFEMTY RFCSQFSKG VYAIFGFYER RTVNMLTSFC GALHVCFITP SFPVDTSNQF VLQLRPELQE ALISIIDHYK WQTFVYIYDA D RGLSVLQR ...String: MPYIFAFFCT GFLGAVVGAD YKDDDDKNFP NNIQIGGLFP NQQSQEHAAF RFALSQLTEP PKLLPQIDIV NISDSFEMTY RFCSQFSKG VYAIFGFYER RTVNMLTSFC GALHVCFITP SFPVDTSNQF VLQLRPELQE ALISIIDHYK WQTFVYIYDA D RGLSVLQR VLDTAAEKNW QVTAVNILTT TEEGYRMLFQ DLEKKKERLV VVDCESERLN AILGQIVKLE KNGIGYHYIL AN LGFMDID LNKFKESGAN VTGFQLVNYT DTIPARIMQQ WRTSDSRDHT RVDWKRPKYT SALTYDGVKV MAEAFQSLRR QRI DISRRG NAGDCLANPA VPWGQGIDIQ RALQQVRFEG LTGNVQFNEK GRRTNYTLHV IEMKHDGIRK IGYWNEDDKF VPAA TDAQA GGDNSSVQNR TYIVTTILED PYVMLKKNAN QFEGNDRYEG YCVELAAEIA KHVGYSYRLE IVSDGKYGAR DPDTK AWNG MVGELVYGRA DVAVAPLTIT LVREEVIDFS KPFMSLGISI MIKKPQKSKP GVFSFLDPLA YEIWMCIVFA YIGVSV VLF LVSRFSPYEW HSEEFEEGRD QTTSDQSNEF GIFNSLWFSL GAFMQQGCDI SPRSLSGRIV GGVWWFFTLI IISSYTA NL AAFLTVERMV SPIESAEDLA KQTEIAYGTL EAGSTKEFFR RSKIAVFEKM WTYMKSAEPS VFVRTTEEGM IRVRKSKG K YAYLLESTMN EYIEQRKPCD TMKVGGNLDS KGYGIATPKG SALRGPVNLA VLKLSEQGVL DKLKSKWWYD KGECGSKDS GSKDKTSALS LSNVAGVFYI LIGGLGLAML VALIEFCYKS RSESKRMKGF CLIPQQSINE AIRTSTLPRN SGAGASGGGG SGENGRVVS QDFPKSMQSI PCMSHSSGMP LGATGL UniProtKB: Glutamate receptor 1 |
-Macromolecule #2: Glutamate receptor 2
| Macromolecule | Name: Glutamate receptor 2 / type: protein_or_peptide / ID: 2 / Number of copies: 2 / Enantiomer: LEVO |
|---|---|
| Source (natural) | Organism:  |
| Molecular weight | Theoretical: 96.247055 KDa |
| Recombinant expression | Organism:  Homo sapiens (human) Homo sapiens (human) |
| Sequence | String: MQKIMHISVL LSPVLWGLIF GVSSNSIQIG GLFPRGADQE YSAFRVGMVQ FSTSEFRLTP HIDNLEVANS FAVTNAFCSQ FSRGVYAIF GFYDKKSVNT ITSFCGTLHV SFITPSFPTD GTHPFVIQMR PDLKGALLSL IEYYQWDKFA YLYDSDRGLS T LQAVLDSA ...String: MQKIMHISVL LSPVLWGLIF GVSSNSIQIG GLFPRGADQE YSAFRVGMVQ FSTSEFRLTP HIDNLEVANS FAVTNAFCSQ FSRGVYAIF GFYDKKSVNT ITSFCGTLHV SFITPSFPTD GTHPFVIQMR PDLKGALLSL IEYYQWDKFA YLYDSDRGLS T LQAVLDSA AEKKWQVTAI NVGNINNDKK DETYRSLFQD LELKKERRVI LDCERDKVND IVDQVITIGK HVKGYHYIIA NL GFTDGDL LKIQFGGANV SGFQIVDYDD SLVSKFIERW STLEEKEYPG AHTATIKYTS ALTYDAVQVM TEAFRNLRKQ RIE ISRRGN AGDCLANPAV PWGQGVEIER ALKQVQVEGL SGNIKFDQNG KRINYTINIM ELKTNGPRKI GYWSEVDKMV VTLT ELPSG NDTSGLENKT VVVTTILESP YVMMKKNHEM LEGNERYEGY CVDLAAEIAK HCGFKYKLTI VGDGKYGARD ADTKI WNGM VGELVYGKAD IAIAPLTITL VREEVIDFSK PFMSLGISIM IKKPQKSKPG VFSFLDPLAY EIWMCIVFAY IGVSVV LFL VSRFSPYEWH TEEFEDGRET QSSESTNEFG IFNSLWFSLG AFMRQGCDIS PRSLSGRIVG GVWWFFTLII ISSYTAN LA AFLTVERMVS PIESAEDLSK QTEIAYGTLD SGSTKEFFRR SKIAVFDKMW TYMRSAEPSV FVRTTAEGVA RVRKSKGK Y AYLLESTMNE YIEQRKPCDT MKVGGNLDSK GYGIATPKGS SLGTPVNLAV LKLSEQGVLD KLKNKWWYDK GECGAKDSG SKEKTSALSL SNVAGVFYIL VGGLGLAMLV ALIEFCYKSR AEAKRMKVAK NPQNINPSSS UniProtKB: Glutamate receptor 2 |
-Macromolecule #3: Protein cornichon homolog 2
| Macromolecule | Name: Protein cornichon homolog 2 / type: protein_or_peptide / ID: 3 / Number of copies: 2 / Enantiomer: LEVO |
|---|---|
| Source (natural) | Organism:  |
| Molecular weight | Theoretical: 22.000605 KDa |
| Recombinant expression | Organism:  Homo sapiens (human) Homo sapiens (human) |
| Sequence | String: MAFTFAAFCY MLTLVLCASL IFFVIWHIIA FDELRTDFKN PIDQGNPARA RERLKNIERI CCLLRKLVVP EYSIHGLFCL MFLCAAEWV TLGLNIPLLF YHLWRYFHRP ADGSEVMYDA VSIMNADILN YCQKESWCKL AFYLLSFFYY LYSMVYTLVS F ENLYFQSG GSTETSQVAP AYPYDVPDYA UniProtKB: Protein cornichon homolog 2 |
-Macromolecule #4: Voltage-dependent calcium channel gamma-8 subunit
| Macromolecule | Name: Voltage-dependent calcium channel gamma-8 subunit / type: protein_or_peptide / ID: 4 / Number of copies: 2 / Enantiomer: LEVO |
|---|---|
| Source (natural) | Organism:  |
| Molecular weight | Theoretical: 43.576004 KDa |
| Recombinant expression | Organism:  Homo sapiens (human) Homo sapiens (human) |
| Sequence | String: GESLKRWNEE RGLWCEKGVQ VLLTTIGAFA AFGLMTIAIS TDYWLYTRAL ICNTTNLTAG DDGPPHRGGS GSSEKKDPGG LTHSGLWRI CCLEGLKRGV CVKINHFPED TDYDHDSAEY LLRVVRASSI FPILSAILLL LGGVCVAASR VYKSKRNIIL G AGILFVAA ...String: GESLKRWNEE RGLWCEKGVQ VLLTTIGAFA AFGLMTIAIS TDYWLYTRAL ICNTTNLTAG DDGPPHRGGS GSSEKKDPGG LTHSGLWRI CCLEGLKRGV CVKINHFPED TDYDHDSAEY LLRVVRASSI FPILSAILLL LGGVCVAASR VYKSKRNIIL G AGILFVAA GLSNIIGVIV YISANAGEPG PKRDEEKKNH YSYGWSFYFG GLSFILAEVI GVLAVNIYIE RSREAHCQSR SD LLKAGGG AGGSGGSGPS AILRLPSYRF RYRRRSRSSS RGSSEASPSR DASPGGPGGP GFASTDISMY TLSRDPSKGS VAA GLASAG GGGGGAGVGA YGGAAGAAGG GGTGSERDRG SSAGFLTLHN AFPKEAASGV TVTVTGPPAA PAPAPPAPAA PAPG TLSKE AAASNTNTLN RKLEVLFQ UniProtKB: Voltage-dependent calcium channel gamma-8 subunit |
-Macromolecule #7: 6-nitro-2,3-bis(oxidanylidene)-1,4-dihydrobenzo[f]quinoxaline-7-s...
| Macromolecule | Name: 6-nitro-2,3-bis(oxidanylidene)-1,4-dihydrobenzo[f]quinoxaline-7-sulfonamide type: ligand / ID: 7 / Number of copies: 4 / Formula: E2Q |
|---|---|
| Molecular weight | Theoretical: 336.28 Da |
| Chemical component information | 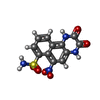 ChemComp-E2Q: |
-Macromolecule #8: 2-acetamido-2-deoxy-beta-D-glucopyranose
| Macromolecule | Name: 2-acetamido-2-deoxy-beta-D-glucopyranose / type: ligand / ID: 8 / Number of copies: 6 / Formula: NAG |
|---|---|
| Molecular weight | Theoretical: 221.208 Da |
| Chemical component information |  ChemComp-NAG: |
-Macromolecule #9: 1,2-DIACYL-SN-GLYCERO-3-PHOSPHOCHOLINE
| Macromolecule | Name: 1,2-DIACYL-SN-GLYCERO-3-PHOSPHOCHOLINE / type: ligand / ID: 9 / Number of copies: 46 / Formula: PC1 |
|---|---|
| Molecular weight | Theoretical: 790.145 Da |
| Chemical component information | 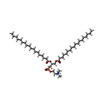 ChemComp-PC1: |
-Macromolecule #10: CHOLESTEROL
| Macromolecule | Name: CHOLESTEROL / type: ligand / ID: 10 / Number of copies: 2 / Formula: CLR |
|---|---|
| Molecular weight | Theoretical: 386.654 Da |
| Chemical component information |  ChemComp-CLR: |
-Experimental details
-Structure determination
| Method | cryo EM |
|---|---|
 Processing Processing | single particle reconstruction |
| Aggregation state | particle |
- Sample preparation
Sample preparation
| Buffer | pH: 8 |
|---|---|
| Vitrification | Cryogen name: ETHANE |
- Electron microscopy
Electron microscopy
| Microscope | FEI TITAN KRIOS |
|---|---|
| Image recording | Film or detector model: GATAN K3 (6k x 4k) / Average electron dose: 50.0 e/Å2 |
| Electron beam | Acceleration voltage: 300 kV / Electron source:  FIELD EMISSION GUN FIELD EMISSION GUN |
| Electron optics | Illumination mode: FLOOD BEAM / Imaging mode: BRIGHT FIELD |
| Experimental equipment |  Model: Titan Krios / Image courtesy: FEI Company |
- Image processing
Image processing
| Startup model | Type of model: EMDB MAP |
|---|---|
| Final reconstruction | Resolution.type: BY AUTHOR / Resolution: 3.4 Å / Resolution method: FSC 0.143 CUT-OFF / Number images used: 218320 |
| Initial angle assignment | Type: MAXIMUM LIKELIHOOD |
| Final angle assignment | Type: MAXIMUM LIKELIHOOD |
 Movie
Movie Controller
Controller










 Z (Sec.)
Z (Sec.) Y (Row.)
Y (Row.) X (Col.)
X (Col.)





















