[English] 日本語
 Yorodumi
Yorodumi- EMDB-10339: Respiratory mucin MUC5B; C-terminal dimerization domain structure -
+ Open data
Open data
- Basic information
Basic information
| Entry | Database: EMDB / ID: EMD-10339 | |||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
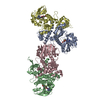
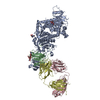
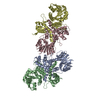
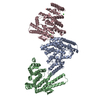
| Title | Respiratory mucin MUC5B; C-terminal dimerization domain structure | |||||||||
 Map data Map data | Base of the C2 symmetric MUC5B models | |||||||||
 Sample Sample |
| |||||||||
| Biological species |  Homo sapiens (human) Homo sapiens (human) | |||||||||
| Method | single particle reconstruction / cryo EM / Resolution: 7.5 Å | |||||||||
 Authors Authors | Lockhart-Lockhart MP / Ridley C / Collins RF / Baldock C / Thornton DJ | |||||||||
| Funding support |  United Kingdom, 1 items United Kingdom, 1 items
| |||||||||
 Citation Citation |  Journal: J Biol Chem / Year: 2019 Journal: J Biol Chem / Year: 2019Title: The C-terminal dimerization domain of the respiratory mucin MUC5B functions in mucin stability and intracellular packaging before secretion. Authors: Caroline Ridley / Michael P Lockhart-Cairns / Richard F Collins / Thomas A Jowitt / Durai B Subramani / Mehmet Kesimer / Clair Baldock / David J Thornton /  Abstract: Mucin 5B (MUC5B) has an essential role in mucociliary clearance that protects the pulmonary airways. Accordingly, knowledge of MUC5B structure and its interactions with itself and other proteins is ...Mucin 5B (MUC5B) has an essential role in mucociliary clearance that protects the pulmonary airways. Accordingly, knowledge of MUC5B structure and its interactions with itself and other proteins is critical to better understand airway mucus biology and improve the management of lung diseases such as asthma, cystic fibrosis, and chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD). The role of an N-terminal multimerization domain in the supramolecular organization of MUC5B has been previously described, but less is known about its C-terminal dimerization domain. Here, using cryogenic electron microscopy (cryo-EM) and small-angle X-ray scattering (SAXS) analyses of recombinant disulfide-linked dimeric MUC5B dimerization domain we identified an asymmetric, elongated twisted structure, with a double globular base. We found that the dimerization domain is more resistant to disruption than the multimerization domain suggesting the twisted structure of the dimerization domain confers additional stability to MUC5B polymers. Size-exclusion chromatography-multiangle light scattering (SEC-MALS), SPR-based biophysical analyses and microscale thermophoresis of the dimerization domain disclosed no further assembly, but did reveal reversible, calcium-dependent interactions between the dimerization and multimerization domains that were most active at acidic pH, suggesting that these domains have a role in MUC5B intragranular organization. In summary, our results suggest a role for the C-terminal dimerization domain of MUC5B in compaction of mucin chains during granular packaging via interactions with the N-terminal multimerization domain. Our findings further suggest that the less stable multimerization domain provides a potential target for mucin depolymerization to remove mucus plugs in COPD and other lung pathologies. | |||||||||
| History |
|
- Structure visualization
Structure visualization
| Movie |
 Movie viewer Movie viewer |
|---|---|
| Structure viewer | EM map:  SurfView SurfView Molmil Molmil Jmol/JSmol Jmol/JSmol |
| Supplemental images |
- Downloads & links
Downloads & links
-EMDB archive
| Map data |  emd_10339.map.gz emd_10339.map.gz | 59.6 MB |  EMDB map data format EMDB map data format | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Header (meta data) |  emd-10339-v30.xml emd-10339-v30.xml emd-10339.xml emd-10339.xml | 13.7 KB 13.7 KB | Display Display |  EMDB header EMDB header |
| Images |  emd_10339.png emd_10339.png | 11.2 KB | ||
| Archive directory |  http://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/structures/EMD-10339 http://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/structures/EMD-10339 ftp://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/structures/EMD-10339 ftp://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/structures/EMD-10339 | HTTPS FTP |
-Related structure data
| Related structure data | C: citing same article ( |
|---|---|
| Similar structure data |
- Links
Links
| EMDB pages |  EMDB (EBI/PDBe) / EMDB (EBI/PDBe) /  EMDataResource EMDataResource |
|---|
- Map
Map
| File |  Download / File: emd_10339.map.gz / Format: CCP4 / Size: 64 MB / Type: IMAGE STORED AS FLOATING POINT NUMBER (4 BYTES) Download / File: emd_10339.map.gz / Format: CCP4 / Size: 64 MB / Type: IMAGE STORED AS FLOATING POINT NUMBER (4 BYTES) | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Annotation | Base of the C2 symmetric MUC5B models | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Projections & slices | Image control
Images are generated by Spider. | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Voxel size | X=Y=Z: 2.0371 Å | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Density |
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Symmetry | Space group: 1 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Details | EMDB XML:
CCP4 map header:
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
-Supplemental data
- Sample components
Sample components
-Entire : Dimeric structure of C-terminal MUC5B base region.
| Entire | Name: Dimeric structure of C-terminal MUC5B base region. |
|---|---|
| Components |
|
-Supramolecule #1: Dimeric structure of C-terminal MUC5B base region.
| Supramolecule | Name: Dimeric structure of C-terminal MUC5B base region. / type: complex / ID: 1 / Parent: 0 / Macromolecule list: all |
|---|---|
| Source (natural) | Organism:  Homo sapiens (human) Homo sapiens (human) |
| Recombinant expression | Organism:  Homo sapiens (human) / Recombinant cell: HEK293-EBNA / Recombinant plasmid: pCEP-His Homo sapiens (human) / Recombinant cell: HEK293-EBNA / Recombinant plasmid: pCEP-His |
| Molecular weight | Experimental: 260 kDa/nm |
-Macromolecule #1: MUC5B
| Macromolecule | Name: MUC5B / type: protein_or_peptide / ID: 1 / Enantiomer: LEVO |
|---|---|
| Source (natural) | Organism:  Homo sapiens (human) Homo sapiens (human) |
| Recombinant expression | Organism:  Homo sapiens (human) Homo sapiens (human) |
| Sequence | String: EVIYNKTDRA GCHFYAVCNQ HCDID RFQG ACPTSPPPVS SAPLSSPSPA PGCDNAIPLR QVNETWTLEN CTVARCVGDN RVVLLD PKP VANVTCVNKH LPIKVSDPSQ PCDFHYECEC ICSMWGGSHY STFDGTSYTF RGNCTYV LM REIHARFGNL SLYLDNHYCT ...String: EVIYNKTDRA GCHFYAVCNQ HCDID RFQG ACPTSPPPVS SAPLSSPSPA PGCDNAIPLR QVNETWTLEN CTVARCVGDN RVVLLD PKP VANVTCVNKH LPIKVSDPSQ PCDFHYECEC ICSMWGGSHY STFDGTSYTF RGNCTYV LM REIHARFGNL SLYLDNHYCT ASATAAAARC PRALSIHYKS MDIVLTVTMV HGKEEGLI L FDQIPVSSGF SKNGVLVSVL GTTTMRVDIP ALGVSVTFNG QVFQARLPYS LFHNNTEGQ CGTCTNNQRD DCLQRDGTTA ASCKDMAKTW LVPDSRKDGC WAPTGTPPTA SPAAPVSSTP TPTPCPPQP LCDLMLSQVF AECHNLVPPG PFFNACISDH CRGRLEVPCQ SLEAYAELCR A RGVCSDWR GATGGLCDLT CPPTKVYKPC GPIQPATCNS RNQSPQLEGM AEGCFCPEDQ IL FNAHMGI CVQACPCVGP DGFPKFPGER WVSNCQSCVC DEGSVSVQCK PLPCDAQGQP PPC NRPGFV TVTRPRAENP CCPETVCVCN TTTCPQSLPV CPPGQESICT QEEGDCCPTF RCRP QLCSY NGTFYGVGAT FPGALPCHMC TCLSGDTQDP TVQCQEDACN NTTCPQGFEY KRVAG QCCG ECVQTACLTP DGQPVQLNET WVNSHVDNCT VYLCEAEGGV HLLTPQPASC PDVSSC RGS LRKTGCCYSC EEDSCQVRIN TTILWHQGCE TEVNITFCEG SCPGASKYSA EAQAMQH QC TCCQERRVHE ETVPLHCPNG SAILHTYTHV DECGCTPFCV PAPMAPPHTR GFPAQEAT A V |
-Experimental details
-Structure determination
| Method | cryo EM |
|---|---|
 Processing Processing | single particle reconstruction |
| Aggregation state | particle |
- Sample preparation
Sample preparation
| Concentration | 0.25 mg/mL | |||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Buffer | pH: 7.4 Component:
Details: Buffers were filtered and degassed before use. | |||||||||
| Vitrification | Cryogen name: ETHANE / Chamber humidity: 100 % / Chamber temperature: 277 K / Instrument: FEI VITROBOT MARK IV |
- Electron microscopy
Electron microscopy
| Microscope | FEI TITAN KRIOS |
|---|---|
| Specialist optics | Phase plate: VOLTA PHASE PLATE |
| Image recording | Film or detector model: GATAN K2 SUMMIT (4k x 4k) / Detector mode: COUNTING / Number grids imaged: 1 / Average electron dose: 40.0 e/Å2 |
| Electron beam | Acceleration voltage: 300 kV / Electron source:  FIELD EMISSION GUN FIELD EMISSION GUN |
| Electron optics | Illumination mode: OTHER / Imaging mode: BRIGHT FIELD |
| Sample stage | Specimen holder model: FEI TITAN KRIOS AUTOGRID HOLDER |
| Experimental equipment |  Model: Titan Krios / Image courtesy: FEI Company |
 Movie
Movie Controller
Controller









 Z (Sec.)
Z (Sec.) Y (Row.)
Y (Row.) X (Col.)
X (Col.)





















