[English] 日本語
 Yorodumi
Yorodumi- SASDE88: Solution structure of phosphoglucosamine mutase (GlmM) from Staph... -
+ Open data
Open data
- Basic information
Basic information
| Entry | Database: SASBDB / ID: SASDE88 |
|---|---|
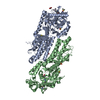
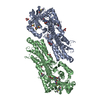
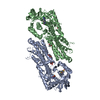
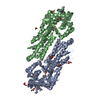
 Sample Sample | Solution structure of phosphoglucosamine mutase (GlmM) from Staphylococcus aureus
|
| Function / homology |  Function and homology information Function and homology informationphosphoglucosamine mutase / phosphoglucosamine mutase activity / phosphomannomutase activity / UDP-N-acetylglucosamine biosynthetic process / peptidoglycan biosynthetic process / carbohydrate metabolic process / magnesium ion binding / cytosol Similarity search - Function |
| Biological species |  Staphylococcus aureus (strain USA300) (bacteria) Staphylococcus aureus (strain USA300) (bacteria) |
 Citation Citation |  Journal: PLoS Pathog / Year: 2019 Journal: PLoS Pathog / Year: 2019Title: Inhibition of the Staphylococcus aureus c-di-AMP cyclase DacA by direct interaction with the phosphoglucosamine mutase GlmM. Authors: Tommaso Tosi / Fumiya Hoshiga / Charlotte Millership / Rahul Singh / Charles Eldrid / Delphine Patin / Dominique Mengin-Lecreulx / Konstantinos Thalassinos / Paul Freemont / Angelika Gründling /   Abstract: c-di-AMP is an important second messenger molecule that plays a pivotal role in regulating fundamental cellular processes, including osmotic and cell wall homeostasis in many Gram-positive organisms. ...c-di-AMP is an important second messenger molecule that plays a pivotal role in regulating fundamental cellular processes, including osmotic and cell wall homeostasis in many Gram-positive organisms. In the opportunistic human pathogen Staphylococcus aureus, c-di-AMP is produced by the membrane-anchored DacA enzyme. Inactivation of this enzyme leads to a growth arrest under standard laboratory growth conditions and a re-sensitization of methicillin-resistant S. aureus (MRSA) strains to ß-lactam antibiotics. The gene coding for DacA is part of the conserved three-gene dacA/ybbR/glmM operon that also encodes the proposed DacA regulator YbbR and the essential phosphoglucosamine mutase GlmM, which is required for the production of glucosamine-1-phosphate, an early intermediate of peptidoglycan synthesis. These three proteins are thought to form a complex in vivo and, in this manner, help to fine-tune the cellular c-di-AMP levels. To further characterize this important regulatory complex, we conducted a comprehensive structural and functional analysis of the S. aureus DacA and GlmM enzymes by determining the structures of the S. aureus GlmM enzyme and the catalytic domain of DacA. Both proteins were found to be dimers in solution as well as in the crystal structures. Further site-directed mutagenesis, structural and enzymatic studies showed that multiple DacA dimers need to interact for enzymatic activity. We also show that DacA and GlmM form a stable complex in vitro and that S. aureus GlmM, but not Escherichia coli or Pseudomonas aeruginosa GlmM, acts as a strong inhibitor of DacA function without the requirement of any additional cellular factor. Based on Small Angle X-ray Scattering (SAXS) data, a model of the complex revealed that GlmM likely inhibits DacA by masking the active site of the cyclase and preventing higher oligomer formation. Together these results provide an important mechanistic insight into how c-di-AMP production can be regulated in the cell. |
 Contact author Contact author |
|
- Structure visualization
Structure visualization
| Structure viewer | Molecule:  Molmil Molmil Jmol/JSmol Jmol/JSmol |
|---|
- Downloads & links
Downloads & links
-Models
| Model #2647 | 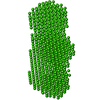 Type: dummy / Software: (5.0) / Radius of dummy atoms: 3.25 A / Chi-square value: 1.218 / P-value: 0.363345  Search similar-shape structures of this assembly by Omokage search (details) Search similar-shape structures of this assembly by Omokage search (details) |
|---|
- Sample
Sample
 Sample Sample | Name: Solution structure of phosphoglucosamine mutase (GlmM) from Staphylococcus aureus |
|---|---|
| Buffer | Name: 30 mM Tris, 150 mM NaCl / pH: 7.5 |
| Entity #1392 | Name: GlmM / Type: protein / Description: Phosphoglucosamine mutase / Formula weight: 49.731 / Num. of mol.: 2 / Source: Staphylococcus aureus (strain USA300) / References: UniProt: Q2FEX1 Sequence: MGKYFGTDGV RGVANQELTP ELAFKLGRYG GYVLAHNKGE KHPRVLVGRD TRVSGEMLES ALIAGLISIG AEVMRLGIIS TPGVAYLTRD MGAELGVMIS ASHNPVADNG IKFFGSDGFK LSDEQENEIE ALLDQENPEL PRPVGNDIVH YSDYFEGAQK YLSYLKSTVD ...Sequence: MGKYFGTDGV RGVANQELTP ELAFKLGRYG GYVLAHNKGE KHPRVLVGRD TRVSGEMLES ALIAGLISIG AEVMRLGIIS TPGVAYLTRD MGAELGVMIS ASHNPVADNG IKFFGSDGFK LSDEQENEIE ALLDQENPEL PRPVGNDIVH YSDYFEGAQK YLSYLKSTVD VNFEGLKIAL DGANGSTSSL APFLFGDLEA DTETIGCSPD GYNINEKCGS THPEKLAEKV VETESDFGLA FDGDGDRIIA VDENGQIVDG DQIMFIIGQE MHKNQELNND MIVSTVMSNL GFYKALEQEG IKSNKTKVGD RYVVEEMRRG NYNLGGEQSG HIVMMDYNTT GDGLLTGIQL ASVIKMTGKS LSELAGQMKK YPQSLINVRV TDKYRVEENV DVKEVMTKVE VEMNGEGRIL VRPSGTEPLV RVMVEAATDE DAERFAQQIA DVVQDKMGLD KLVPR |
-Experimental information
| Beam | Instrument name: Diamond Light Source B21 / City: Oxfordshire / 国: UK  / Shape: 1 x 5 mm / Type of source: X-ray synchrotron / Wavelength: 0.1 Å / Dist. spec. to detc.: 4.014 mm / Shape: 1 x 5 mm / Type of source: X-ray synchrotron / Wavelength: 0.1 Å / Dist. spec. to detc.: 4.014 mm | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Detector | Name: Pilatus 2M | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Scan | Measurement date: May 7, 2018 / Storage temperature: 20 °C / Cell temperature: 20 °C / Exposure time: 3 sec. / Unit: 1/A /
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Distance distribution function P(R) |
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Result |
|
 Movie
Movie Controller
Controller

 SASDE88
SASDE88