[English] 日本語
 Yorodumi
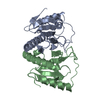
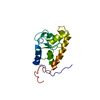
Yorodumi- SASDCJ6: MmoQ Response regulator (fragment 20-298) from Methylococcus caps... -
+ Open data
Open data
- Basic information
Basic information
| Entry | Database: SASBDB / ID: SASDCJ6 |
|---|---|
 Sample Sample | MmoQ Response regulator (fragment 20-298) from Methylococcus capsulatus str. Bath, Northeast Structural Genomics Consortium Target McR175G
|
| Function / homology |  Function and homology information Function and homology informationnegative regulation of bacterial-type flagellum-dependent cell motility / diguanylate cyclase / diguanylate cyclase activity / cell adhesion involved in single-species biofilm formation / phosphorelay signal transduction system / plasma membrane Similarity search - Function |
| Biological species |  Methylococcus capsulatus (bacteria) Methylococcus capsulatus (bacteria) |
 Citation Citation |  Journal: Biopolymers / Year: 2011 Journal: Biopolymers / Year: 2011Title: Small angle X-ray scattering as a complementary tool for high-throughput structural studies. Authors: Thomas D Grant / Joseph R Luft / Jennifer R Wolfley / Hiro Tsuruta / Anne Martel / Gaetano T Montelione / Edward H Snell /  Abstract: Structural crystallography and nuclear magnetic resonance (NMR) spectroscopy are the predominant techniques for understanding the biological world on a molecular level. Crystallography is constrained ...Structural crystallography and nuclear magnetic resonance (NMR) spectroscopy are the predominant techniques for understanding the biological world on a molecular level. Crystallography is constrained by the ability to form a crystal that diffracts well and NMR is constrained to smaller proteins. Although powerful techniques, they leave many soluble, purified structurally uncharacterized protein samples. Small angle X-ray scattering (SAXS) is a solution technique that provides data on the size and multiple conformations of a sample, and can be used to reconstruct a low-resolution molecular envelope of a macromolecule. In this study, SAXS has been used in a high-throughput manner on a subset of 28 proteins, where structural information is available from crystallographic and/or NMR techniques. These crystallographic and NMR structures were used to validate the accuracy of molecular envelopes reconstructed from SAXS data on a statistical level, to compare and highlight complementary structural information that SAXS provides, and to leverage biological information derived by crystallographers and spectroscopists from their structures. All the ab initio molecular envelopes calculated from the SAXS data agree well with the available structural information. SAXS is a powerful albeit low-resolution technique that can provide additional structural information in a high-throughput and complementary manner to improve the functional interpretation of high-resolution structures. |
- Structure visualization
Structure visualization
| Structure viewer | Molecule:  Molmil Molmil Jmol/JSmol Jmol/JSmol |
|---|
- Downloads & links
Downloads & links
-Data source
| SASBDB page |  SASDCJ6 SASDCJ6 |
|---|
-Related structure data
| Related structure data | C: citing same article ( |
|---|---|
| Similar structure data |
- External links
External links
| Related items in Molecule of the Month |
|---|
-Models
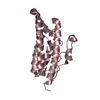
| Model #1437 |  Type: atomic / Radius of dummy atoms: 1.90 A / Chi-square value: 8.497225  Search similar-shape structures of this assembly by Omokage search (details) Search similar-shape structures of this assembly by Omokage search (details) |
|---|---|
| Model #1438 |  Type: dummy / Radius of dummy atoms: 2.00 A / Chi-square value: 2.319529  Search similar-shape structures of this assembly by Omokage search (details) Search similar-shape structures of this assembly by Omokage search (details) |
- Sample
Sample
 Sample Sample | Name: MmoQ Response regulator (fragment 20-298) from Methylococcus capsulatus str. Bath, Northeast Structural Genomics Consortium Target McR175G Specimen concentration: 2.50-5.25 |
|---|---|
| Buffer | Name: 5 mM DTT 100 mM NaCl 10 mM Tris-HCl 0.02 % NaN3 / pH: 7.5 |
| Entity #753 | Type: protein / Description: MmoQ / Formula weight: 32.023 / Num. of mol.: 1 / Source: Methylococcus capsulatus / References: UniProt: Q7WZ31 Sequence: MDRWNMHKPM LCDSLPTASR TAAAILNLAQ REDVTAEALA QLIQTDPALT GRILRFANAP AQGTRRPVAS VIDAIDLVGL PAVRQFALSL SLIDAHREGR CEAFDYAAYW QKSLARAVAL QSITAQASTV APKEAFTLGL LADVGRLALA TAWPEEYSEC LRKADGEALI ...Sequence: MDRWNMHKPM LCDSLPTASR TAAAILNLAQ REDVTAEALA QLIQTDPALT GRILRFANAP AQGTRRPVAS VIDAIDLVGL PAVRQFALSL SLIDAHREGR CEAFDYAAYW QKSLARAVAL QSITAQASTV APKEAFTLGL LADVGRLALA TAWPEEYSEC LRKADGEALI ALERERFATD HDELTRMLLT DWGFPQVFID ALQLSQQDEI RDEGRTGRFA RQLALAQHIA DHRLAEEPRR AALSPLLRAE ARRCGLGDED LARLLADPPA DWLDWTRTIG LEHHHHHH |
-Experimental information
| Beam | Instrument name: Stanford Synchrotron Radiation Lightsource (SSRL) BL4-2 City: Stanford, CA / 国: USA  / Type of source: X-ray synchrotron / Wavelength: 0.13 Å / Dist. spec. to detc.: 1.5 mm / Type of source: X-ray synchrotron / Wavelength: 0.13 Å / Dist. spec. to detc.: 1.5 mm | ||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Detector | Name: Rayonix MX225-HE | ||||||||||||||||||
| Scan | Measurement date: Feb 12, 2010 / Storage temperature: -80 °C / Cell temperature: 20 °C / Exposure time: 1 sec. / Number of frames: 20 / Unit: 1/A /
| ||||||||||||||||||
| Distance distribution function P(R) |
| ||||||||||||||||||
| Result |
|
 Movie
Movie Controller
Controller