[English] 日本語
 Yorodumi
Yorodumi- PDB-8vrd: Rigid body fitted model for free recombinant gamma tubulin ring c... -
+ Open data
Open data
- Basic information
Basic information
| Entry | Database: PDB / ID: 8vrd | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Title | Rigid body fitted model for free recombinant gamma tubulin ring complex. | ||||||
 Components Components |
| ||||||
 Keywords Keywords | CYTOSOLIC PROTEIN / Complex | ||||||
| Function / homology |  Function and homology information Function and homology informationmicrotubule nucleation by interphase microtubule organizing center / gamma-tubulin complex localization / microtubule nucleator activity / positive regulation of norepinephrine uptake / cellular response to cytochalasin B / polar microtubule / interphase microtubule organizing center / bBAF complex / gamma-tubulin complex / gamma-tubulin ring complex ...microtubule nucleation by interphase microtubule organizing center / gamma-tubulin complex localization / microtubule nucleator activity / positive regulation of norepinephrine uptake / cellular response to cytochalasin B / polar microtubule / interphase microtubule organizing center / bBAF complex / gamma-tubulin complex / gamma-tubulin ring complex / npBAF complex / regulation of transepithelial transport / nBAF complex / mitotic spindle microtubule / brahma complex / meiotic spindle organization / morphogenesis of a polarized epithelium / protein localization to adherens junction / postsynaptic actin cytoskeleton / structural constituent of postsynaptic actin cytoskeleton / GBAF complex / Formation of annular gap junctions / Formation of the dystrophin-glycoprotein complex (DGC) / Tat protein binding / Gap junction degradation / regulation of G0 to G1 transition / Folding of actin by CCT/TriC / dense body / Cell-extracellular matrix interactions / microtubule nucleation / regulation of nucleotide-excision repair / Prefoldin mediated transfer of substrate to CCT/TriC / RSC-type complex / apical protein localization / regulation of double-strand break repair / gamma-tubulin binding / adherens junction assembly / RHOF GTPase cycle / Adherens junctions interactions / non-motile cilium / tight junction / Sensory processing of sound by outer hair cells of the cochlea / Interaction between L1 and Ankyrins / SWI/SNF complex / regulation of mitotic metaphase/anaphase transition / Sensory processing of sound by inner hair cells of the cochlea / positive regulation of T cell differentiation / regulation of norepinephrine uptake / apical junction complex / transporter regulator activity / positive regulation of double-strand break repair / nitric-oxide synthase binding / maintenance of blood-brain barrier / pericentriolar material / NuA4 histone acetyltransferase complex / establishment or maintenance of cell polarity / cortical cytoskeleton / positive regulation of stem cell population maintenance / cell leading edge / Regulation of MITF-M-dependent genes involved in pigmentation / Recycling pathway of L1 / microtubule organizing center / regulation of G1/S transition of mitotic cell cycle / brush border / mitotic sister chromatid segregation / regulation of synaptic vesicle endocytosis / kinesin binding / EPH-ephrin mediated repulsion of cells / negative regulation of cell differentiation / single fertilization / mitotic spindle assembly / RHO GTPases Activate WASPs and WAVEs / positive regulation of myoblast differentiation / RHO GTPases activate IQGAPs / positive regulation of double-strand break repair via homologous recombination / regulation of protein localization to plasma membrane / spindle assembly / cytoplasmic microtubule / cytoplasmic microtubule organization / cytoskeleton organization / EPHB-mediated forward signaling / centriole / substantia nigra development / calyx of Held / Loss of Nlp from mitotic centrosomes / Loss of proteins required for interphase microtubule organization from the centrosome / Recruitment of mitotic centrosome proteins and complexes / Recruitment of NuMA to mitotic centrosomes / Anchoring of the basal body to the plasma membrane / axonogenesis / condensed nuclear chromosome / AURKA Activation by TPX2 / mitotic spindle organization / meiotic cell cycle / Translocation of SLC2A4 (GLUT4) to the plasma membrane / Regulation of endogenous retroelements by Piwi-interacting RNAs (piRNAs) / adherens junction / actin filament / positive regulation of cell differentiation / FCGR3A-mediated phagocytosis Similarity search - Function | ||||||
| Biological species |  Homo sapiens (human) Homo sapiens (human) | ||||||
| Method | ELECTRON MICROSCOPY / single particle reconstruction / cryo EM / Resolution: 7 Å | ||||||
 Authors Authors | Aher, A. / Urnavicius, L. / Kapoor, T.M. | ||||||
| Funding support |  United States, 1items United States, 1items
| ||||||
 Citation Citation |  Journal: Nat Struct Mol Biol / Year: 2024 Journal: Nat Struct Mol Biol / Year: 2024Title: Structure of the γ-tubulin ring complex-capped microtubule. Authors: Amol Aher / Linas Urnavicius / Allen Xue / Kasahun Neselu / Tarun M Kapoor /  Abstract: Microtubules are composed of α-tubulin and β-tubulin dimers positioned head-to-tail to form protofilaments that associate laterally in varying numbers. It is not known how cellular microtubules ...Microtubules are composed of α-tubulin and β-tubulin dimers positioned head-to-tail to form protofilaments that associate laterally in varying numbers. It is not known how cellular microtubules assemble with the canonical 13-protofilament architecture, resulting in micrometer-scale α/β-tubulin tracks for intracellular transport that align with, rather than spiral along, the long axis of the filament. We report that the human ~2.3 MDa γ-tubulin ring complex (γ-TuRC), an essential regulator of microtubule formation that contains 14 γ-tubulins, selectively nucleates 13-protofilament microtubules. Cryogenic electron microscopy reconstructions of γ-TuRC-capped microtubule minus ends reveal the extensive intra-domain and inter-domain motions of γ-TuRC subunits that accommodate luminal bridge components and establish lateral and longitudinal interactions between γ-tubulins and α-tubulins. Our structures suggest that γ-TuRC, an inefficient nucleation template owing to its splayed conformation, can transform into a compacted cap at the microtubule minus end and set the lattice architecture of cellular microtubules. | ||||||
| History |
|
- Structure visualization
Structure visualization
| Structure viewer | Molecule:  Molmil Molmil Jmol/JSmol Jmol/JSmol |
|---|
- Downloads & links
Downloads & links
- Download
Download
| PDBx/mmCIF format |  8vrd.cif.gz 8vrd.cif.gz | 2 MB | Display |  PDBx/mmCIF format PDBx/mmCIF format |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| PDB format |  pdb8vrd.ent.gz pdb8vrd.ent.gz | 1.3 MB | Display |  PDB format PDB format |
| PDBx/mmJSON format |  8vrd.json.gz 8vrd.json.gz | Tree view |  PDBx/mmJSON format PDBx/mmJSON format | |
| Others |  Other downloads Other downloads |
-Validation report
| Summary document |  8vrd_validation.pdf.gz 8vrd_validation.pdf.gz | 1.5 MB | Display |  wwPDB validaton report wwPDB validaton report |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Full document |  8vrd_full_validation.pdf.gz 8vrd_full_validation.pdf.gz | 1.5 MB | Display | |
| Data in XML |  8vrd_validation.xml.gz 8vrd_validation.xml.gz | 245.3 KB | Display | |
| Data in CIF |  8vrd_validation.cif.gz 8vrd_validation.cif.gz | 428.4 KB | Display | |
| Arichive directory |  https://data.pdbj.org/pub/pdb/validation_reports/vr/8vrd https://data.pdbj.org/pub/pdb/validation_reports/vr/8vrd ftp://data.pdbj.org/pub/pdb/validation_reports/vr/8vrd ftp://data.pdbj.org/pub/pdb/validation_reports/vr/8vrd | HTTPS FTP |
-Related structure data
| Related structure data |  43481MC  8va2C  8vrjC  8vrkC  8vt7C M: map data used to model this data C: citing same article ( |
|---|---|
| Similar structure data | Similarity search - Function & homology  F&H Search F&H Search |
- Links
Links
- Assembly
Assembly
| Deposited unit | 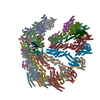
|
|---|---|
| 1 |
|
- Components
Components
-Gamma-tubulin complex component ... , 2 types, 7 molecules OBDFHNJ
| #1: Protein | Mass: 103710.102 Da / Num. of mol.: 6 Source method: isolated from a genetically manipulated source Source: (gene. exp.)  Homo sapiens (human) / Gene: TUBGCP3, GCP3 / Production host: Homo sapiens (human) / Gene: TUBGCP3, GCP3 / Production host:  Trichoplusia ni (cabbage looper) / References: UniProt: Q96CW5 Trichoplusia ni (cabbage looper) / References: UniProt: Q96CW5#8: Protein | | Mass: 118367.406 Da / Num. of mol.: 1 Source method: isolated from a genetically manipulated source Source: (gene. exp.)  Homo sapiens (human) / Gene: TUBGCP5, GCP5, KIAA1899 / Production host: Homo sapiens (human) / Gene: TUBGCP5, GCP5, KIAA1899 / Production host:  Trichoplusia ni (cabbage looper) / References: UniProt: Q96RT8 Trichoplusia ni (cabbage looper) / References: UniProt: Q96RT8 |
|---|
-Protein , 6 types, 27 molecules PLTQRSACEGMabcdefghijklmnIK
| #2: Protein | Mass: 199732.516 Da / Num. of mol.: 3 Source method: isolated from a genetically manipulated source Source: (gene. exp.)  Homo sapiens (human) / Gene: TUBGCP6 / Production host: Homo sapiens (human) / Gene: TUBGCP6 / Production host:  Trichoplusia ni (cabbage looper) / References: UniProt: B2RWN4 Trichoplusia ni (cabbage looper) / References: UniProt: B2RWN4#3: Protein | Mass: 8485.724 Da / Num. of mol.: 2 Source method: isolated from a genetically manipulated source Source: (gene. exp.)  Homo sapiens (human) / Gene: MZT1, C13orf37, MOZART1 / Production host: Homo sapiens (human) / Gene: MZT1, C13orf37, MOZART1 / Production host:  Trichoplusia ni (cabbage looper) / References: UniProt: Q08AG7 Trichoplusia ni (cabbage looper) / References: UniProt: Q08AG7#4: Protein | | Mass: 41782.660 Da / Num. of mol.: 1 Source method: isolated from a genetically manipulated source Source: (gene. exp.)  Homo sapiens (human) / Gene: ACTB / Production host: Homo sapiens (human) / Gene: ACTB / Production host:  Trichoplusia ni (cabbage looper) / References: UniProt: P60709 Trichoplusia ni (cabbage looper) / References: UniProt: P60709#5: Protein | Mass: 105581.500 Da / Num. of mol.: 5 Source method: isolated from a genetically manipulated source Source: (gene. exp.)  Homo sapiens (human) / Gene: TUBGCP2, GCP2 / Production host: Homo sapiens (human) / Gene: TUBGCP2, GCP2 / Production host:  Trichoplusia ni (cabbage looper) / References: UniProt: Q9BSJ2 Trichoplusia ni (cabbage looper) / References: UniProt: Q9BSJ2#6: Protein | Mass: 52022.617 Da / Num. of mol.: 14 Source method: isolated from a genetically manipulated source Source: (gene. exp.)  Homo sapiens (human) / Gene: TUBG1, TUBG / Production host: Homo sapiens (human) / Gene: TUBG1, TUBG / Production host:  Trichoplusia ni (cabbage looper) / References: UniProt: P23258 Trichoplusia ni (cabbage looper) / References: UniProt: P23258#7: Protein | Mass: 76108.898 Da / Num. of mol.: 2 Source method: isolated from a genetically manipulated source Source: (gene. exp.)  Homo sapiens (human) / Gene: TUBGCP4, 76P, GCP4 / Production host: Homo sapiens (human) / Gene: TUBGCP4, 76P, GCP4 / Production host:  Trichoplusia ni (cabbage looper) / References: UniProt: Q9UGJ1 Trichoplusia ni (cabbage looper) / References: UniProt: Q9UGJ1 |
|---|
-Details
| Has protein modification | N |
|---|
-Experimental details
-Experiment
| Experiment | Method: ELECTRON MICROSCOPY |
|---|---|
| EM experiment | Aggregation state: PARTICLE / 3D reconstruction method: single particle reconstruction |
- Sample preparation
Sample preparation
| Component | Name: Gamma tubulin ring complex / Type: COMPLEX / Entity ID: #5, #1, #7-#8, #2-#4, #6 / Source: RECOMBINANT |
|---|---|
| Source (natural) | Organism:  Homo sapiens (human) Homo sapiens (human) |
| Source (recombinant) | Organism:  Trichoplusia ni (cabbage looper) Trichoplusia ni (cabbage looper) |
| Buffer solution | pH: 6.8 |
| Specimen | Embedding applied: NO / Shadowing applied: NO / Staining applied: NO / Vitrification applied: YES |
| Vitrification | Cryogen name: ETHANE / Humidity: 100 % |
- Electron microscopy imaging
Electron microscopy imaging
| Experimental equipment |  Model: Titan Krios / Image courtesy: FEI Company |
|---|---|
| Microscopy | Model: FEI TITAN KRIOS |
| Electron gun | Electron source:  FIELD EMISSION GUN / Accelerating voltage: 300 kV / Illumination mode: FLOOD BEAM FIELD EMISSION GUN / Accelerating voltage: 300 kV / Illumination mode: FLOOD BEAM |
| Electron lens | Mode: BRIGHT FIELD / Nominal defocus max: 3500 nm / Nominal defocus min: 1500 nm |
| Image recording | Electron dose: 60 e/Å2 / Film or detector model: GATAN K3 (6k x 4k) |
- Processing
Processing
| CTF correction | Type: PHASE FLIPPING AND AMPLITUDE CORRECTION |
|---|---|
| 3D reconstruction | Resolution: 7 Å / Resolution method: FSC 0.143 CUT-OFF / Num. of particles: 98558 / Symmetry type: POINT |
| Atomic model building | Protocol: RIGID BODY FIT |
 Movie
Movie Controller
Controller






 PDBj
PDBj


















