+ Open data
Open data
- Basic information
Basic information
| Entry | Database: PDB / ID: 8v4k | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
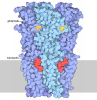
| Title | CCP5 in complex with microtubules class1 | ||||||
 Components Components |
| ||||||
 Keywords Keywords | HYDROLASE/SUBSTRATE / STRUCTURAL PROTEIN / carboxypeptidase deglutamylation branch glutamate removal microtubule / HYDROLASE / HYDROLASE-SUBSTRATE complex / HYDROLASE-SUBSTRATE / STRUCTURAL PROTEIN complex | ||||||
| Function / homology |  Function and homology information Function and homology informationtubulin-glutamate carboxypeptidase / protein deglutamylation / protein side chain deglutamylation / protein branching point deglutamylation / C-terminal protein deglutamylation / Carboxyterminal post-translational modifications of tubulin / Microtubule-dependent trafficking of connexons from Golgi to the plasma membrane / Resolution of Sister Chromatid Cohesion / Hedgehog 'off' state / Cilium Assembly ...tubulin-glutamate carboxypeptidase / protein deglutamylation / protein side chain deglutamylation / protein branching point deglutamylation / C-terminal protein deglutamylation / Carboxyterminal post-translational modifications of tubulin / Microtubule-dependent trafficking of connexons from Golgi to the plasma membrane / Resolution of Sister Chromatid Cohesion / Hedgehog 'off' state / Cilium Assembly / Intraflagellar transport / COPI-dependent Golgi-to-ER retrograde traffic / Mitotic Prometaphase / Carboxyterminal post-translational modifications of tubulin / RHOH GTPase cycle / EML4 and NUDC in mitotic spindle formation / Sealing of the nuclear envelope (NE) by ESCRT-III / Kinesins / PKR-mediated signaling / Separation of Sister Chromatids / The role of GTSE1 in G2/M progression after G2 checkpoint / Aggrephagy / RHO GTPases activate IQGAPs / RHO GTPases Activate Formins / HSP90 chaperone cycle for steroid hormone receptors (SHR) in the presence of ligand / MHC class II antigen presentation / Recruitment of NuMA to mitotic centrosomes / COPI-mediated anterograde transport / Hydrolases; Acting on peptide bonds (peptidases); Metallocarboxypeptidases / metallocarboxypeptidase activity / tubulin binding / structural constituent of cytoskeleton / microtubule cytoskeleton organization / neuron migration / mitotic spindle / mitotic cell cycle / microtubule cytoskeleton / midbody / defense response to virus / Hydrolases; Acting on acid anhydrides; Acting on GTP to facilitate cellular and subcellular movement / microtubule / GTPase activity / GTP binding / proteolysis / zinc ion binding / metal ion binding / nucleus / cytosol / cytoplasm Similarity search - Function | ||||||
| Biological species |  Homo sapiens (human) Homo sapiens (human) | ||||||
| Method | ELECTRON MICROSCOPY / single particle reconstruction / cryo EM / Resolution: 3.1 Å | ||||||
 Authors Authors | Chen, J. / Zehr, E.A. / Gruschus, J.M. / Szyk, A. / Liu, Y. / Tanner, M.E. / Tjandra, N. / Roll-Mecak, A. | ||||||
| Funding support |  United States, 1items United States, 1items
| ||||||
 Citation Citation |  Journal: Nature / Year: 2024 Journal: Nature / Year: 2024Title: Tubulin code eraser CCP5 binds branch glutamates by substrate deformation. Authors: Jiayi Chen / Elena A Zehr / James M Gruschus / Agnieszka Szyk / Yanjie Liu / Martin E Tanner / Nico Tjandra / Antonina Roll-Mecak /   Abstract: Microtubule function is modulated by the tubulin code, diverse posttranslational modifications that are altered dynamically by writer and eraser enzymes. Glutamylation-the addition of branched ...Microtubule function is modulated by the tubulin code, diverse posttranslational modifications that are altered dynamically by writer and eraser enzymes. Glutamylation-the addition of branched (isopeptide-linked) glutamate chains-is the most evolutionarily widespread tubulin modification. It is introduced by tubulin tyrosine ligase-like enzymes and erased by carboxypeptidases of the cytosolic carboxypeptidase (CCP) family. Glutamylation homeostasis, achieved through the balance of writers and erasers, is critical for normal cell function, and mutations in CCPs lead to human disease. Here we report cryo-electron microscopy structures of the glutamylation eraser CCP5 in complex with the microtubule, and X-ray structures in complex with transition-state analogues. Combined with NMR analysis, these analyses show that CCP5 deforms the tubulin main chain into a unique turn that enables lock-and-key recognition of the branch glutamate in a cationic pocket that is unique to CCP family proteins. CCP5 binding of the sequences flanking the branch point primarily through peptide backbone atoms enables processing of diverse tubulin isotypes and non-tubulin substrates. Unexpectedly, CCP5 exhibits inefficient processing of an abundant β-tubulin isotype in the brain. This work provides an atomistic view into glutamate branch recognition and resolution, and sheds light on homeostasis of the tubulin glutamylation syntax. | ||||||
| History |
|
- Structure visualization
Structure visualization
| Structure viewer | Molecule:  Molmil Molmil Jmol/JSmol Jmol/JSmol |
|---|
- Downloads & links
Downloads & links
- Download
Download
| PDBx/mmCIF format |  8v4k.cif.gz 8v4k.cif.gz | 447.6 KB | Display |  PDBx/mmCIF format PDBx/mmCIF format |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| PDB format |  pdb8v4k.ent.gz pdb8v4k.ent.gz | 355.6 KB | Display |  PDB format PDB format |
| PDBx/mmJSON format |  8v4k.json.gz 8v4k.json.gz | Tree view |  PDBx/mmJSON format PDBx/mmJSON format | |
| Others |  Other downloads Other downloads |
-Validation report
| Arichive directory |  https://data.pdbj.org/pub/pdb/validation_reports/v4/8v4k https://data.pdbj.org/pub/pdb/validation_reports/v4/8v4k ftp://data.pdbj.org/pub/pdb/validation_reports/v4/8v4k ftp://data.pdbj.org/pub/pdb/validation_reports/v4/8v4k | HTTPS FTP |
|---|
-Related structure data
| Related structure data |  42971MC  8v3mC  8v3nC  8v3oC  8v3pC  8v3qC  8v3rC  8v3sC  8v4lC  8v4mC C: citing same article ( M: map data used to model this data |
|---|---|
| Similar structure data | Similarity search - Function & homology  F&H Search F&H Search |
- Links
Links
- Assembly
Assembly
| Deposited unit | 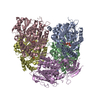
|
|---|---|
| 1 |
|
- Components
Components
-Protein , 3 types, 5 molecules ACBDE
| #1: Protein | Mass: 50204.445 Da / Num. of mol.: 2 / Source method: isolated from a natural source / Source: (natural)  #2: Protein | Mass: 49504.801 Da / Num. of mol.: 2 / Source method: isolated from a natural source Details: Beta tubulin from porcine brain microtubules, heterogeneous in tail sequence Source: (natural)  #3: Protein | | Mass: 68229.547 Da / Num. of mol.: 1 / Fragment: residues 2-605 / Mutation: E516A Source method: isolated from a genetically manipulated source Source: (gene. exp.)  Homo sapiens (human) / Gene: AGBL5 / Plasmid: pFastBac / Details (production host): His_MBP_Asn10_TEV / Production host: Homo sapiens (human) / Gene: AGBL5 / Plasmid: pFastBac / Details (production host): His_MBP_Asn10_TEV / Production host:  |
|---|
-Non-polymers , 5 types, 10 molecules 

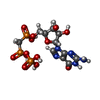

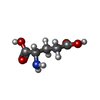




| #4: Chemical | ChemComp-MG / #5: Chemical | #6: Chemical | #7: Chemical | ChemComp-ZN / | #8: Chemical | ChemComp-GLU / | |
|---|
-Details
| Has ligand of interest | Y |
|---|---|
| Has protein modification | Y |
| Sequence details | Brain tubulin contains multiple tubulin isotypes. The tubulin body was modeled using the sequence ...Brain tubulin contains multiple tubulin isotypes. The tubulin body was modeled using the sequence of betaII, the most abundant isotype in brain. The residues in the variable tails are modeled as UNK. |
-Experimental details
-Experiment
| Experiment | Method: ELECTRON MICROSCOPY |
|---|---|
| EM experiment | Aggregation state: PARTICLE / 3D reconstruction method: single particle reconstruction |
- Sample preparation
Sample preparation
| Component | Name: CCP5 in complex with microtubules / Type: COMPLEX / Details: Composite structure of CCP5:microtubule class#1 / Entity ID: #1, #3 / Source: MULTIPLE SOURCES | ||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Molecular weight | Experimental value: NO | ||||||||||||||||||||
| Buffer solution | pH: 7.4 | ||||||||||||||||||||
| Buffer component |
| ||||||||||||||||||||
| Specimen | Conc.: 0.3 mg/ml / Embedding applied: NO / Shadowing applied: NO / Staining applied: NO / Vitrification applied: YES | ||||||||||||||||||||
| Specimen support | Grid material: GOLD / Grid type: Au-flat 1.2/1.3 | ||||||||||||||||||||
| Vitrification | Instrument: LEICA EM GP / Cryogen name: ETHANE / Humidity: 90 % / Chamber temperature: 303 K |
- Electron microscopy imaging
Electron microscopy imaging
| Experimental equipment |  Model: Titan Krios / Image courtesy: FEI Company |
|---|---|
| Microscopy | Model: FEI TITAN KRIOS |
| Electron gun | Electron source:  FIELD EMISSION GUN / Accelerating voltage: 300 kV / Illumination mode: FLOOD BEAM FIELD EMISSION GUN / Accelerating voltage: 300 kV / Illumination mode: FLOOD BEAM |
| Electron lens | Mode: BRIGHT FIELD / Nominal magnification: 135000 X / Nominal defocus max: 2200 nm / Nominal defocus min: 800 nm / Cs: 2.7 mm / C2 aperture diameter: 70 µm / Alignment procedure: COMA FREE |
| Specimen holder | Cryogen: NITROGEN |
| Image recording | Average exposure time: 1.651 sec. / Electron dose: 53.34 e/Å2 / Film or detector model: GATAN K3 (6k x 4k) |
| EM imaging optics | Energyfilter slit width: 20 eV |
- Processing
Processing
| EM software | Name: PHENIX / Category: model refinement | |||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| CTF correction | Type: NONE | |||||||||||||||||||||
| Particle selection | Num. of particles selected: 162521 | |||||||||||||||||||||
| Symmetry | Point symmetry: C1 (asymmetric) | |||||||||||||||||||||
| 3D reconstruction | Resolution: 3.1 Å / Resolution method: FSC 0.143 CUT-OFF / Num. of particles: 239209 / Symmetry type: POINT | |||||||||||||||||||||
| Atomic model building | Protocol: RIGID BODY FIT / Space: REAL / Target criteria: Cross-correlation coefficient | |||||||||||||||||||||
| Atomic model building |
|
 Movie
Movie Controller
Controller










 PDBj
PDBj