+ Open data
Open data
- Basic information
Basic information
| Entry | Database: PDB / ID: 8tzr | ||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Title | Structure of human Wnt3a bound to WLS and CALR | ||||||||||||
 Components Components |
| ||||||||||||
 Keywords Keywords | SIGNALING PROTEIN | ||||||||||||
| Function / homology |  Function and homology information Function and homology informationWnt signaling pathway involved in forebrain neuroblast division / positive regulation of dermatome development / calcium ion transmembrane transport via low voltage-gated calcium channel / positive regulation of collateral sprouting in absence of injury / positive regulation of mesodermal cell fate specification / paraxial mesodermal cell fate commitment / axis elongation involved in somitogenesis / cell proliferation in midbrain / spinal cord association neuron differentiation / Wnt protein secretion ...Wnt signaling pathway involved in forebrain neuroblast division / positive regulation of dermatome development / calcium ion transmembrane transport via low voltage-gated calcium channel / positive regulation of collateral sprouting in absence of injury / positive regulation of mesodermal cell fate specification / paraxial mesodermal cell fate commitment / axis elongation involved in somitogenesis / cell proliferation in midbrain / spinal cord association neuron differentiation / Wnt protein secretion / Formation of the posterior neural plate / Calnexin/calreticulin cycle / COP9 signalosome assembly / Wnt-Frizzled-LRP5/6 complex / cytolytic granule / positive regulation of cell-cell adhesion mediated by cadherin / positive regulation of Wnt protein secretion / Negative regulation of TCF-dependent signaling by WNT ligand antagonists / positive regulation of dendritic cell chemotaxis / synaptic vesicle recycling / WNT ligand biogenesis and trafficking / Signaling by RNF43 mutants / Assembly of Viral Components at the Budding Site / positive regulation of cardiac muscle cell differentiation / ATF6 (ATF6-alpha) activates chaperone genes / negative regulation of trophoblast cell migration / cortical granule / cell proliferation in forebrain / negative regulation of axon extension involved in axon guidance / nuclear receptor-mediated glucocorticoid signaling pathway / cellular response to electrical stimulus / complement component C1q complex binding / regulation of meiotic nuclear division / negative regulation of retinoic acid receptor signaling pathway / secondary palate development / response to glycoside / Specification of the neural plate border / endoplasmic reticulum quality control compartment / cementum mineralization / sequestering of calcium ion / somatic stem cell division / cardiac muscle cell fate commitment / sarcoplasmic reticulum lumen / protein folding in endoplasmic reticulum / co-receptor binding / hormone binding / presynapse assembly / non-canonical Wnt signaling pathway / hindbrain development / positive regulation of skeletal muscle tissue development / negative regulation of intracellular steroid hormone receptor signaling pathway / negative regulation of dopaminergic neuron differentiation / Wnt-protein binding / nuclear export signal receptor activity / midbrain dopaminergic neuron differentiation / mammary gland development / dorsal/ventral neural tube patterning / regulation of postsynapse to nucleus signaling pathway / cardiac muscle cell differentiation / exocrine pancreas development / post-anal tail morphogenesis / molecular sequestering activity / positive regulation of neural precursor cell proliferation / frizzled binding / Class B/2 (Secretin family receptors) / positive regulation of hepatocyte proliferation / myoblast differentiation / Disassembly of the destruction complex and recruitment of AXIN to the membrane / anterior/posterior axis specification / Scavenging by Class A Receptors / inner ear morphogenesis / Scavenging by Class F Receptors / protein maturation by protein folding / midbrain development / cortical actin cytoskeleton organization / nuclear androgen receptor binding / cellular response to lithium ion / regulation of synapse organization / negative regulation of fat cell differentiation / organelle membrane / fat cell differentiation / B cell proliferation / heart looping / Formation of paraxial mesoderm / positive regulation of receptor internalization / skeletal muscle cell differentiation / response to testosterone / hemopoiesis / positive regulation of Wnt signaling pathway / mesoderm formation / protein localization to nucleus / regulation of presynapse assembly / negative regulation of neuron differentiation / cell fate commitment / endomembrane system / positive regulation of cell cycle / smooth endoplasmic reticulum / canonical Wnt signaling pathway / Transcriptional and post-translational regulation of MITF-M expression and activity / regulation of microtubule cytoskeleton organization Similarity search - Function | ||||||||||||
| Biological species |  Homo sapiens (human) Homo sapiens (human) | ||||||||||||
| Method | ELECTRON MICROSCOPY / single particle reconstruction / cryo EM / Resolution: 3.5 Å | ||||||||||||
 Authors Authors | Qi, X. / Hu, Q. / Li, X. | ||||||||||||
| Funding support |  United States, 3items United States, 3items
| ||||||||||||
 Citation Citation |  Journal: Cell / Year: 2023 Journal: Cell / Year: 2023Title: Molecular basis of Wnt biogenesis, secretion, and Wnt7-specific signaling. Authors: Xiaofeng Qi / Qinli Hu / Nadia Elghobashi-Meinhardt / Tao Long / Hongwen Chen / Xiaochun Li /   Abstract: Wnt proteins are enzymatically lipidated by Porcupine (PORCN) in the ER and bind to Wntless (WLS) for intracellular transport and secretion. Mechanisms governing the transfer of these low-solubility ...Wnt proteins are enzymatically lipidated by Porcupine (PORCN) in the ER and bind to Wntless (WLS) for intracellular transport and secretion. Mechanisms governing the transfer of these low-solubility Wnts from the ER to the extracellular space remain unclear. Through structural and functional analyses of Wnt7a, a crucial Wnt involved in central nervous system angiogenesis and blood-brain barrier maintenance, we have elucidated the principles of Wnt biogenesis and Wnt7-specific signaling. The Wnt7a-WLS complex binds to calreticulin (CALR), revealing that CALR functions as a chaperone to facilitate Wnt transfer from PORCN to WLS during Wnt biogenesis. Our structures, functional analyses, and molecular dynamics simulations demonstrate that a phospholipid in the core of Wnt-bound WLS regulates the association and dissociation between Wnt and WLS, suggesting a lipid-mediated Wnt secretion mechanism. Finally, the structure of Wnt7a bound to RECK, a cell-surface Wnt7 co-receptor, reveals how RECK engages the N-terminal domain of Wnt7a to activate Wnt7-specific signaling. | ||||||||||||
| History |
|
- Structure visualization
Structure visualization
| Structure viewer | Molecule:  Molmil Molmil Jmol/JSmol Jmol/JSmol |
|---|
- Downloads & links
Downloads & links
- Download
Download
| PDBx/mmCIF format |  8tzr.cif.gz 8tzr.cif.gz | 214.9 KB | Display |  PDBx/mmCIF format PDBx/mmCIF format |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| PDB format |  pdb8tzr.ent.gz pdb8tzr.ent.gz | 164.1 KB | Display |  PDB format PDB format |
| PDBx/mmJSON format |  8tzr.json.gz 8tzr.json.gz | Tree view |  PDBx/mmJSON format PDBx/mmJSON format | |
| Others |  Other downloads Other downloads |
-Validation report
| Summary document |  8tzr_validation.pdf.gz 8tzr_validation.pdf.gz | 1.4 MB | Display |  wwPDB validaton report wwPDB validaton report |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Full document |  8tzr_full_validation.pdf.gz 8tzr_full_validation.pdf.gz | 1.5 MB | Display | |
| Data in XML |  8tzr_validation.xml.gz 8tzr_validation.xml.gz | 42.6 KB | Display | |
| Data in CIF |  8tzr_validation.cif.gz 8tzr_validation.cif.gz | 61.6 KB | Display | |
| Arichive directory |  https://data.pdbj.org/pub/pdb/validation_reports/tz/8tzr https://data.pdbj.org/pub/pdb/validation_reports/tz/8tzr ftp://data.pdbj.org/pub/pdb/validation_reports/tz/8tzr ftp://data.pdbj.org/pub/pdb/validation_reports/tz/8tzr | HTTPS FTP |
-Related structure data
| Related structure data |  41767MC  8tzoC 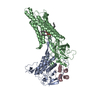 8tzpC  8tzsC M: map data used to model this data C: citing same article ( |
|---|---|
| Similar structure data | Similarity search - Function & homology  F&H Search F&H Search |
- Links
Links
- Assembly
Assembly
| Deposited unit | 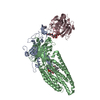
|
|---|---|
| 1 |
|
- Components
Components
-Protein , 3 types, 3 molecules ABC
| #1: Protein | Mass: 39421.832 Da / Num. of mol.: 1 Source method: isolated from a genetically manipulated source Source: (gene. exp.)  Homo sapiens (human) / Gene: WNT3A / Production host: Homo sapiens (human) / Gene: WNT3A / Production host:  Homo sapiens (human) / References: UniProt: P56704 Homo sapiens (human) / References: UniProt: P56704 |
|---|---|
| #2: Protein | Mass: 62317.973 Da / Num. of mol.: 1 Source method: isolated from a genetically manipulated source Source: (gene. exp.)  Homo sapiens (human) / Gene: WLS / Production host: Homo sapiens (human) / Gene: WLS / Production host:  Homo sapiens (human) / References: UniProt: Q5T9L3 Homo sapiens (human) / References: UniProt: Q5T9L3 |
| #3: Protein | Mass: 48198.379 Da / Num. of mol.: 1 / Source method: isolated from a natural source / Source: (natural)  Homo sapiens (human) / References: UniProt: P27797 Homo sapiens (human) / References: UniProt: P27797 |
-Sugars , 1 types, 1 molecules
| #4: Polysaccharide | alpha-D-glucopyranose-(1-3)-alpha-D-mannopyranose-(1-2)-alpha-D-mannopyranose-(1-2)-alpha-D- ...alpha-D-glucopyranose-(1-3)-alpha-D-mannopyranose-(1-2)-alpha-D-mannopyranose-(1-2)-alpha-D-mannopyranose-(1-3)-beta-D-mannopyranose-(1-4)-2-acetamido-2-deoxy-beta-D-glucopyranose-(1-4)-2-acetamido-2-deoxy-beta-D-glucopyranose Type: oligosaccharide / Mass: 1235.105 Da / Num. of mol.: 1 Source method: isolated from a genetically manipulated source |
|---|
-Non-polymers , 2 types, 2 molecules 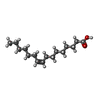


| #5: Chemical | ChemComp-PAM / |
|---|---|
| #6: Chemical | ChemComp-POV / ( |
-Details
| Has ligand of interest | Y |
|---|---|
| Has protein modification | Y |
-Experimental details
-Experiment
| Experiment | Method: ELECTRON MICROSCOPY |
|---|---|
| EM experiment | Aggregation state: PARTICLE / 3D reconstruction method: single particle reconstruction |
- Sample preparation
Sample preparation
| Component | Name: Wnt3a-WLS-CALR Complex / Type: COMPLEX / Entity ID: #1-#3 / Source: MULTIPLE SOURCES |
|---|---|
| Source (natural) | Organism:  Homo sapiens (human) Homo sapiens (human) |
| Source (recombinant) | Organism:  Homo sapiens (human) Homo sapiens (human) |
| Buffer solution | pH: 7.5 |
| Specimen | Embedding applied: NO / Shadowing applied: NO / Staining applied: NO / Vitrification applied: YES |
| Vitrification | Cryogen name: ETHANE |
- Electron microscopy imaging
Electron microscopy imaging
| Experimental equipment |  Model: Titan Krios / Image courtesy: FEI Company |
|---|---|
| Microscopy | Model: FEI TITAN KRIOS |
| Electron gun | Electron source:  FIELD EMISSION GUN / Accelerating voltage: 300 kV / Illumination mode: FLOOD BEAM FIELD EMISSION GUN / Accelerating voltage: 300 kV / Illumination mode: FLOOD BEAM |
| Electron lens | Mode: BRIGHT FIELD / Nominal defocus max: 2000 nm / Nominal defocus min: 1000 nm |
| Image recording | Electron dose: 60 e/Å2 / Film or detector model: GATAN K3 (6k x 4k) |
- Processing
Processing
| CTF correction | Type: NONE | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 3D reconstruction | Resolution: 3.5 Å / Resolution method: FSC 0.143 CUT-OFF / Num. of particles: 113802 / Symmetry type: POINT | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Refine LS restraints |
|
 Movie
Movie Controller
Controller






 PDBj
PDBj









