[English] 日本語
 Yorodumi
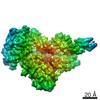
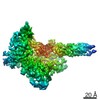
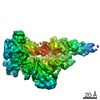
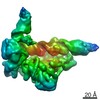
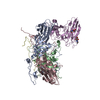
Yorodumi- PDB-6wb2: +3 extended HIV-1 reverse transcriptase initiation complex core (... -
+ Open data
Open data
- Basic information
Basic information
| Entry | Database: PDB / ID: 6wb2 | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
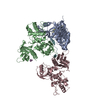
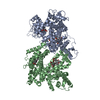
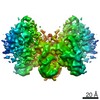
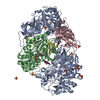
| Title | +3 extended HIV-1 reverse transcriptase initiation complex core (displaced state) | ||||||
 Components Components |
| ||||||
 Keywords Keywords | VIRAL PROTEIN/RNA / reverse transcriptase / RNA / protein-RNA complex / tRNA / polymerase / VIRAL PROTEIN / VIRAL PROTEIN-RNA complex | ||||||
| Function / homology |  Function and homology information Function and homology informationintegrase activity / Integration of viral DNA into host genomic DNA / Autointegration results in viral DNA circles / Minus-strand DNA synthesis / Plus-strand DNA synthesis / Uncoating of the HIV Virion / 2-LTR circle formation / Vpr-mediated nuclear import of PICs / Early Phase of HIV Life Cycle / Integration of provirus ...integrase activity / Integration of viral DNA into host genomic DNA / Autointegration results in viral DNA circles / Minus-strand DNA synthesis / Plus-strand DNA synthesis / Uncoating of the HIV Virion / 2-LTR circle formation / Vpr-mediated nuclear import of PICs / Early Phase of HIV Life Cycle / Integration of provirus / APOBEC3G mediated resistance to HIV-1 infection / Binding and entry of HIV virion / viral life cycle / HIV-1 retropepsin / symbiont-mediated activation of host apoptosis / retroviral ribonuclease H / exoribonuclease H / exoribonuclease H activity / Assembly Of The HIV Virion / Budding and maturation of HIV virion / protein processing / DNA integration / viral genome integration into host DNA / RNA-directed DNA polymerase / establishment of integrated proviral latency / RNA stem-loop binding / viral penetration into host nucleus / host multivesicular body / RNA-directed DNA polymerase activity / RNA-DNA hybrid ribonuclease activity / Transferases; Transferring phosphorus-containing groups; Nucleotidyltransferases / peptidase activity / host cell / viral nucleocapsid / DNA recombination / DNA-directed DNA polymerase / aspartic-type endopeptidase activity / Hydrolases; Acting on ester bonds / DNA-directed DNA polymerase activity / symbiont-mediated suppression of host gene expression / viral translational frameshifting / symbiont entry into host cell / lipid binding / host cell nucleus / host cell plasma membrane / virion membrane / structural molecule activity / proteolysis / DNA binding / zinc ion binding / identical protein binding / membrane Similarity search - Function | ||||||
| Biological species |   Human immunodeficiency virus 1 Human immunodeficiency virus 1 Homo sapiens (human) Homo sapiens (human) | ||||||
| Method | ELECTRON MICROSCOPY / single particle reconstruction / cryo EM / Resolution: 4.5 Å | ||||||
 Authors Authors | Larsen, K.P. / Jackson, L.N. / Kappel, K. / Zhang, J. / Chen, D.H. / Puglisi, E.V. | ||||||
| Funding support |  United States, 1items United States, 1items
| ||||||
 Citation Citation |  Journal: J Mol Biol / Year: 2020 Journal: J Mol Biol / Year: 2020Title: Distinct Conformational States Underlie Pausing during Initiation of HIV-1 Reverse Transcription. Authors: Kevin P Larsen / Junhong Choi / Lynnette N Jackson / Kalli Kappel / Jingji Zhang / Betty Ha / Dong-Hua Chen / Elisabetta Viani Puglisi /  Abstract: A hallmark of the initiation step of HIV-1 reverse transcription, in which viral RNA genome is converted into double-stranded DNA, is that it is slow and non-processive. Biochemical studies have ...A hallmark of the initiation step of HIV-1 reverse transcription, in which viral RNA genome is converted into double-stranded DNA, is that it is slow and non-processive. Biochemical studies have identified specific sites along the viral RNA genomic template in which reverse transcriptase (RT) stalls. These stalling points, which occur after the addition of three and five template dNTPs, may serve as checkpoints to regulate the precise timing of HIV-1 reverse transcription following viral entry. Structural studies of reverse transcriptase initiation complexes (RTICs) have revealed unique conformations that may explain the slow rate of incorporation; however, questions remain about the temporal evolution of the complex and features that contribute to strong pausing during initiation. Here we present cryo-electron microscopy and single-molecule characterization of an RTIC after three rounds of dNTP incorporation (+3), the first major pausing point during reverse transcription initiation. Cryo-electron microscopy structures of a +3 extended RTIC reveal conformational heterogeneity within the RTIC core. Three distinct conformations were identified, two of which adopt unique, likely off-pathway, intermediates in the canonical polymerization cycle. Single-molecule Förster resonance energy transfer experiments confirm that the +3 RTIC is more structurally dynamic than earlier-stage RTICs. These alternative conformations were selectively disrupted through structure-guided point mutations to shift single-molecule Förster resonance energy transfer populations back toward the on-pathway conformation. Our results support the hypothesis that conformational heterogeneity within the HIV-1 RTIC during pausing serves as an additional means of regulating HIV-1 replication. | ||||||
| History |
|
- Structure visualization
Structure visualization
| Movie |
 Movie viewer Movie viewer |
|---|---|
| Structure viewer | Molecule:  Molmil Molmil Jmol/JSmol Jmol/JSmol |
- Downloads & links
Downloads & links
- Download
Download
| PDBx/mmCIF format |  6wb2.cif.gz 6wb2.cif.gz | 213.4 KB | Display |  PDBx/mmCIF format PDBx/mmCIF format |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| PDB format |  pdb6wb2.ent.gz pdb6wb2.ent.gz | 155.8 KB | Display |  PDB format PDB format |
| PDBx/mmJSON format |  6wb2.json.gz 6wb2.json.gz | Tree view |  PDBx/mmJSON format PDBx/mmJSON format | |
| Others |  Other downloads Other downloads |
-Validation report
| Arichive directory |  https://data.pdbj.org/pub/pdb/validation_reports/wb/6wb2 https://data.pdbj.org/pub/pdb/validation_reports/wb/6wb2 ftp://data.pdbj.org/pub/pdb/validation_reports/wb/6wb2 ftp://data.pdbj.org/pub/pdb/validation_reports/wb/6wb2 | HTTPS FTP |
|---|
-Related structure data
| Related structure data |  21585MC 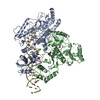 6wazC  6wb0C  6wb1C M: map data used to model this data C: citing same article ( |
|---|---|
| Similar structure data |
- Links
Links
- Assembly
Assembly
| Deposited unit | 
|
|---|---|
| 1 |
|
- Components
Components
| #1: RNA chain | Mass: 32623.477 Da / Num. of mol.: 1 / Source method: obtained synthetically / Source: (synth.)   Human immunodeficiency virus 1 / References: GenBank: 60651827 Human immunodeficiency virus 1 / References: GenBank: 60651827 |
|---|---|
| #2: DNA/RNA hybrid | Mass: 25354.061 Da / Num. of mol.: 1 / Source method: obtained synthetically / Source: (synth.)  Homo sapiens (human) Homo sapiens (human) |
| #3: Protein | Mass: 65558.320 Da / Num. of mol.: 1 / Mutation: Q258C, E478Q Source method: isolated from a genetically manipulated source Source: (gene. exp.)   Human immunodeficiency virus 1 / Production host: Human immunodeficiency virus 1 / Production host:  References: UniProt: P03366, UniProt: P04585*PLUS, RNA-directed DNA polymerase, DNA-directed DNA polymerase, retroviral ribonuclease H |
| #4: Protein | Mass: 51585.293 Da / Num. of mol.: 1 / Mutation: C879S Source method: isolated from a genetically manipulated source Source: (gene. exp.)   Human immunodeficiency virus 1 / Production host: Human immunodeficiency virus 1 / Production host:  |
| Has protein modification | N |
-Experimental details
-Experiment
| Experiment | Method: ELECTRON MICROSCOPY |
|---|---|
| EM experiment | Aggregation state: PARTICLE / 3D reconstruction method: single particle reconstruction |
- Sample preparation
Sample preparation
| Component |
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Molecular weight |
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Source (natural) |
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Source (recombinant) |
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Buffer solution | pH: 8 Details: Full complex was prepared 5-8 hours before freezing. Beta-OG was added just prior to freezing. | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Buffer component |
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Specimen | Conc.: 5 mg/ml / Embedding applied: NO / Shadowing applied: NO / Staining applied: NO / Vitrification applied: YES / Details: Sample was monodisperse | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Vitrification | Instrument: LEICA EM GP / Cryogen name: ETHANE / Humidity: 95 % / Chamber temperature: 292 K / Details: 3 microliters applied, 2s pre-blot, 2.5s blot. |
- Electron microscopy imaging
Electron microscopy imaging
| Experimental equipment |  Model: Titan Krios / Image courtesy: FEI Company |
|---|---|
| Microscopy | Model: FEI TITAN KRIOS |
| Electron gun | Electron source:  FIELD EMISSION GUN / Accelerating voltage: 300 kV / Illumination mode: FLOOD BEAM FIELD EMISSION GUN / Accelerating voltage: 300 kV / Illumination mode: FLOOD BEAM |
| Electron lens | Mode: BRIGHT FIELD |
| Image recording | Electron dose: 77.6 e/Å2 / Detector mode: COUNTING / Film or detector model: GATAN K2 SUMMIT (4k x 4k) |
- Processing
Processing
| EM software |
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| CTF correction | Type: PHASE FLIPPING AND AMPLITUDE CORRECTION | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 3D reconstruction | Resolution: 4.5 Å / Resolution method: FSC 0.143 CUT-OFF / Num. of particles: 291904 / Symmetry type: POINT | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Atomic model building | Space: REAL |
 Movie
Movie Controller
Controller










 PDBj
PDBj