+ Open data
Open data
- Basic information
Basic information
| Entry | Database: PDB / ID: 6vzp | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
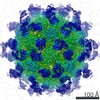
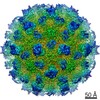
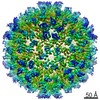
| Title | HBV wild type capsid | ||||||
 Components Components | Capsid protein | ||||||
 Keywords Keywords | VIRUS / HBV / Core protein | ||||||
| Function / homology |  Function and homology information Function and homology informationmicrotubule-dependent intracellular transport of viral material towards nucleus / T=4 icosahedral viral capsid / viral penetration into host nucleus / host cell / host cell cytoplasm / symbiont entry into host cell / structural molecule activity / DNA binding / RNA binding / identical protein binding Similarity search - Function | ||||||
| Biological species |  Hepatitis B virus genotype D subtype adw Hepatitis B virus genotype D subtype adw | ||||||
| Method | ELECTRON MICROSCOPY / single particle reconstruction / cryo EM / Resolution: 3.6 Å | ||||||
 Authors Authors | Zhao, Z. / Wang, J. / Zlotnick, A. | ||||||
| Funding support |  United States, 1items United States, 1items
| ||||||
 Citation Citation |  Journal: ACS Chem Biol / Year: 2020 Journal: ACS Chem Biol / Year: 2020Title: The Integrity of the Intradimer Interface of the Hepatitis B Virus Capsid Protein Dimer Regulates Capsid Self-Assembly. Authors: Zhongchao Zhao / Joseph Che-Yen Wang / Carolina Pérez Segura / Jodi A Hadden-Perilla / Adam Zlotnick /  Abstract: During the hepatitis B virus lifecycle, 120 copies of homodimeric capsid protein assemble around a copy of reverse transcriptase and viral RNA and go on to produce an infectious virion. Assembly ...During the hepatitis B virus lifecycle, 120 copies of homodimeric capsid protein assemble around a copy of reverse transcriptase and viral RNA and go on to produce an infectious virion. Assembly needs to be tightly regulated by protein conformational change to ensure symmetry, fidelity, and reproducibility. Here, we show that structures at the intradimer interface regulate conformational changes at the distal interdimer interface and so regulate assembly. A pair of interacting charged residues, D78 from each monomer, conspicuously located at the top of a four-helix bundle that forms the intradimer interface, were mutated to serine to disrupt communication between the two monomers. The mutation slowed assembly and destabilized the dimer to thermal and chemical denaturation. Mutant dimers showed evidence of transient partial unfolding based on the appearance of new proteolytically sensitive sites. Though the mutant dimer was less stable, the resulting capsids were as stable as the wildtype, based on assembly and thermal denaturation studies. Cryo-EM image reconstructions of capsid indicated that the subunits adopted an "open" state more usually associated with a free dimer and that the spike tips were either disordered or highly flexible. Molecular dynamics simulations provide mechanistic explanations for these results, suggesting that D78 stabilizes helix 4a, which forms part of the intradimer interface, by capping its N-terminus and hydrogen-bonding to nearby residues, whereas the D78S mutation disrupts these interactions, leading to partial unwinding of helix 4a. This in turn weakens the connection from helix 4 and the intradimer interface to helix 5, which forms the interdimer interface. | ||||||
| History |
|
- Structure visualization
Structure visualization
| Movie |
 Movie viewer Movie viewer |
|---|---|
| Structure viewer | Molecule:  Molmil Molmil Jmol/JSmol Jmol/JSmol |
- Downloads & links
Downloads & links
- Download
Download
| PDBx/mmCIF format |  6vzp.cif.gz 6vzp.cif.gz | 110.1 KB | Display |  PDBx/mmCIF format PDBx/mmCIF format |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| PDB format |  pdb6vzp.ent.gz pdb6vzp.ent.gz | 87.7 KB | Display |  PDB format PDB format |
| PDBx/mmJSON format |  6vzp.json.gz 6vzp.json.gz | Tree view |  PDBx/mmJSON format PDBx/mmJSON format | |
| Others |  Other downloads Other downloads |
-Validation report
| Summary document |  6vzp_validation.pdf.gz 6vzp_validation.pdf.gz | 859.6 KB | Display |  wwPDB validaton report wwPDB validaton report |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Full document |  6vzp_full_validation.pdf.gz 6vzp_full_validation.pdf.gz | 862.1 KB | Display | |
| Data in XML |  6vzp_validation.xml.gz 6vzp_validation.xml.gz | 22.9 KB | Display | |
| Data in CIF |  6vzp_validation.cif.gz 6vzp_validation.cif.gz | 32.7 KB | Display | |
| Arichive directory |  https://data.pdbj.org/pub/pdb/validation_reports/vz/6vzp https://data.pdbj.org/pub/pdb/validation_reports/vz/6vzp ftp://data.pdbj.org/pub/pdb/validation_reports/vz/6vzp ftp://data.pdbj.org/pub/pdb/validation_reports/vz/6vzp | HTTPS FTP |
-Related structure data
| Related structure data |  21495MC  6w0kC M: map data used to model this data C: citing same article ( |
|---|---|
| Similar structure data |
- Links
Links
- Assembly
Assembly
| Deposited unit | 
|
|---|---|
| 1 | x 60
|
| 2 |
|
| 3 | x 5
|
| 4 | x 6
|
| 5 | 
|
| Symmetry | Point symmetry: (Schoenflies symbol: I (icosahedral)) |
- Components
Components
| #1: Protein | Mass: 16784.158 Da / Num. of mol.: 4 Source method: isolated from a genetically manipulated source Source: (gene. exp.)  Hepatitis B virus genotype D subtype adw (isolate United Kingdom/adyw/1979) Hepatitis B virus genotype D subtype adw (isolate United Kingdom/adyw/1979)Strain: isolate United Kingdom/adyw/1979 / Production host:  Has protein modification | Y | |
|---|
-Experimental details
-Experiment
| Experiment | Method: ELECTRON MICROSCOPY |
|---|---|
| EM experiment | Aggregation state: PARTICLE / 3D reconstruction method: single particle reconstruction |
- Sample preparation
Sample preparation
| Component | Name: HBV wild type capsid / Type: COMPLEX / Entity ID: all / Source: RECOMBINANT |
|---|---|
| Source (natural) | Organism:  Hepatitis B virus genotype D subtype adw (isolate United Kingdom/adyw/1979) Hepatitis B virus genotype D subtype adw (isolate United Kingdom/adyw/1979)Strain: isolate United Kingdom/adyw/1979 |
| Source (recombinant) | Organism:  |
| Buffer solution | pH: 7.5 |
| Specimen | Conc.: 15 mg/ml / Embedding applied: NO / Shadowing applied: NO / Staining applied: NO / Vitrification applied: YES |
| Specimen support | Details: unspecified |
| Vitrification | Cryogen name: ETHANE |
- Electron microscopy imaging
Electron microscopy imaging
| Experimental equipment |  Model: Talos Arctica / Image courtesy: FEI Company |
|---|---|
| Microscopy | Model: FEI TALOS ARCTICA |
| Electron gun | Electron source:  FIELD EMISSION GUN / Accelerating voltage: 200 kV / Illumination mode: FLOOD BEAM FIELD EMISSION GUN / Accelerating voltage: 200 kV / Illumination mode: FLOOD BEAM |
| Electron lens | Mode: BRIGHT FIELD |
| Image recording | Electron dose: 30 e/Å2 / Film or detector model: FEI FALCON III (4k x 4k) |
- Processing
Processing
| CTF correction | Type: PHASE FLIPPING AND AMPLITUDE CORRECTION |
|---|---|
| 3D reconstruction | Resolution: 3.6 Å / Resolution method: FSC 0.143 CUT-OFF / Num. of particles: 139740 / Symmetry type: POINT |
| Atomic model building | Protocol: RIGID BODY FIT |
 Movie
Movie Controller
Controller









 PDBj
PDBj

