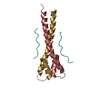
登録情報 データベース : PDB / ID : 6o4jタイトル Amyloid Beta KLVFFAENVGS 16-26 D23N Iowa mutation Amyloid-beta precursor protein キーワード / 機能・相同性 分子機能 ドメイン・相同性 構成要素
/ / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / 生物種 Homo sapiens (ヒト)手法 / / / 解像度 : 1.402 Å データ登録者 Griner, S.L. / Sawaya, M.R. / Rodriguez, J.A. / Cascio, D. / Gonen, T. 資金援助 組織 認可番号 国 National Institutes of Health/National Human Genome Research Institute (NIH/NHGRI) R01 AG029430
ジャーナル : Elife / 年 : 2019タイトル : Structure-based inhibitors of amyloid beta core suggest a common interface with tau.著者: Sarah L Griner / Paul Seidler / Jeannette Bowler / Kevin A Murray / Tianxiao Peter Yang / Shruti Sahay / Michael R Sawaya / Duilio Cascio / Jose A Rodriguez / Stephan Philipp / Justyna Sosna ... 著者 : Sarah L Griner / Paul Seidler / Jeannette Bowler / Kevin A Murray / Tianxiao Peter Yang / Shruti Sahay / Michael R Sawaya / Duilio Cascio / Jose A Rodriguez / Stephan Philipp / Justyna Sosna / Charles G Glabe / Tamir Gonen / David S Eisenberg / 要旨 : Alzheimer's disease (AD) pathology is characterized by plaques of amyloid beta (Aβ) and neurofibrillary tangles of tau. Aβ aggregation is thought to occur at early stages of the disease, and ... Alzheimer's disease (AD) pathology is characterized by plaques of amyloid beta (Aβ) and neurofibrillary tangles of tau. Aβ aggregation is thought to occur at early stages of the disease, and ultimately gives way to the formation of tau tangles which track with cognitive decline in humans. Here, we report the crystal structure of an Aβ core segment determined by MicroED and in it, note characteristics of both fibrillar and oligomeric structure. Using this structure, we designed peptide-based inhibitors that reduce Aβ aggregation and toxicity of already-aggregated species. Unexpectedly, we also found that these inhibitors reduce the efficiency of Aβ-mediated tau aggregation, and moreover reduce aggregation and self-seeding of tau fibrils. The ability of these inhibitors to interfere with both Aβ and tau seeds suggests these fibrils share a common epitope, and supports the hypothesis that cross-seeding is one mechanism by which amyloid is linked to tau aggregation and could promote cognitive decline. 履歴 登録 2019年2月28日 登録サイト / 処理サイト 改定 1.0 2019年10月30日 Provider / タイプ 改定 1.1 2019年12月18日 Group / カテゴリ / Item 改定 1.2 2023年10月11日 Group / Database references / Refinement descriptionカテゴリ chem_comp_atom / chem_comp_bond ... chem_comp_atom / chem_comp_bond / database_2 / em_3d_fitting_list / pdbx_initial_refinement_model / struct_ncs_dom_lim Item _database_2.pdbx_DOI / _database_2.pdbx_database_accession ... _database_2.pdbx_DOI / _database_2.pdbx_database_accession / _em_3d_fitting_list.accession_code / _em_3d_fitting_list.initial_refinement_model_id / _em_3d_fitting_list.source_name / _em_3d_fitting_list.type / _struct_ncs_dom_lim.beg_auth_comp_id / _struct_ncs_dom_lim.beg_label_asym_id / _struct_ncs_dom_lim.beg_label_comp_id / _struct_ncs_dom_lim.beg_label_seq_id / _struct_ncs_dom_lim.end_auth_comp_id / _struct_ncs_dom_lim.end_label_asym_id / _struct_ncs_dom_lim.end_label_comp_id / _struct_ncs_dom_lim.end_label_seq_id 改定 1.3 2024年10月23日 Group / Structure summaryカテゴリ / pdbx_entry_details / pdbx_modification_featureItem
すべて表示 表示を減らす
 データを開く
データを開く 基本情報
基本情報 要素
要素 キーワード
キーワード 機能・相同性情報
機能・相同性情報 Homo sapiens (ヒト)
Homo sapiens (ヒト) 分子置換 / クライオ電子顕微鏡法 / 解像度: 1.402 Å
分子置換 / クライオ電子顕微鏡法 / 解像度: 1.402 Å  データ登録者
データ登録者 米国, 1件
米国, 1件  引用
引用 ジャーナル: Elife / 年: 2019
ジャーナル: Elife / 年: 2019

 構造の表示
構造の表示 ムービービューア
ムービービューア Molmil
Molmil Jmol/JSmol
Jmol/JSmol ダウンロードとリンク
ダウンロードとリンク ダウンロード
ダウンロード 6o4j.cif.gz
6o4j.cif.gz PDBx/mmCIF形式
PDBx/mmCIF形式 pdb6o4j.ent.gz
pdb6o4j.ent.gz PDB形式
PDB形式 6o4j.json.gz
6o4j.json.gz PDBx/mmJSON形式
PDBx/mmJSON形式 その他のダウンロード
その他のダウンロード 6o4j_validation.pdf.gz
6o4j_validation.pdf.gz wwPDB検証レポート
wwPDB検証レポート 6o4j_full_validation.pdf.gz
6o4j_full_validation.pdf.gz 6o4j_validation.xml.gz
6o4j_validation.xml.gz 6o4j_validation.cif.gz
6o4j_validation.cif.gz https://data.pdbj.org/pub/pdb/validation_reports/o4/6o4j
https://data.pdbj.org/pub/pdb/validation_reports/o4/6o4j ftp://data.pdbj.org/pub/pdb/validation_reports/o4/6o4j
ftp://data.pdbj.org/pub/pdb/validation_reports/o4/6o4j リンク
リンク 集合体
集合体
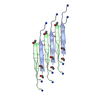
 要素
要素 Homo sapiens (ヒト) / 参照: UniProt: P05067
Homo sapiens (ヒト) / 参照: UniProt: P05067 試料調製
試料調製 Homo sapiens (ヒト)
Homo sapiens (ヒト)
 FIELD EMISSION GUN / 加速電圧: 200 kV / 照射モード: FLOOD BEAM
FIELD EMISSION GUN / 加速電圧: 200 kV / 照射モード: FLOOD BEAM 解析
解析 分子置換
分子置換 ムービー
ムービー コントローラー
コントローラー







 PDBj
PDBj