[English] 日本語
 Yorodumi
Yorodumi- PDB-6avq: The Therapeutic Antibody LM609 Selectively Inhibits Ligand Bindin... -
+ Open data
Open data
- Basic information
Basic information
| Entry | Database: PDB / ID: 6avq | |||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Title | The Therapeutic Antibody LM609 Selectively Inhibits Ligand Binding to Human alpha-V beta-3 Integrin via Steric Hindrance | |||||||||
 Components Components |
| |||||||||
 Keywords Keywords | SIGNALING PROTEIN / alpha-V beta-3 integrin / LM609 / vitaxin / abegrin | |||||||||
| Function / homology |  Function and homology information Function and homology informationintegrin alphav-beta8 complex / integrin alphav-beta6 complex / transforming growth factor beta production / negative regulation of entry of bacterium into host cell / integrin alphav-beta5 complex / opsonin binding / integrin alphav-beta1 complex / Cross-presentation of particulate exogenous antigens (phagosomes) / extracellular matrix protein binding / regulation of serotonin uptake ...integrin alphav-beta8 complex / integrin alphav-beta6 complex / transforming growth factor beta production / negative regulation of entry of bacterium into host cell / integrin alphav-beta5 complex / opsonin binding / integrin alphav-beta1 complex / Cross-presentation of particulate exogenous antigens (phagosomes) / extracellular matrix protein binding / regulation of serotonin uptake / positive regulation of adenylate cyclase-inhibiting opioid receptor signaling pathway / tube development / alpha9-beta1 integrin-ADAM8 complex / regulation of trophoblast cell migration / integrin alphaIIb-beta3 complex / regulation of postsynaptic neurotransmitter receptor diffusion trapping / alphav-beta3 integrin-vitronectin complex / maintenance of postsynaptic specialization structure / regulation of extracellular matrix organization / positive regulation of glomerular mesangial cell proliferation / Laminin interactions / platelet alpha granule membrane / integrin alphav-beta3 complex / negative regulation of lipoprotein metabolic process / entry into host cell by a symbiont-containing vacuole / alphav-beta3 integrin-PKCalpha complex / fibrinogen binding / alphav-beta3 integrin-HMGB1 complex / vascular endothelial growth factor receptor 2 binding / negative regulation of lipid transport / regulation of phagocytosis / positive regulation of vascular endothelial growth factor signaling pathway / Elastic fibre formation / mesodermal cell differentiation / cell-substrate junction assembly / alphav-beta3 integrin-IGF-1-IGF1R complex / positive regulation of bone resorption / transforming growth factor beta binding / platelet-derived growth factor receptor binding / glycinergic synapse / positive regulation of small GTPase mediated signal transduction / regulation of release of sequestered calcium ion into cytosol / filopodium membrane / extracellular matrix binding / wound healing, spreading of epidermal cells / positive regulation of vascular endothelial growth factor receptor signaling pathway / apolipoprotein A-I-mediated signaling pathway / positive regulation of cell adhesion mediated by integrin / negative regulation of low-density lipoprotein particle clearance / regulation of bone resorption / angiogenesis involved in wound healing / apoptotic cell clearance / positive regulation of fibroblast migration / integrin complex / positive regulation of smooth muscle cell migration / heterotypic cell-cell adhesion / smooth muscle cell migration / Molecules associated with elastic fibres / cell adhesion mediated by integrin / negative chemotaxis / positive regulation of cell-matrix adhesion / Mechanical load activates signaling by PIEZO1 and integrins in osteocytes / Syndecan interactions / p130Cas linkage to MAPK signaling for integrins / cellular response to insulin-like growth factor stimulus / protein disulfide isomerase activity / regulation of postsynaptic neurotransmitter receptor internalization / positive regulation of osteoblast proliferation / microvillus membrane / cell-substrate adhesion / platelet-derived growth factor receptor signaling pathway / endodermal cell differentiation / PECAM1 interactions / GRB2:SOS provides linkage to MAPK signaling for Integrins / TGF-beta receptor signaling activates SMADs / fibronectin binding / lamellipodium membrane / positive regulation of intracellular signal transduction / blood coagulation, fibrin clot formation / negative regulation of macrophage derived foam cell differentiation / negative regulation of lipid storage / ECM proteoglycans / Integrin cell surface interactions / negative regulation of endothelial cell apoptotic process / positive regulation of T cell migration / vasculogenesis / specific granule membrane / voltage-gated calcium channel activity / coreceptor activity / phagocytic vesicle / cellular response to platelet-derived growth factor stimulus / ERK1 and ERK2 cascade / positive regulation of endothelial cell proliferation / Integrin signaling / extrinsic apoptotic signaling pathway in absence of ligand / positive regulation of substrate adhesion-dependent cell spreading / cell adhesion molecule binding / positive regulation of endothelial cell migration / positive regulation of smooth muscle cell proliferation / substrate adhesion-dependent cell spreading Similarity search - Function | |||||||||
| Biological species |  Homo sapiens (human) Homo sapiens (human) | |||||||||
| Method | ELECTRON MICROSCOPY / single particle reconstruction / negative staining / Resolution: 35 Å | |||||||||
 Authors Authors | Borst, A.J. / James, Z.N. / Zagotta, W.N. / Ginsberg, M. / Rey, F.A. / DiMaio, F. / Backovic, M. / Veesler, D. | |||||||||
| Funding support |  United States, 2items United States, 2items
| |||||||||
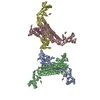
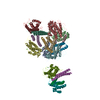
 Citation Citation |  Journal: Structure / Year: 2017 Journal: Structure / Year: 2017Title: The Therapeutic Antibody LM609 Selectively Inhibits Ligand Binding to Human αβ Integrin via Steric Hindrance. Authors: Andrew J Borst / Zachary M James / William N Zagotta / Mark Ginsberg / Felix A Rey / Frank DiMaio / Marija Backovic / David Veesler /   Abstract: The LM609 antibody specifically recognizes αβ integrin and inhibits angiogenesis, bone resorption, and viral infections in an arginine-glycine-aspartate-independent manner. LM609 entered phase II ...The LM609 antibody specifically recognizes αβ integrin and inhibits angiogenesis, bone resorption, and viral infections in an arginine-glycine-aspartate-independent manner. LM609 entered phase II clinical trials for the treatment of several cancers and was also used for αβ-targeted radioimmunotherapy. To elucidate the mechanisms of recognition and inhibition of αβ integrin, we solved the structure of the LM609 antigen-binding fragment by X-ray crystallography and determined its binding affinity for αβ. Using single-particle electron microscopy, we show that LM609 binds at the interface between the β-propeller domain of the α chain and the βI domain of the β chain, near the RGD-binding site, of all observed integrin conformational states. Integrating these data with fluorescence size-exclusion chromatography, we demonstrate that LM609 sterically hinders access of large ligands to the RGD-binding pocket, without obstructing it. This work provides a structural framework to expedite future efforts utilizing LM609 as a diagnostic or therapeutic tool. | |||||||||
| History |
|
- Structure visualization
Structure visualization
| Movie |
 Movie viewer Movie viewer |
|---|---|
| Structure viewer | Molecule:  Molmil Molmil Jmol/JSmol Jmol/JSmol |
- Downloads & links
Downloads & links
- Download
Download
| PDBx/mmCIF format |  6avq.cif.gz 6avq.cif.gz | 308.5 KB | Display |  PDBx/mmCIF format PDBx/mmCIF format |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| PDB format |  pdb6avq.ent.gz pdb6avq.ent.gz | 210.6 KB | Display |  PDB format PDB format |
| PDBx/mmJSON format |  6avq.json.gz 6avq.json.gz | Tree view |  PDBx/mmJSON format PDBx/mmJSON format | |
| Others |  Other downloads Other downloads |
-Validation report
| Arichive directory |  https://data.pdbj.org/pub/pdb/validation_reports/av/6avq https://data.pdbj.org/pub/pdb/validation_reports/av/6avq ftp://data.pdbj.org/pub/pdb/validation_reports/av/6avq ftp://data.pdbj.org/pub/pdb/validation_reports/av/6avq | HTTPS FTP |
|---|
-Related structure data
| Related structure data | 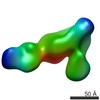 7011MC 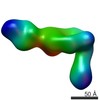 7012C  7013C  5opyC  6avrC  6avuC C: citing same article ( M: map data used to model this data |
|---|---|
| Similar structure data |
- Links
Links
- Assembly
Assembly
| Deposited unit | 
|
|---|---|
| 1 |
|
- Components
Components
| #1: Protein | Mass: 105894.188 Da / Num. of mol.: 1 / Fragment: UNP residues 31-987 Source method: isolated from a genetically manipulated source Source: (gene. exp.)  Homo sapiens (human) / Gene: ITGAV, MSK8, VNRA, VTNR / Production host: Homo sapiens (human) / Gene: ITGAV, MSK8, VNRA, VTNR / Production host:  |
|---|---|
| #2: Protein | Mass: 76523.125 Da / Num. of mol.: 1 / Fragment: UNP residues 27-718 Source method: isolated from a genetically manipulated source Source: (gene. exp.)  Homo sapiens (human) / Gene: ITGB3, GP3A / Production host: Homo sapiens (human) / Gene: ITGB3, GP3A / Production host:  |
| #3: Antibody | Mass: 27223.100 Da / Num. of mol.: 1 Source method: isolated from a genetically manipulated source Source: (gene. exp.)   |
| #4: Antibody | Mass: 23628.977 Da / Num. of mol.: 1 Source method: isolated from a genetically manipulated source Source: (gene. exp.)   |
-Experimental details
-Experiment
| Experiment | Method: ELECTRON MICROSCOPY |
|---|---|
| EM experiment | Aggregation state: PARTICLE / 3D reconstruction method: single particle reconstruction |
- Sample preparation
Sample preparation
| Component | Name: Quaternary complex of human alpha-V beta-3 integrin with the Fab LM609 Type: COMPLEX / Entity ID: all / Source: RECOMBINANT |
|---|---|
| Molecular weight | Value: 0.23 MDa / Experimental value: NO |
| Source (natural) | Organism:  Homo sapiens (human) Homo sapiens (human) |
| Source (recombinant) | Organism:  |
| Buffer solution | pH: 8 |
| Specimen | Embedding applied: NO / Shadowing applied: NO / Staining applied: YES / Vitrification applied: NO |
| EM staining | Type: NEGATIVE / Material: Uranyl formate |
| Specimen support | Grid material: COPPER / Grid mesh size: 400 divisions/in. / Grid type: C-flat 2/0.5 |
- Electron microscopy imaging
Electron microscopy imaging
| Microscopy | Model: FEI TECNAI 12 |
|---|---|
| Electron gun | Electron source: LAB6 / Accelerating voltage: 120 kV / Illumination mode: FLOOD BEAM |
| Electron lens | Mode: BRIGHT FIELD |
| Image recording | Electron dose: 30 e/Å2 / Film or detector model: GATAN ULTRASCAN 4000 (4k x 4k) |
- Processing
Processing
| EM software |
| |||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| CTF correction | Type: NONE | |||||||||
| Symmetry | Point symmetry: C1 (asymmetric) | |||||||||
| 3D reconstruction | Resolution: 35 Å / Resolution method: FSC 0.5 CUT-OFF / Num. of particles: 650 / Symmetry type: POINT | |||||||||
| Atomic model building | Protocol: FLEXIBLE FIT / Space: REAL |
 Movie
Movie Controller
Controller


 UCSF Chimera
UCSF Chimera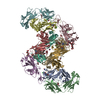





 PDBj
PDBj













