[English] 日本語
 Yorodumi
Yorodumi- EMDB-7031: Architecture of HIV-1 reverse transcriptase initiation complex core -
+ Open data
Open data
- Basic information
Basic information
| Entry | Database: EMDB / ID: EMD-7031 | |||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Title | Architecture of HIV-1 reverse transcriptase initiation complex core | |||||||||
 Map data Map data | HIV-1 RTIC core | |||||||||
 Sample Sample |
| |||||||||
 Keywords Keywords | Reverse Transcriptase / tRNA / HIV-1 / Reverse Transcription / RNA / Transcription / Complex / RNA-binding protein / backbone model / VIRAL PROTEIN-RNA complex | |||||||||
| Function / homology |  Function and homology information Function and homology informationHIV-1 retropepsin / symbiont-mediated activation of host apoptosis / retroviral ribonuclease H / exoribonuclease H / exoribonuclease H activity / DNA integration / viral genome integration into host DNA / establishment of integrated proviral latency / RNA-directed DNA polymerase / RNA stem-loop binding ...HIV-1 retropepsin / symbiont-mediated activation of host apoptosis / retroviral ribonuclease H / exoribonuclease H / exoribonuclease H activity / DNA integration / viral genome integration into host DNA / establishment of integrated proviral latency / RNA-directed DNA polymerase / RNA stem-loop binding / viral penetration into host nucleus / host multivesicular body / RNA-directed DNA polymerase activity / RNA-DNA hybrid ribonuclease activity / Transferases; Transferring phosphorus-containing groups; Nucleotidyltransferases / host cell / viral nucleocapsid / DNA recombination / DNA-directed DNA polymerase / aspartic-type endopeptidase activity / Hydrolases; Acting on ester bonds / DNA-directed DNA polymerase activity / symbiont-mediated suppression of host gene expression / viral translational frameshifting / symbiont entry into host cell / lipid binding / host cell nucleus / host cell plasma membrane / virion membrane / structural molecule activity / proteolysis / DNA binding / zinc ion binding / membrane Similarity search - Function | |||||||||
| Biological species |   Human immunodeficiency virus 1 / Human immunodeficiency virus 1 /  Homo sapiens (human) Homo sapiens (human) | |||||||||
| Method | single particle reconstruction / cryo EM / Resolution: 4.5 Å | |||||||||
 Authors Authors | Larsen KP / Mathiharan YK / Chen DH / Puglisi JD / Skiniotis G / Puglisi EV | |||||||||
| Funding support |  United States, 1 items United States, 1 items
| |||||||||
 Citation Citation |  Journal: Nature / Year: 2018 Journal: Nature / Year: 2018Title: Architecture of an HIV-1 reverse transcriptase initiation complex. Authors: Kevin P Larsen / Yamuna Kalyani Mathiharan / Kalli Kappel / Aaron T Coey / Dong-Hua Chen / Daniel Barrero / Lauren Madigan / Joseph D Puglisi / Georgios Skiniotis / Elisabetta Viani Puglisi /  Abstract: Reverse transcription of the HIV-1 RNA genome into double-stranded DNA is a central step in viral infection and a common target of antiretroviral drugs . The reaction is catalysed by viral reverse ...Reverse transcription of the HIV-1 RNA genome into double-stranded DNA is a central step in viral infection and a common target of antiretroviral drugs . The reaction is catalysed by viral reverse transcriptase (RT) that is packaged in an infectious virion with two copies of viral genomic RNA each bound to host lysine 3 transfer RNA (tRNA), which acts as a primer for initiation of reverse transcription. Upon viral entry into cells, initiation is slow and non-processive compared to elongation. Despite extensive efforts, the structural basis of RT function during initiation has remained a mystery. Here we use cryo-electron microscopy to determine a three-dimensional structure of an HIV-1 RT initiation complex. In our structure, RT is in an inactive polymerase conformation with open fingers and thumb and with the nucleic acid primer-template complex shifted away from the active site. The primer binding site (PBS) helix formed between tRNA and HIV-1 RNA lies in the cleft of RT and is extended by additional pairing interactions. The 5' end of the tRNA refolds and stacks on the PBS to create a long helical structure, while the remaining viral RNA forms two helical stems positioned above the RT active site, with a linker that connects these helices to the RNase H region of the PBS. Our results illustrate how RNA structure in the initiation complex alters RT conformation to decrease activity, highlighting a potential target for drug action. | |||||||||
| History |
|
- Structure visualization
Structure visualization
| Movie |
 Movie viewer Movie viewer |
|---|---|
| Structure viewer | EM map:  SurfView SurfView Molmil Molmil Jmol/JSmol Jmol/JSmol |
| Supplemental images |
- Downloads & links
Downloads & links
-EMDB archive
| Map data |  emd_7031.map.gz emd_7031.map.gz | 40.1 MB |  EMDB map data format EMDB map data format | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Header (meta data) |  emd-7031-v30.xml emd-7031-v30.xml emd-7031.xml emd-7031.xml | 20.8 KB 20.8 KB | Display Display |  EMDB header EMDB header |
| Images |  emd_7031.png emd_7031.png | 43.8 KB | ||
| Filedesc metadata |  emd-7031.cif.gz emd-7031.cif.gz | 7.2 KB | ||
| Archive directory |  http://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/structures/EMD-7031 http://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/structures/EMD-7031 ftp://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/structures/EMD-7031 ftp://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/structures/EMD-7031 | HTTPS FTP |
-Related structure data
| Related structure data |  6b19MC  7032C  7540C C: citing same article ( M: atomic model generated by this map |
|---|---|
| Similar structure data |
- Links
Links
| EMDB pages |  EMDB (EBI/PDBe) / EMDB (EBI/PDBe) /  EMDataResource EMDataResource |
|---|---|
| Related items in Molecule of the Month |
- Map
Map
| File |  Download / File: emd_7031.map.gz / Format: CCP4 / Size: 42.9 MB / Type: IMAGE STORED AS FLOATING POINT NUMBER (4 BYTES) Download / File: emd_7031.map.gz / Format: CCP4 / Size: 42.9 MB / Type: IMAGE STORED AS FLOATING POINT NUMBER (4 BYTES) | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
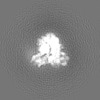
| Annotation | HIV-1 RTIC core | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
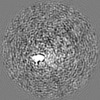
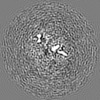
| Projections & slices | Image control
Images are generated by Spider. | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Voxel size | X=Y=Z: 1 Å | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
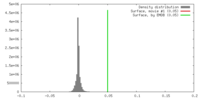
| Density |
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Symmetry | Space group: 1 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Details | EMDB XML:
CCP4 map header:
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
-Supplemental data
- Sample components
Sample components
-Entire : HIV-1 reverse transcription initiation complex core
| Entire | Name: HIV-1 reverse transcription initiation complex core |
|---|---|
| Components |
|
-Supramolecule #1: HIV-1 reverse transcription initiation complex core
| Supramolecule | Name: HIV-1 reverse transcription initiation complex core / type: complex / ID: 1 / Parent: 0 / Macromolecule list: all Details: Peripheral dynamic RNA elements belonging to tRNA primer and viral RNA template have been masked out for higher resolution structure determination. |
|---|---|
| Molecular weight | Theoretical: 175 KDa |
-Supramolecule #2: HIV-1 reverse transcriptase
| Supramolecule | Name: HIV-1 reverse transcriptase / type: complex / ID: 2 / Parent: 1 / Macromolecule list: #1-#2 Details: The COOH-terminus of p66 contains an unstructured linker and a six-histidine tag that was cleaved before full complex formation. A cysteine mutation for crosslinking was introduced into ...Details: The COOH-terminus of p66 contains an unstructured linker and a six-histidine tag that was cleaved before full complex formation. A cysteine mutation for crosslinking was introduced into helix H of p66 (Q258C). The protein used in this study also had the C280S mutation, introduced in prior structural work and the E478Q mutation, introduced to eliminate RNase H activity. |
|---|---|
| Source (natural) | Organism:   Human immunodeficiency virus 1 Human immunodeficiency virus 1 |
| Molecular weight | Theoretical: 117 KDa |
-Supramolecule #3: HIV-1 RNA genome fragment
| Supramolecule | Name: HIV-1 RNA genome fragment / type: complex / ID: 3 / Parent: 1 / Macromolecule list: #3 Details: HIV-1 RNA genome fragment. 101 bases in length before masking. Contains the primer binding site (PBS), primer activation signal (PAS), A-rich loop, and C-rich region. |
|---|---|
| Source (natural) | Organism:   Human immunodeficiency virus 1 Human immunodeficiency virus 1 |
| Molecular weight | Theoretical: 33 KDa |
-Supramolecule #4: tRNA lysine3 primer
| Supramolecule | Name: tRNA lysine3 primer / type: complex / ID: 4 / Parent: 1 / Macromolecule list: #4 Details: Chemically synthesized and extended tRNA lysine3 primer. A modified nucleotide containing a N2-cystamine was placed at position 71. The tRNA primer has been extended by one ddCTP, bringing ...Details: Chemically synthesized and extended tRNA lysine3 primer. A modified nucleotide containing a N2-cystamine was placed at position 71. The tRNA primer has been extended by one ddCTP, bringing its total length in the full complex to 77 nucleotides before masking. |
|---|---|
| Source (natural) | Organism:  Homo sapiens (human) Homo sapiens (human) |
| Molecular weight | Theoretical: 25 KDa |
-Macromolecule #1: reverse transcriptase p66 subunit
| Macromolecule | Name: reverse transcriptase p66 subunit / type: protein_or_peptide / ID: 1 / Number of copies: 1 / Enantiomer: LEVO / EC number: RNA-directed DNA polymerase |
|---|---|
| Source (natural) | Organism:   Human immunodeficiency virus 1 Human immunodeficiency virus 1 |
| Molecular weight | Theoretical: 65.55832 KDa |
| Recombinant expression | Organism:  |
| Sequence | String: MVPISPIETV PVKLKPGMDG PKVKQWPLTE EKIKALVEIC TEMEKEGKIS KIGPENPYNT PVFAIKKKDS TKWRKLVDFR ELNKRTQDF WEVQLGIPHP AGLKKKKSVT VLDVGDAYFS VPLDEDFRKY TAFTIPSINN ETPGIRYQYN VLPQGWKGSP A IFQSSMTK ...String: MVPISPIETV PVKLKPGMDG PKVKQWPLTE EKIKALVEIC TEMEKEGKIS KIGPENPYNT PVFAIKKKDS TKWRKLVDFR ELNKRTQDF WEVQLGIPHP AGLKKKKSVT VLDVGDAYFS VPLDEDFRKY TAFTIPSINN ETPGIRYQYN VLPQGWKGSP A IFQSSMTK ILEPFKKQNP DIVIYQYMDD LYVGSDLEIG QHRTKIEELR QHLLRWGLTT PDKKHQKEPP FLWMGYELHP DK WTVQPIV LPEKDSWTVN DICKLVGKLN WASQIYPGIK VRQLSKLLRG TKALTEVIPL TEEAELELAE NREILKEPVH GVY YDPSKD LIAEIQKQGQ GQWTYQIYQE PFKNLKTGKY ARMRGAHTND VKQLTEAVQK ITTESIVIWG KTPKFKLPIQ KETW ETWWT EYWQATWIPE WEFVNTPPLV KLWYQLEKEP IVGAETFYVD GAANRETKLG KAGYVTNKGR QKVVPLTNTT NQKTQ LQAI YLALQDSGLE VNIVTDSQYA LGIIQAQPDK SESELVNQII EQLIKKEKVY LAWVPAHKGI GGNEQVDKLV SAGIRK ILD LGTLVPR UniProtKB: Gag-Pol polyprotein |
-Macromolecule #2: reverse transcriptase p51 subunit
| Macromolecule | Name: reverse transcriptase p51 subunit / type: protein_or_peptide / ID: 2 / Number of copies: 1 / Enantiomer: LEVO / EC number: RNA-directed DNA polymerase |
|---|---|
| Source (natural) | Organism:   Human immunodeficiency virus 1 Human immunodeficiency virus 1 |
| Molecular weight | Theoretical: 51.585293 KDa |
| Recombinant expression | Organism:  |
| Sequence | String: MVPISPIETV PVKLKPGMDG PKVKQWPLTE EKIKALVEIC TEMEKEGKIS KIGPENPYNT PVFAIKKKDS TKWRKLVDFR ELNKRTQDF WEVQLGIPHP AGLKKKKSVT VLDVGDAYFS VPLDEDFRKY TAFTIPSINN ETPGIRYQYN VLPQGWKGSP A IFQSSMTK ...String: MVPISPIETV PVKLKPGMDG PKVKQWPLTE EKIKALVEIC TEMEKEGKIS KIGPENPYNT PVFAIKKKDS TKWRKLVDFR ELNKRTQDF WEVQLGIPHP AGLKKKKSVT VLDVGDAYFS VPLDEDFRKY TAFTIPSINN ETPGIRYQYN VLPQGWKGSP A IFQSSMTK ILEPFKKQNP DIVIYQYMDD LYVGSDLEIG QHRTKIEELR QHLLRWGLTT PDKKHQKEPP FLWMGYELHP DK WTVQPIV LPEKDSWTVN DIQKLVGKLN WASQIYPGIK VRQLSKLLRG TKALTEVIPL TEEAELELAE NREILKEPVH GVY YDPSKD LIAEIQKQGQ GQWTYQIYQE PFKNLKTGKY ARMRGAHTND VKQLTEAVQK ITTESIVIWG KTPKFKLPIQ KETW ETWWT EYWQATWIPE WEFVNTPPLV KLWYQLEKEP IVGAETF UniProtKB: Gag-Pol polyprotein |
-Macromolecule #3: RNA genome fragment
| Macromolecule | Name: RNA genome fragment / type: rna / ID: 3 / Number of copies: 1 |
|---|---|
| Source (natural) | Organism:   Human immunodeficiency virus 1 Human immunodeficiency virus 1 |
| Molecular weight | Theoretical: 32.623477 KDa |
| Sequence | String: GACUCUGGUA ACUAGAGAUC CCUCAGACCC UUUUAGUCAG UGUGGAAAAU CUCUAGCAGU GGCGCCCGAA CAGGGACUUG AAAGCGAAA GUAAAGCCAG AG GENBANK: GENBANK: AY835748.1 |
-Macromolecule #4: tRNA lysine3
| Macromolecule | Name: tRNA lysine3 / type: other / ID: 4 / Number of copies: 1 Classification: polydeoxyribonucleotide/polyribonucleotide hybrid |
|---|---|
| Source (natural) | Organism:  Homo sapiens (human) Homo sapiens (human) |
| Molecular weight | Theoretical: 24.720664 KDa |
| Sequence | String: GCCCGGAUAG CUCAGUCGGU AGAGCAUCAG ACUUUUAAUC UGAGGGUCCA GGGUUCAAGU CCCUGUUCGG (DG)CGCCA (DC) |
-Experimental details
-Structure determination
| Method | cryo EM |
|---|---|
 Processing Processing | single particle reconstruction |
| Aggregation state | particle |
- Sample preparation
Sample preparation
| Concentration | 5.0 mg/mL | ||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Buffer | pH: 8 Component:
Details: Beta-OG was added just prior to freezing. | ||||||||||||
| Grid | Model: Quantifoil R2/2 / Material: COPPER / Mesh: 200 / Pretreatment - Type: GLOW DISCHARGE | ||||||||||||
| Vitrification | Cryogen name: ETHANE / Chamber humidity: 85 % / Chamber temperature: 292 K / Instrument: FEI VITROBOT MARK IV Details: Blotted for 3.5 sec before plunging into liquid ethane.. | ||||||||||||
| Details | Sample was monodisperse. |
- Electron microscopy
Electron microscopy
| Microscope | FEI TITAN KRIOS |
|---|---|
| Image recording | Film or detector model: GATAN K2 SUMMIT (4k x 4k) / Detector mode: COUNTING / Digitization - Frames/image: 1-40 / Number real images: 4209 / Average exposure time: 8.0 sec. / Average electron dose: 70.0 e/Å2 |
| Electron beam | Acceleration voltage: 300 kV / Electron source:  FIELD EMISSION GUN FIELD EMISSION GUN |
| Electron optics | Calibrated magnification: 50000 / Illumination mode: FLOOD BEAM / Imaging mode: BRIGHT FIELD / Cs: 2.7 mm / Nominal defocus max: 2.5 µm / Nominal defocus min: 1.3 µm / Nominal magnification: 29000 |
| Sample stage | Specimen holder model: FEI TITAN KRIOS AUTOGRID HOLDER / Cooling holder cryogen: NITROGEN |
| Experimental equipment |  Model: Titan Krios / Image courtesy: FEI Company |
+ Image processing
Image processing
-Atomic model buiding 1
| Details | Main chain backbone for protein |
|---|---|
| Refinement | Space: REAL / Protocol: BACKBONE TRACE |
| Output model |  PDB-6b19: |
 Movie
Movie Controller
Controller





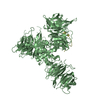
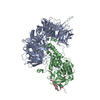

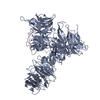

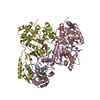



 Z (Sec.)
Z (Sec.) Y (Row.)
Y (Row.) X (Col.)
X (Col.)