[English] 日本語
 Yorodumi
Yorodumi- EMDB-42769: Structure of PKA phosphorylated human RyR2-R420W in the open stat... -
+ Open data
Open data
- Basic information
Basic information
| Entry |  | |||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
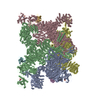
| Title | Structure of PKA phosphorylated human RyR2-R420W in the open state in the presence of calcium and calmodulin | |||||||||
 Map data Map data | Composite map of the Structure of PKA phosphorylated human RyR2-R420W in the open state in the presence of calcium and calmodulin | |||||||||
 Sample Sample |
| |||||||||
 Keywords Keywords | calcium channel / MEMBRANE PROTEIN | |||||||||
| Function / homology |  Function and homology information Function and homology informationjunctional sarcoplasmic reticulum membrane / establishment of protein localization to endoplasmic reticulum / type B pancreatic cell apoptotic process / Purkinje myocyte to ventricular cardiac muscle cell signaling / suramin binding / regulation of SA node cell action potential / regulation of atrial cardiac muscle cell action potential / left ventricular cardiac muscle tissue morphogenesis / regulation of AV node cell action potential / calcium-induced calcium release activity ...junctional sarcoplasmic reticulum membrane / establishment of protein localization to endoplasmic reticulum / type B pancreatic cell apoptotic process / Purkinje myocyte to ventricular cardiac muscle cell signaling / suramin binding / regulation of SA node cell action potential / regulation of atrial cardiac muscle cell action potential / left ventricular cardiac muscle tissue morphogenesis / regulation of AV node cell action potential / calcium-induced calcium release activity / sarcoplasmic reticulum calcium ion transport / cell communication by electrical coupling involved in cardiac conduction / regulation of ventricular cardiac muscle cell action potential / ventricular cardiac muscle cell action potential / positive regulation of sequestering of calcium ion / cyclic nucleotide binding / negative regulation of calcium-mediated signaling / embryonic heart tube morphogenesis / cardiac muscle hypertrophy / negative regulation of insulin secretion involved in cellular response to glucose stimulus / regulation of cardiac muscle contraction by calcium ion signaling / negative regulation of release of sequestered calcium ion into cytosol / neuronal action potential propagation / insulin secretion involved in cellular response to glucose stimulus / ryanodine-sensitive calcium-release channel activity / CaM pathway / response to caffeine / calcium ion transport into cytosol / Cam-PDE 1 activation / response to muscle activity / Sodium/Calcium exchangers / release of sequestered calcium ion into cytosol by sarcoplasmic reticulum / Calmodulin induced events / response to redox state / Reduction of cytosolic Ca++ levels / protein maturation by protein folding / CREB1 phosphorylation through the activation of CaMKII/CaMKK/CaMKIV cascasde / Activation of Ca-permeable Kainate Receptor / Loss of phosphorylation of MECP2 at T308 / 'de novo' protein folding / CREB1 phosphorylation through the activation of Adenylate Cyclase / PKA activation / negative regulation of high voltage-gated calcium channel activity / CaMK IV-mediated phosphorylation of CREB / Glycogen breakdown (glycogenolysis) / positive regulation of cyclic-nucleotide phosphodiesterase activity / negative regulation of heart rate / organelle localization by membrane tethering / negative regulation of calcium ion export across plasma membrane / autophagosome membrane docking / positive regulation of heart rate / mitochondrion-endoplasmic reticulum membrane tethering / CLEC7A (Dectin-1) induces NFAT activation / Activation of RAC1 downstream of NMDARs / regulation of cardiac muscle cell action potential / FK506 binding / positive regulation of ryanodine-sensitive calcium-release channel activity / positive regulation of axon regeneration / regulation of cell communication by electrical coupling involved in cardiac conduction / Synthesis of IP3 and IP4 in the cytosol / negative regulation of peptidyl-threonine phosphorylation / Negative regulation of NMDA receptor-mediated neuronal transmission / protein kinase A regulatory subunit binding / Phase 0 - rapid depolarisation / Unblocking of NMDA receptors, glutamate binding and activation / cellular response to caffeine / negative regulation of ryanodine-sensitive calcium-release channel activity / protein kinase A catalytic subunit binding / channel regulator activity / positive regulation of the force of heart contraction / protein phosphatase activator activity / RHO GTPases activate PAKs / intracellularly gated calcium channel activity / Ion transport by P-type ATPases / : / Uptake and function of anthrax toxins / Long-term potentiation / Regulation of MECP2 expression and activity / Calcineurin activates NFAT / catalytic complex / DARPP-32 events / detection of calcium ion / regulation of cardiac muscle contraction / smooth muscle contraction / Smooth Muscle Contraction / response to vitamin E / regulation of ryanodine-sensitive calcium-release channel activity / RHO GTPases activate IQGAPs / smooth endoplasmic reticulum / regulation of cardiac muscle contraction by regulation of the release of sequestered calcium ion / calcium channel inhibitor activity / cellular response to interferon-beta / eNOS activation / Protein methylation / voltage-gated potassium channel complex / cardiac muscle contraction / Activation of AMPK downstream of NMDARs / striated muscle contraction / T cell proliferation / regulation of release of sequestered calcium ion into cytosol by sarcoplasmic reticulum Similarity search - Function | |||||||||
| Biological species |  Homo sapiens (human) Homo sapiens (human) | |||||||||
| Method | single particle reconstruction / cryo EM / Resolution: 3.56 Å | |||||||||
 Authors Authors | Miotto MC / Marks AR | |||||||||
| Funding support |  United States, 1 items United States, 1 items
| |||||||||
 Citation Citation |  Journal: Nat Commun / Year: 2024 Journal: Nat Commun / Year: 2024Title: Structural basis for ryanodine receptor type 2 leak in heart failure and arrhythmogenic disorders. Authors: Marco C Miotto / Steven Reiken / Anetta Wronska / Qi Yuan / Haikel Dridi / Yang Liu / Gunnar Weninger / Carl Tchagou / Andrew R Marks /  Abstract: Heart failure, the leading cause of mortality and morbidity in the developed world, is characterized by cardiac ryanodine receptor 2 channels that are hyperphosphorylated, oxidized, and depleted of ...Heart failure, the leading cause of mortality and morbidity in the developed world, is characterized by cardiac ryanodine receptor 2 channels that are hyperphosphorylated, oxidized, and depleted of the stabilizing subunit calstabin-2. This results in a diastolic sarcoplasmic reticulum Ca leak that impairs cardiac contractility and triggers arrhythmias. Genetic mutations in ryanodine receptor 2 can also cause Ca leak, leading to arrhythmias and sudden cardiac death. Here, we solved the cryogenic electron microscopy structures of ryanodine receptor 2 variants linked either to heart failure or inherited sudden cardiac death. All are in the primed state, part way between closed and open. Binding of Rycal drugs to ryanodine receptor 2 channels reverts the primed state back towards the closed state, decreasing Ca leak, improving cardiac function, and preventing arrhythmias. We propose a structural-physiological mechanism whereby the ryanodine receptor 2 channel primed state underlies the arrhythmias in heart failure and arrhythmogenic disorders. | |||||||||
| History |
|
- Structure visualization
Structure visualization
| Supplemental images |
|---|
- Downloads & links
Downloads & links
-EMDB archive
| Map data |  emd_42769.map.gz emd_42769.map.gz | 245.5 MB |  EMDB map data format EMDB map data format | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Header (meta data) |  emd-42769-v30.xml emd-42769-v30.xml emd-42769.xml emd-42769.xml | 24.8 KB 24.8 KB | Display Display |  EMDB header EMDB header |
| Images |  emd_42769.png emd_42769.png | 206.9 KB | ||
| Filedesc metadata |  emd-42769.cif.gz emd-42769.cif.gz | 9.7 KB | ||
| Archive directory |  http://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/structures/EMD-42769 http://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/structures/EMD-42769 ftp://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/structures/EMD-42769 ftp://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/structures/EMD-42769 | HTTPS FTP |
-Validation report
| Summary document |  emd_42769_validation.pdf.gz emd_42769_validation.pdf.gz | 513.3 KB | Display |  EMDB validaton report EMDB validaton report |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Full document |  emd_42769_full_validation.pdf.gz emd_42769_full_validation.pdf.gz | 512.8 KB | Display | |
| Data in XML |  emd_42769_validation.xml.gz emd_42769_validation.xml.gz | 8.1 KB | Display | |
| Data in CIF |  emd_42769_validation.cif.gz emd_42769_validation.cif.gz | 9.3 KB | Display | |
| Arichive directory |  https://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/validation_reports/EMD-42769 https://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/validation_reports/EMD-42769 ftp://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/validation_reports/EMD-42769 ftp://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/validation_reports/EMD-42769 | HTTPS FTP |
-Related structure data
| Related structure data |  8uxmMC  8uq2C  8uq3C  8uq4C  8uq5C  8uxcC  8uxeC  8uxfC  8uxgC  8uxhC  8uxiC  8uxlC C: citing same article ( M: atomic model generated by this map |
|---|---|
| Similar structure data | Similarity search - Function & homology  F&H Search F&H Search |
- Links
Links
| EMDB pages |  EMDB (EBI/PDBe) / EMDB (EBI/PDBe) /  EMDataResource EMDataResource |
|---|---|
| Related items in Molecule of the Month |
- Map
Map
| File |  Download / File: emd_42769.map.gz / Format: CCP4 / Size: 512 MB / Type: IMAGE STORED AS FLOATING POINT NUMBER (4 BYTES) Download / File: emd_42769.map.gz / Format: CCP4 / Size: 512 MB / Type: IMAGE STORED AS FLOATING POINT NUMBER (4 BYTES) | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Annotation | Composite map of the Structure of PKA phosphorylated human RyR2-R420W in the open state in the presence of calcium and calmodulin | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
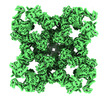
| Projections & slices | Image control
Images are generated by Spider. | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Voxel size | X=Y=Z: 0.8425 Å | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
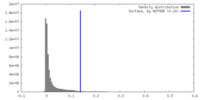
| Density |
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Symmetry | Space group: 1 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Details | EMDB XML:
|
-Supplemental data
- Sample components
Sample components
+Entire : Complex of RyR2-R420W, Calstabin-2, and Calmodulin
+Supramolecule #1: Complex of RyR2-R420W, Calstabin-2, and Calmodulin
+Supramolecule #2: Ryanodine Receptor 2
+Supramolecule #3: Peptidyl- cis-trans isomerase FKBP1B
+Supramolecule #4: Calmodulin
+Macromolecule #1: Calmodulin-1
+Macromolecule #2: Ryanodine receptor 2
+Macromolecule #3: Peptidyl-prolyl cis-trans isomerase FKBP1B
+Macromolecule #4: CALCIUM ION
+Macromolecule #5: ZINC ION
+Macromolecule #6: ADENOSINE-5'-TRIPHOSPHATE
-Experimental details
-Structure determination
| Method | cryo EM |
|---|---|
 Processing Processing | single particle reconstruction |
| Aggregation state | particle |
- Sample preparation
Sample preparation
| Concentration | 2.5 mg/mL | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Buffer | pH: 7.4 Component:
Details: 0.020 mM Calmodulin was added to the final sample | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Vitrification | Cryogen name: ETHANE |
- Electron microscopy
Electron microscopy
| Microscope | FEI TITAN KRIOS |
|---|---|
| Temperature | Min: 80.0 K / Max: 100.0 K |
| Specialist optics | Energy filter - Name: GIF Bioquantum / Energy filter - Slit width: 20 eV |
| Image recording | Film or detector model: GATAN K3 BIOQUANTUM (6k x 4k) / Digitization - Dimensions - Width: 5760 pixel / Digitization - Dimensions - Height: 4092 pixel / Average electron dose: 58.0 e/Å2 |
| Electron beam | Acceleration voltage: 300 kV / Electron source:  FIELD EMISSION GUN FIELD EMISSION GUN |
| Electron optics | C2 aperture diameter: 100.0 µm / Illumination mode: FLOOD BEAM / Imaging mode: BRIGHT FIELD / Cs: 2.7 mm / Nominal defocus max: 1.2 µm / Nominal defocus min: 0.5 µm |
| Sample stage | Specimen holder model: FEI TITAN KRIOS AUTOGRID HOLDER / Cooling holder cryogen: NITROGEN |
| Experimental equipment |  Model: Titan Krios / Image courtesy: FEI Company |
- Image processing
Image processing
| Startup model | Type of model: INSILICO MODEL / In silico model: CryoSPARC ab initio |
|---|---|
| Final reconstruction | Resolution.type: BY AUTHOR / Resolution: 3.56 Å / Resolution method: FSC 0.143 CUT-OFF / Software - Name: cryoSPARC / Number images used: 49606 |
| Initial angle assignment | Type: MAXIMUM LIKELIHOOD / Software - Name: cryoSPARC |
| Final angle assignment | Type: MAXIMUM LIKELIHOOD |
 Movie
Movie Controller
Controller





















































































 Z (Sec.)
Z (Sec.) Y (Row.)
Y (Row.) X (Col.)
X (Col.)