[English] 日本語
 Yorodumi
Yorodumi- EMDB-42762: Structure of PKA phosphorylated human RyR2-R420W in the primed state -
+ Open data
Open data
- Basic information
Basic information
| Entry |  | |||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
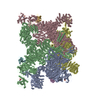
| Title | Structure of PKA phosphorylated human RyR2-R420W in the primed state | |||||||||
 Map data Map data | Composite map of the Structure of PKA phosphorylated human RyR2-R420W in the primed state | |||||||||
 Sample Sample |
| |||||||||
 Keywords Keywords | calcium channel / MEMBRANE PROTEIN | |||||||||
| Function / homology |  Function and homology information Function and homology informationsarcoplasmic reticulum calcium ion transport / establishment of protein localization to endoplasmic reticulum / junctional sarcoplasmic reticulum membrane / type B pancreatic cell apoptotic process / Purkinje myocyte to ventricular cardiac muscle cell signaling / regulation of atrial cardiac muscle cell action potential / calcium-induced calcium release activity / left ventricular cardiac muscle tissue morphogenesis / suramin binding / regulation of AV node cell action potential ...sarcoplasmic reticulum calcium ion transport / establishment of protein localization to endoplasmic reticulum / junctional sarcoplasmic reticulum membrane / type B pancreatic cell apoptotic process / Purkinje myocyte to ventricular cardiac muscle cell signaling / regulation of atrial cardiac muscle cell action potential / calcium-induced calcium release activity / left ventricular cardiac muscle tissue morphogenesis / suramin binding / regulation of AV node cell action potential / regulation of SA node cell action potential / cell communication by electrical coupling involved in cardiac conduction / regulation of ventricular cardiac muscle cell action potential / ventricular cardiac muscle cell action potential / : / embryonic heart tube morphogenesis / negative regulation of calcium-mediated signaling / cardiac muscle hypertrophy / negative regulation of insulin secretion involved in cellular response to glucose stimulus / neuronal action potential propagation / negative regulation of release of sequestered calcium ion into cytosol / calcium ion transport into cytosol / insulin secretion involved in cellular response to glucose stimulus / ryanodine-sensitive calcium-release channel activity / regulation of cardiac muscle contraction by calcium ion signaling / response to caffeine / release of sequestered calcium ion into cytosol by sarcoplasmic reticulum / response to redox state / negative regulation of heart rate / cellular response to caffeine / 'de novo' protein folding / FK506 binding / response to muscle activity / protein kinase A catalytic subunit binding / protein kinase A regulatory subunit binding / positive regulation of the force of heart contraction / intracellularly gated calcium channel activity / smooth endoplasmic reticulum / smooth muscle contraction / detection of calcium ion / regulation of cytosolic calcium ion concentration / regulation of cardiac muscle contraction / T cell proliferation / positive regulation of heart rate / regulation of cardiac muscle contraction by regulation of the release of sequestered calcium ion / calcium channel inhibitor activity / cardiac muscle contraction / regulation of release of sequestered calcium ion into cytosol by sarcoplasmic reticulum / Ion homeostasis / response to muscle stretch / release of sequestered calcium ion into cytosol / cellular response to epinephrine stimulus / calcium channel complex / sarcoplasmic reticulum membrane / regulation of heart rate / sarcoplasmic reticulum / protein maturation / peptidylprolyl isomerase / calcium channel regulator activity / peptidyl-prolyl cis-trans isomerase activity / establishment of localization in cell / calcium-mediated signaling / sarcolemma / calcium channel activity / Stimuli-sensing channels / Z disc / intracellular calcium ion homeostasis / calcium ion transport / positive regulation of cytosolic calcium ion concentration / protein refolding / transmembrane transporter binding / response to hypoxia / calmodulin binding / signaling receptor binding / calcium ion binding / enzyme binding / protein-containing complex / identical protein binding / membrane / plasma membrane / cytoplasm Similarity search - Function | |||||||||
| Biological species |  Homo sapiens (human) Homo sapiens (human) | |||||||||
| Method | single particle reconstruction / cryo EM / Resolution: 3.13 Å | |||||||||
 Authors Authors | Miotto MC / Marks AR | |||||||||
| Funding support |  United States, 1 items United States, 1 items
| |||||||||
 Citation Citation |  Journal: Nat Commun / Year: 2024 Journal: Nat Commun / Year: 2024Title: Structural basis for ryanodine receptor type 2 leak in heart failure and arrhythmogenic disorders. Authors: Marco C Miotto / Steven Reiken / Anetta Wronska / Qi Yuan / Haikel Dridi / Yang Liu / Gunnar Weninger / Carl Tchagou / Andrew R Marks /  Abstract: Heart failure, the leading cause of mortality and morbidity in the developed world, is characterized by cardiac ryanodine receptor 2 channels that are hyperphosphorylated, oxidized, and depleted of ...Heart failure, the leading cause of mortality and morbidity in the developed world, is characterized by cardiac ryanodine receptor 2 channels that are hyperphosphorylated, oxidized, and depleted of the stabilizing subunit calstabin-2. This results in a diastolic sarcoplasmic reticulum Ca leak that impairs cardiac contractility and triggers arrhythmias. Genetic mutations in ryanodine receptor 2 can also cause Ca leak, leading to arrhythmias and sudden cardiac death. Here, we solved the cryogenic electron microscopy structures of ryanodine receptor 2 variants linked either to heart failure or inherited sudden cardiac death. All are in the primed state, part way between closed and open. Binding of Rycal drugs to ryanodine receptor 2 channels reverts the primed state back towards the closed state, decreasing Ca leak, improving cardiac function, and preventing arrhythmias. We propose a structural-physiological mechanism whereby the ryanodine receptor 2 channel primed state underlies the arrhythmias in heart failure and arrhythmogenic disorders. | |||||||||
| History |
|
- Structure visualization
Structure visualization
| Supplemental images |
|---|
- Downloads & links
Downloads & links
-EMDB archive
| Map data |  emd_42762.map.gz emd_42762.map.gz | 245.6 MB |  EMDB map data format EMDB map data format | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Header (meta data) |  emd-42762-v30.xml emd-42762-v30.xml emd-42762.xml emd-42762.xml | 24.2 KB 24.2 KB | Display Display |  EMDB header EMDB header |
| Images |  emd_42762.png emd_42762.png | 209.2 KB | ||
| Filedesc metadata |  emd-42762.cif.gz emd-42762.cif.gz | 9.5 KB | ||
| Others |  emd_42762_additional_1.map.gz emd_42762_additional_1.map.gz | 254.3 MB | ||
| Archive directory |  http://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/structures/EMD-42762 http://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/structures/EMD-42762 ftp://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/structures/EMD-42762 ftp://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/structures/EMD-42762 | HTTPS FTP |
-Related structure data
| Related structure data |  8uxfMC  8uq2C  8uq3C  8uq4C  8uq5C  8uxcC  8uxeC  8uxgC  8uxhC  8uxiC  8uxlC  8uxmC C: citing same article ( M: atomic model generated by this map |
|---|---|
| Similar structure data | Similarity search - Function & homology  F&H Search F&H Search |
- Links
Links
| EMDB pages |  EMDB (EBI/PDBe) / EMDB (EBI/PDBe) /  EMDataResource EMDataResource |
|---|---|
| Related items in Molecule of the Month |
- Map
Map
| File |  Download / File: emd_42762.map.gz / Format: CCP4 / Size: 512 MB / Type: IMAGE STORED AS FLOATING POINT NUMBER (4 BYTES) Download / File: emd_42762.map.gz / Format: CCP4 / Size: 512 MB / Type: IMAGE STORED AS FLOATING POINT NUMBER (4 BYTES) | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Annotation | Composite map of the Structure of PKA phosphorylated human RyR2-R420W in the primed state | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Projections & slices | Image control
Images are generated by Spider. | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Voxel size | X=Y=Z: 0.8415 Å | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Density |
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Symmetry | Space group: 1 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Details | EMDB XML:
|
-Supplemental data
-Additional map: Raw consensus map of the Structure of PKA...
| File | emd_42762_additional_1.map | ||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Annotation | Raw consensus map of the Structure of PKA phosphorylated human RyR2-R420W in the primed state | ||||||||||||
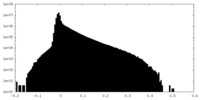
| Projections & Slices |
| ||||||||||||
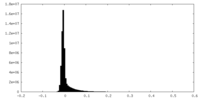
| Density Histograms |
- Sample components
Sample components
-Entire : Complex of RyR2-R420W and Calstabin-2
| Entire | Name: Complex of RyR2-R420W and Calstabin-2 |
|---|---|
| Components |
|
-Supramolecule #1: Complex of RyR2-R420W and Calstabin-2
| Supramolecule | Name: Complex of RyR2-R420W and Calstabin-2 / type: complex / ID: 1 / Parent: 0 / Macromolecule list: #1-#2 |
|---|
-Supramolecule #2: Ryanodine Receptor 2
| Supramolecule | Name: Ryanodine Receptor 2 / type: complex / ID: 2 / Parent: 1 / Macromolecule list: #1 |
|---|---|
| Source (natural) | Organism:  Homo sapiens (human) Homo sapiens (human) |
-Supramolecule #3: Peptidyl- cis-trans isomerase FKBP1B
| Supramolecule | Name: Peptidyl- cis-trans isomerase FKBP1B / type: complex / ID: 3 / Parent: 1 / Macromolecule list: #2 |
|---|---|
| Source (natural) | Organism:  Homo sapiens (human) Homo sapiens (human) |
-Macromolecule #1: Ryanodine receptor 2
| Macromolecule | Name: Ryanodine receptor 2 / type: protein_or_peptide / ID: 1 / Number of copies: 4 / Enantiomer: LEVO |
|---|---|
| Source (natural) | Organism:  Homo sapiens (human) Homo sapiens (human) |
| Molecular weight | Theoretical: 565.315125 KDa |
| Recombinant expression | Organism:  Homo sapiens (human) Homo sapiens (human) |
| Sequence | String: MADGGEGEDE IQFLRTDDEV VLQCTATIHK EQQKLCLAAE GFGNRLCFLE STSNSKNVPP DLSICTFVLE QSLSVRALQE MLANTVEKS EGQVDVEKWK FMMKTAQGGG HRTLLYGHAI LLRHSYSGMY LCCLSTSRSS TDKLAFDVGL QEDTTGEACW W TIHPASKQ ...String: MADGGEGEDE IQFLRTDDEV VLQCTATIHK EQQKLCLAAE GFGNRLCFLE STSNSKNVPP DLSICTFVLE QSLSVRALQE MLANTVEKS EGQVDVEKWK FMMKTAQGGG HRTLLYGHAI LLRHSYSGMY LCCLSTSRSS TDKLAFDVGL QEDTTGEACW W TIHPASKQ RSEGEKVRVG DDLILVSVSS ERYLHLSYGN GSLHVDAAFQ QTLWSVAPIS SGSEAAQGYL IGGDVLRLLH GH MDECLTV PSGEHGEEQR RTVHYEGGAV SVHARSLWRL ETLRVAWSGS HIRWGQPFRL RHVTTGKYLS LMEDKNLLLM DKE KADVKS TAFTFRSSKE KLDVGVRKEV DGMGTSEIKY GDSVCYIQHV DTGLWLTYQS VDVKSVRMGS IQRKAIMHHE GHMD DGISL SRSQHEESRT ARVIWSTVFL FNRFIRGLDA LSKKAKASTV DLPIESVSLS LQDLIGYFHP PDEHLEHEDK QNRLR ALKN RQNLFQEEGM INLVLECIDR LHVYSSAAHF ADVAGREAGE SWKSILNSLY ELLAALIRGN RKNCAQFSGS LDWLIS RLE RLEASSGILE VLHCVLVESP EALNIIKEGH IKSIISLLDK HGRNHKVLDV LCSLCVCHGV AVRSNQHLIC DNLLPGR DL LLQTRLVNHV SSMRPNIFLG VSEGSAQYKK WYYELMVDHT EPFVTAEATH LRVGWASTEG YSPYPGGGEE WGGNGVGD D LFSYGFDGLH LWSGCIARTV SSPNQHLLRT DDVISCCLDL SAPSISFRIN GQPVQGMFEN FNIDGLFFPV VSFSAGIKV RFLLGGRHGE FKFLPPPGYA PCYEAVLPKE KLKVEHSREY KQERTYTRDL LGPTVSLTQA AFTPIPVDTS QIVLPPHLER IREKLAENI HELWVMNKIE LGWQYGPVRD DNKRQHPCLV EFSKLPEQER NYNLQMSLET LKTLLALGCH VGISDEHAED K VKKMKLPK NYQLTSGYKP APMDLSFIKL TPSQEAMVDK LAENAHNVWA RDRIRQGWTY GIQQDVKNRR NPRLVPYTLL DD RTKKSNK DSLREAVRTL LGYGYNLEAP DQDHAARAEV CSGTGERFRI FRAEKTYAVK AGRWYFEFET VTAGDMRVGW SRP GCQPDQ ELGSDERAFA FDGFKAQRWH QGNEHYGRSW QAGDVVGCMV DMNEHTMMFT LNGEILLDDS GSELAFKDFD VGDG FIPVC SLGVAQVGRM NFGKDVSTLK YFTICGLQEG YEPFAVNTNR DITMWLSKRL PQFLQVPSNH EHIEVTRIDG TIDSS PCLK VTQKSFGSQN SNTDIMFYRL SMPIECAEVF SKTVAGGLPG AGLFGPKNDL EDYDADSDFE VLMKTAHGHL VPDRVD KDK EATKPEFNNH KDYAQEKPSR LKQRFLLRRT KPDYSTSHSA RLTEDVLADD RDDYDFLMQT STYYYSVRIF PGQEPAN VW VGWITSDFHQ YDTGFDLDRV RTVTVTLGDE KGKVHESIKR SNCYMVCAGE SMSPGQGRNN NGLEIGCVVD AASGLLTF I ANGKELSTYY QVEPSTKLFP AVFAQATSPN VFQFELGRIK NVMPLSAGLF KSEHKNPVPQ CPPRLHVQFL SHVLWSRMP NQFLKVDVSR ISERQGWLVQ CLDPLQFMSL HIPEENRSVD ILELTEQEEL LKFHYHTLRL YSAVCALGNH RVAHALCSHV DEPQLLYAI ENKYMPGLLR AGYYDLLIDI HLSSYATARL MMNNEYIVPM TEETKSITLF PDENKKHGLP GIGLSTSLRP R MQFSSPSF VSISNECYQY SPEFPLDILK SKTIQMLTEA VKEGSLHARD PVGGTTEFLF VPLIKLFYTL LIMGIFHNED LK HILQLIE PSVFKEAATP EEESDTLEKE LSVDDAKLQG AGEEEAKGGK RPKEGLLQMK LPEPVKLQMC LLLQYLCDCQ VRH RIEAIV AFSDDFVAKL QDNQRFRYNE VMQALNMSAA LTARKTKEFR SPPQEQINML LNFKDDKSEC PCPEEIRDQL LDFH EDLMT HCGIELDEDG SLDGNSDLTI RGRLLSLVEK VTYLKKKQAE KPVESDSKKS STLQQLISET MVRWAQESVI EDPEL VRAM FVLLHRQYDG IGGLVRALPK TYTINGVSVE DTINLLASLG QIRSLLSVRM GKEEEKLMIR GLGDIMNNKV FYQHPN LMR ALGMHETVME VMVNVLGGGE SKEITFPKMV ANCCRFLCYF CRISRQNQKA MFDHLSYLLE NSSVGLASPA MRGSTPL DV AAASVMDNNE LALALREPDL EKVVRYLAGC GLQSCQMLVS KGYPDIGWNP VEGERYLDFL RFAVFCNGES VEENANVV V RLLIRRPECF GPALRGEGGN GLLAAMEEAI KIAEDPSRDG PSPNSGSSKT LDTEEEEDDT IHMGNAIMTF YSALIDLLG RCAPEMHLIH AGKGEAIRIR SILRSLIPLG DLVGVISIAF QMPTIAKDGN VVEPDMSAGF CPDHKAAMVL FLDRVYGIEV QDFLLHLLE VGFLPDLRAA ASLDTAALSA TDMALALNRY LCTAVLPLLT RCAPLFAGTE HHASLIDSLL HTVYRLSKGC S LTKAQRDS IEVCLLSICG QLRPSMMQHL LRRLVFDVPL LNEHAKMPLK LLTNHYERCW KYYCLPGGWG NFGAASEEEL HL SRKLFWG IFDALSQKKY EQELFKLALP CLSAVAGALP PDYMESNYVS MMEKQSSMDS EGNFNPQPVD TSNITIPEKL EYF INKYAE HSHDKWSMDK LANGWIYGEI YSDSSKVQPL MKPYKLLSEK EKEIYRWPIK ESLKTMLAWG WRIERTREGD SMAL YNRTR RISQTSQVSV DAAHGYSPRA IDMSNVTLSR DLHAMAEMMA ENYHNIWAKK KKMELESKGG GNHPLLVPYD TLTAK EKAK DREKAQDILK FLQINGYAVS RGFKDLELDT PSIEKRFAYS FLQQLIRYVD EAHQYILEFD GGSRGKGEHF PYEQEI KFF AKVVLPLIDQ YFKNHRLYFL SAASRPLCSG GHASNKEKEM VTSLFCKLGV LVRHRISLFG NDATSIVNCL HILGQTL DA RTVMKTGLES VKSALRAFLD NAAEDLEKTM ENLKQGQFTH TRNQPKGVTQ IINYTTVALL PMLSSLFEHI GQHQFGED L ILEDVQVSCY RILTSLYALG TSKSIYVERQ RSALGECLAA FAGAFPVAFL ETHLDKHNIY SIYNTKSSRE RAALSLPTN VEDVCPNIPS LEKLMEEIVE LAESGIRYTQ MPHVMEVILP MLCSYMSRWW EHGPENNPER AEMCCTALNS EHMNTLLGNI LKIIYNNLG IDEGAWMKRL AVFSQPIINK VKPQLLKTHF LPLMEKLKKK AATVVSEEDH LKAEARGDMS EAELLILDEF T TLARDLYA FYPLLIRFVD YNRAKWLKEP NPEAEELFRM VAEVFIYWSK SHNFKREEQN FVVQNEINNM SFLITDTKSK MS KAAVSDQ ERKKMKRKGD RYSMQTSLIV AALKRLLPIG LNICAPGDQE LIALAKNRFS LKDTEDEVRD IIRSNIHLQG KLE DPAIRW QMALYKDLPN RTDDTSDPEK TVERVLDIAN VLFHLEQKSK RVGRRHYCLV EHPQRSKKAV WHKLLSKQRK RAVV ACFRM APLYNLPRHR AVNLFLQGYE KSWIETEEHY FEDKLIEDLA KPGAEPPEED EGTKRVDPLH QLILLFSRTA LTEKC KLEE DFLYMAYADI MAKSCHDEED DDGEEEVKSF EEKEMEKQKL LYQQARLHDR GAAEMVLQTI SASKGETGPM VAATLK LGI AILNGGNSTV QQKMLDYLKE KKDVGFFQSL AGLMQSCSVL DLNAFERQNK AEGLGMVTEE GSGEKVLQDD EFTCDLF RF LQLLCEGHNS DFQNYLRTQT GNNTTVNIII STVDYLLRVQ ESISDFYWYY SGKDVIDEQG QRNFSKAIQV AKQVFNTL T EYIQGPCTGN QQSLAHSRLW DAVVGFLHVF AHMQMKLSQD SSQIELLKEL MDLQKDMVVM LLSMLEGNVV NGTIGKQMV DMLVESSNNV EMILKFFDMF LKLKDLTSSD TFKEYDPDGK GVISKRDFHK AMESHKHYTQ SETEFLLSCA ETDENETLDY EEFVKRFHE PAKDIGFNVA VLLTNLSEHM PNDTRLQTFL ELAESVLNYF QPFLGRIEIM GSAKRIERVY FEISESSRTQ W EKPQVKES KRQFIFDVVN EGGEKEKMEL FVNFCEDTIF EMQLAAQISE SDLNERSANK EESEKERPEE QGPRMAFFSI LT VRSALFA LRYNILTLMR MLSLKSLKKQ MKKVKKMTVK DMVTAFFSSY WSIFMTLLHF VASVFRGFFR IICSLLLGGS LVE GAKKIK VAELLANMPD PTQDEVRGDG EEGERKPLEA ALPSEDLTDL KELTEESDLL SDIFGLDLKR EGGQYKLIPH NPNA GLSDL MSNPVPMPEV QEKFQEQKAK EEEKEEKEET KSEPEKAEGE DGEKEEKAKE DKGKQKLRQL HTHRYGEPEV PESAF WKKI IAYQQKLLNY FARNFYNMRM LALFVAFAIN FILLFYKVST SSVVEGKELP TRSSSENAKV TSLDSSSHRI IAVHYV LEE SSGYMEPTLR ILAILHTVIS FFCIIGYYCL KVPLVIFKRE KEVARKLEFD GLYITEQPSE DDIKGQWDRL VINTQSF PN NYWDKFVKRK VMDKYGEFYG RDRISELLGM DKAALDFSDA REKKKPKKDS SLSAVLNSID VKYQMWKLGV VFTDNSFL Y LAWYMTMSVL GHYNNFFFAA HLLDIAMGFK TLRTILSSVT HNGKQLVLTV GLLAVVVYLY TVVAFNFFRK FYNKSEDGD TPDMKCDDML TCYMFHMYVG VRAGGGIGDE IEDPAGDEYE IYRIIFDITF FFFVIVILLA IIQGLIIDAF GELRDQQEQV KEDMETKCF ICGIGNDYFD TVPHGFETHT LQEHNLANYL FFLMYLINKD ETEHTGQESY VWKMYQERCW EFFPAGDCFR K QYEDQLN UniProtKB: Ryanodine receptor 2 |
-Macromolecule #2: Peptidyl-prolyl cis-trans isomerase FKBP1B
| Macromolecule | Name: Peptidyl-prolyl cis-trans isomerase FKBP1B / type: protein_or_peptide / ID: 2 / Number of copies: 4 / Enantiomer: LEVO / EC number: peptidylprolyl isomerase |
|---|---|
| Source (natural) | Organism:  Homo sapiens (human) Homo sapiens (human) |
| Molecular weight | Theoretical: 11.798501 KDa |
| Recombinant expression | Organism:  |
| Sequence | String: MGVEIETISP GDGRTFPKKG QTCVVHYTGM LQNGKKFDSS RDRNKPFKFR IGKQEVIKGF EEGAAQMSLG QRAKLTCTPD VAYGATGHP GVIPPNATLI FDVELLNLE UniProtKB: Peptidyl-prolyl cis-trans isomerase FKBP1B |
-Macromolecule #3: ZINC ION
| Macromolecule | Name: ZINC ION / type: ligand / ID: 3 / Number of copies: 4 / Formula: ZN |
|---|---|
| Molecular weight | Theoretical: 65.409 Da |
-Macromolecule #4: ADENOSINE-5'-TRIPHOSPHATE
| Macromolecule | Name: ADENOSINE-5'-TRIPHOSPHATE / type: ligand / ID: 4 / Number of copies: 8 / Formula: ATP |
|---|---|
| Molecular weight | Theoretical: 507.181 Da |
| Chemical component information |  ChemComp-ATP: |
-Experimental details
-Structure determination
| Method | cryo EM |
|---|---|
 Processing Processing | single particle reconstruction |
| Aggregation state | particle |
- Sample preparation
Sample preparation
| Concentration | 2.5 mg/mL | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Buffer | pH: 7.4 Component:
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Vitrification | Cryogen name: ETHANE |
- Electron microscopy
Electron microscopy
| Microscope | FEI TITAN KRIOS |
|---|---|
| Temperature | Min: 80.0 K / Max: 100.0 K |
| Specialist optics | Energy filter - Name: GIF Bioquantum / Energy filter - Slit width: 20 eV |
| Image recording | Film or detector model: GATAN K3 BIOQUANTUM (6k x 4k) / Digitization - Dimensions - Width: 5760 pixel / Digitization - Dimensions - Height: 4092 pixel / Average electron dose: 58.0 e/Å2 |
| Electron beam | Acceleration voltage: 300 kV / Electron source:  FIELD EMISSION GUN FIELD EMISSION GUN |
| Electron optics | C2 aperture diameter: 100.0 µm / Illumination mode: FLOOD BEAM / Imaging mode: BRIGHT FIELD / Cs: 2.7 mm / Nominal defocus max: 1.2 µm / Nominal defocus min: 0.5 µm |
| Sample stage | Specimen holder model: FEI TITAN KRIOS AUTOGRID HOLDER / Cooling holder cryogen: NITROGEN |
| Experimental equipment |  Model: Titan Krios / Image courtesy: FEI Company |
- Image processing
Image processing
| Startup model | Type of model: INSILICO MODEL / In silico model: CryoSPARC ab initio |
|---|---|
| Final reconstruction | Applied symmetry - Point group: C4 (4 fold cyclic) / Resolution.type: BY AUTHOR / Resolution: 3.13 Å / Resolution method: FSC 0.143 CUT-OFF / Software - Name: cryoSPARC / Number images used: 102478 |
| Initial angle assignment | Type: MAXIMUM LIKELIHOOD / Software - Name: cryoSPARC |
| Final angle assignment | Type: MAXIMUM LIKELIHOOD |
 Movie
Movie Controller
Controller














































































 Z (Sec.)
Z (Sec.) Y (Row.)
Y (Row.) X (Col.)
X (Col.)