+ Open data
Open data
- Basic information
Basic information
| Entry | Database: EMDB / ID: EMD-30267 | |||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
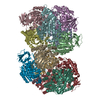
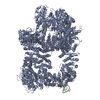
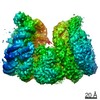
| Title | Human cGAS-nucleosome complex | |||||||||||||||||||||
 Map data Map data | ||||||||||||||||||||||
 Sample Sample |
| |||||||||||||||||||||
 Keywords Keywords | complex / chromatin / NTase / innate immunity / immunity / nucleosome / cGAS / DNA BINDING PROTEIN / DNA BINDING PROTEIN-DNA complex | |||||||||||||||||||||
| Function / homology |  Function and homology information Function and homology information2',3'-cyclic GMP-AMP synthase activity / cyclic GMP-AMP synthase / paracrine signaling / STING mediated induction of host immune responses / poly-ADP-D-ribose modification-dependent protein binding / regulation of immunoglobulin production / cGAS/STING signaling pathway / regulation of T cell activation / pattern recognition receptor signaling pathway / : ...2',3'-cyclic GMP-AMP synthase activity / cyclic GMP-AMP synthase / paracrine signaling / STING mediated induction of host immune responses / poly-ADP-D-ribose modification-dependent protein binding / regulation of immunoglobulin production / cGAS/STING signaling pathway / regulation of T cell activation / pattern recognition receptor signaling pathway / : / cytoplasmic pattern recognition receptor signaling pathway / negative regulation of cGAS/STING signaling pathway / cellular response to exogenous dsRNA / positive regulation of type I interferon production / negative regulation of tumor necrosis factor-mediated signaling pathway / : / negative regulation of double-strand break repair via homologous recombination / nucleosome binding / negative regulation of megakaryocyte differentiation / protein localization to CENP-A containing chromatin / Chromatin modifying enzymes / Replacement of protamines by nucleosomes in the male pronucleus / CENP-A containing nucleosome / positive regulation of defense response to virus by host / phosphatidylinositol-4,5-bisphosphate binding / Packaging Of Telomere Ends / Recognition and association of DNA glycosylase with site containing an affected purine / Cleavage of the damaged purine / Deposition of new CENPA-containing nucleosomes at the centromere / telomere organization / activation of innate immune response / Interleukin-7 signaling / Recognition and association of DNA glycosylase with site containing an affected pyrimidine / Cleavage of the damaged pyrimidine / RNA Polymerase I Promoter Opening / epigenetic regulation of gene expression / Inhibition of DNA recombination at telomere / Assembly of the ORC complex at the origin of replication / Meiotic synapsis / SUMOylation of chromatin organization proteins / Regulation of endogenous retroelements by the Human Silencing Hub (HUSH) complex / DNA methylation / Condensation of Prophase Chromosomes / Chromatin modifications during the maternal to zygotic transition (MZT) / SIRT1 negatively regulates rRNA expression / HCMV Late Events / ERCC6 (CSB) and EHMT2 (G9a) positively regulate rRNA expression / PRC2 methylates histones and DNA / determination of adult lifespan / Regulation of endogenous retroelements by KRAB-ZFP proteins / innate immune response in mucosa / Defective pyroptosis / HDACs deacetylate histones / Regulation of endogenous retroelements by Piwi-interacting RNAs (piRNAs) / RNA Polymerase I Promoter Escape / Nonhomologous End-Joining (NHEJ) / molecular condensate scaffold activity / lipopolysaccharide binding / Transcriptional regulation by small RNAs / Formation of the beta-catenin:TCF transactivating complex / Activated PKN1 stimulates transcription of AR (androgen receptor) regulated genes KLK2 and KLK3 / RUNX1 regulates genes involved in megakaryocyte differentiation and platelet function / HDMs demethylate histones / G2/M DNA damage checkpoint / NoRC negatively regulates rRNA expression / B-WICH complex positively regulates rRNA expression / PKMTs methylate histone lysines / DNA Damage/Telomere Stress Induced Senescence / Pre-NOTCH Transcription and Translation / Meiotic recombination / Activation of anterior HOX genes in hindbrain development during early embryogenesis / Metalloprotease DUBs / RMTs methylate histone arginines / Transcriptional regulation of granulopoiesis / HCMV Early Events / antimicrobial humoral immune response mediated by antimicrobial peptide / structural constituent of chromatin / positive regulation of cellular senescence / UCH proteinases / antibacterial humoral response / heterochromatin formation / nucleosome / nucleosome assembly / E3 ubiquitin ligases ubiquitinate target proteins / Recruitment and ATM-mediated phosphorylation of repair and signaling proteins at DNA double strand breaks / site of double-strand break / HATs acetylate histones / RUNX1 regulates transcription of genes involved in differentiation of HSCs / Factors involved in megakaryocyte development and platelet production / MLL4 and MLL3 complexes regulate expression of PPARG target genes in adipogenesis and hepatic steatosis / chromatin organization / Processing of DNA double-strand break ends / Senescence-Associated Secretory Phenotype (SASP) / double-stranded DNA binding / Oxidative Stress Induced Senescence / defense response to Gram-negative bacterium / gene expression / defense response to virus / Estrogen-dependent gene expression / killing of cells of another organism Similarity search - Function | |||||||||||||||||||||
| Biological species |  Homo sapiens (human) / synthetic construct (others) Homo sapiens (human) / synthetic construct (others) | |||||||||||||||||||||
| Method | single particle reconstruction / cryo EM / Resolution: 3.9 Å | |||||||||||||||||||||
 Authors Authors | Kujirai T / Zierhut C | |||||||||||||||||||||
| Funding support |  Japan, 6 items Japan, 6 items
| |||||||||||||||||||||
 Citation Citation |  Journal: Science / Year: 2020 Journal: Science / Year: 2020Title: Structural basis for the inhibition of cGAS by nucleosomes. Authors: Tomoya Kujirai / Christian Zierhut / Yoshimasa Takizawa / Ryan Kim / Lumi Negishi / Nobuki Uruma / Seiya Hirai / Hironori Funabiki / Hitoshi Kurumizaka /   Abstract: The cyclic guanosine monophosphate-adenosine monophosphate synthase (cGAS) senses invasion of pathogenic DNA and stimulates inflammatory signaling, autophagy, and apoptosis. Organization of host DNA ...The cyclic guanosine monophosphate-adenosine monophosphate synthase (cGAS) senses invasion of pathogenic DNA and stimulates inflammatory signaling, autophagy, and apoptosis. Organization of host DNA into nucleosomes was proposed to limit cGAS autoinduction, but the underlying mechanism was unknown. Here, we report the structural basis for this inhibition. In the cryo-electron microscopy structure of the human cGAS-nucleosome core particle (NCP) complex, two cGAS monomers bridge two NCPs by binding the acidic patch of the histone H2A-H2B dimer and nucleosomal DNA. In this configuration, all three known cGAS DNA binding sites, required for cGAS activation, are repurposed or become inaccessible, and cGAS dimerization, another prerequisite for activation, is inhibited. Mutating key residues linking cGAS and the acidic patch alleviates nucleosomal inhibition. This study establishes a structural framework for why cGAS is silenced on chromatinized self-DNA. | |||||||||||||||||||||
| History |
|
- Structure visualization
Structure visualization
| Movie |
 Movie viewer Movie viewer |
|---|---|
| Structure viewer | EM map:  SurfView SurfView Molmil Molmil Jmol/JSmol Jmol/JSmol |
| Supplemental images |
- Downloads & links
Downloads & links
-EMDB archive
| Map data |  emd_30267.map.gz emd_30267.map.gz | 5.2 MB |  EMDB map data format EMDB map data format | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Header (meta data) |  emd-30267-v30.xml emd-30267-v30.xml emd-30267.xml emd-30267.xml | 17.8 KB 17.8 KB | Display Display |  EMDB header EMDB header |
| FSC (resolution estimation) |  emd_30267_fsc.xml emd_30267_fsc.xml | 8.9 KB | Display |  FSC data file FSC data file |
| Images |  emd_30267.png emd_30267.png | 66.9 KB | ||
| Filedesc metadata |  emd-30267.cif.gz emd-30267.cif.gz | 6.4 KB | ||
| Archive directory |  http://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/structures/EMD-30267 http://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/structures/EMD-30267 ftp://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/structures/EMD-30267 ftp://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/structures/EMD-30267 | HTTPS FTP |
-Related structure data
| Related structure data |  7c0mMC M: atomic model generated by this map C: citing same article ( |
|---|---|
| Similar structure data |
- Links
Links
| EMDB pages |  EMDB (EBI/PDBe) / EMDB (EBI/PDBe) /  EMDataResource EMDataResource |
|---|---|
| Related items in Molecule of the Month |
- Map
Map
| File |  Download / File: emd_30267.map.gz / Format: CCP4 / Size: 59.6 MB / Type: IMAGE STORED AS FLOATING POINT NUMBER (4 BYTES) Download / File: emd_30267.map.gz / Format: CCP4 / Size: 59.6 MB / Type: IMAGE STORED AS FLOATING POINT NUMBER (4 BYTES) | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Projections & slices | Image control
Images are generated by Spider. | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Voxel size | X=Y=Z: 1.05 Å | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Density |
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Symmetry | Space group: 1 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Details | EMDB XML:
CCP4 map header:
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
-Supplemental data
- Sample components
Sample components
-Entire : Human cGAS-nucleosome complex
| Entire | Name: Human cGAS-nucleosome complex |
|---|---|
| Components |
|
-Supramolecule #1: Human cGAS-nucleosome complex
| Supramolecule | Name: Human cGAS-nucleosome complex / type: complex / ID: 1 / Parent: 0 / Macromolecule list: #1-#7 |
|---|---|
| Source (natural) | Organism:  Homo sapiens (human) Homo sapiens (human) |
-Macromolecule #1: Histone H3.1
| Macromolecule | Name: Histone H3.1 / type: protein_or_peptide / ID: 1 / Number of copies: 4 / Enantiomer: LEVO |
|---|---|
| Source (natural) | Organism:  Homo sapiens (human) Homo sapiens (human) |
| Molecular weight | Theoretical: 15.719445 KDa |
| Recombinant expression | Organism:  |
| Sequence | String: GSHMARTKQT ARKSTGGKAP RKQLATKAAR KSAPATGGVK KPHRYRPGTV ALREIRRYQK STELLIRKLP FQRLVREIAQ DFKTDLRFQ SSAVMALQEA CEAYLVGLFE DTNLCAIHAK RVTIMPKDIQ LARRIRGERA UniProtKB: Histone H3.1 |
-Macromolecule #2: Histone H4
| Macromolecule | Name: Histone H4 / type: protein_or_peptide / ID: 2 / Number of copies: 4 / Enantiomer: LEVO |
|---|---|
| Source (natural) | Organism:  Homo sapiens (human) Homo sapiens (human) |
| Molecular weight | Theoretical: 11.676703 KDa |
| Recombinant expression | Organism:  |
| Sequence | String: GSHMSGRGKG GKGLGKGGAK RHRKVLRDNI QGITKPAIRR LARRGGVKRI SGLIYEETRG VLKVFLENVI RDAVTYTEHA KRKTVTAMD VVYALKRQGR TLYGFGG UniProtKB: Histone H4 |
-Macromolecule #3: Histone H2A type 1-B/E
| Macromolecule | Name: Histone H2A type 1-B/E / type: protein_or_peptide / ID: 3 / Number of copies: 4 / Enantiomer: LEVO |
|---|---|
| Source (natural) | Organism:  Homo sapiens (human) Homo sapiens (human) |
| Molecular weight | Theoretical: 14.447825 KDa |
| Recombinant expression | Organism:  |
| Sequence | String: GSHMSGRGKQ GGKARAKAKT RSSRAGLQFP VGRVHRLLRK GNYSERVGAG APVYLAAVLE YLTAEILELA GNAARDNKKT RIIPRHLQL AIRNDEELNK LLGRVTIAQG GVLPNIQAVL LPKKTESHHK AKGK UniProtKB: Histone H2A type 1-B/E |
-Macromolecule #4: Histone H2B type 1-J
| Macromolecule | Name: Histone H2B type 1-J / type: protein_or_peptide / ID: 4 / Number of copies: 4 / Enantiomer: LEVO |
|---|---|
| Source (natural) | Organism:  Homo sapiens (human) Homo sapiens (human) |
| Molecular weight | Theoretical: 14.217516 KDa |
| Recombinant expression | Organism:  |
| Sequence | String: GSHMPEPAKS APAPKKGSKK AVTKAQKKDG KKRKRSRKES YSIYVYKVLK QVHPDTGISS KAMGIMNSFV NDIFERIAGE ASRLAHYNK RSTITSREIQ TAVRLLLPGE LAKHAVSEGT KAVTKYTSAK UniProtKB: Histone H2B type 1-J |
-Macromolecule #7: Cyclic GMP-AMP synthase
| Macromolecule | Name: Cyclic GMP-AMP synthase / type: protein_or_peptide / ID: 7 / Number of copies: 2 / Enantiomer: LEVO / EC number: cyclic GMP-AMP synthase |
|---|---|
| Source (natural) | Organism:  Homo sapiens (human) Homo sapiens (human) |
| Molecular weight | Theoretical: 44.435191 KDa |
| Recombinant expression | Organism:  |
| Sequence | String: GSPILVRRDA APGASKLRAV LEKLKLSRDD ISTAAGMVKG VVDHLLLRLK CDSAFRGVGL LNTGSYYEHV KISAPNEFDV MFKLEVPRI QLEEYSNTRA YYFVKFKRNP KENPLSQFLE GEILSASKML SKFRKIIKEE INDIKDTDVI MKRKRGGSPA V TLLISEKI ...String: GSPILVRRDA APGASKLRAV LEKLKLSRDD ISTAAGMVKG VVDHLLLRLK CDSAFRGVGL LNTGSYYEHV KISAPNEFDV MFKLEVPRI QLEEYSNTRA YYFVKFKRNP KENPLSQFLE GEILSASKML SKFRKIIKEE INDIKDTDVI MKRKRGGSPA V TLLISEKI SVDITLALES KSSWPASTQE GLRIQNWLSA KVRKQLRLKP FYLVPKHAKE GNGFQEETWR LSFSHIEKEI LN NHGKSKT CCENKEEKCC RKDCLKLMKY LLEQLKERFK DKKHLDKFSS YHVKTAFFHV CTQNPQDSQW DRKDLGLCFD NCV TYFLQC LRTEKLENYF IPEFNLFSSN LIDKRSKEFL TKQIEYERNN EFPVFDEFEN LYFQ UniProtKB: Cyclic GMP-AMP synthase |
-Macromolecule #5: DNA (145-MER)
| Macromolecule | Name: DNA (145-MER) / type: dna / ID: 5 / Number of copies: 2 / Classification: DNA |
|---|---|
| Source (natural) | Organism: synthetic construct (others) |
| Molecular weight | Theoretical: 44.520383 KDa |
| Sequence | String: (DA)(DT)(DC)(DA)(DG)(DA)(DA)(DT)(DC)(DC) (DC)(DG)(DG)(DT)(DG)(DC)(DC)(DG)(DA)(DG) (DG)(DC)(DC)(DG)(DC)(DT)(DC)(DA)(DA) (DT)(DT)(DG)(DG)(DT)(DC)(DG)(DT)(DA)(DG) (DA) (DC)(DA)(DG)(DC)(DT)(DC) ...String: (DA)(DT)(DC)(DA)(DG)(DA)(DA)(DT)(DC)(DC) (DC)(DG)(DG)(DT)(DG)(DC)(DC)(DG)(DA)(DG) (DG)(DC)(DC)(DG)(DC)(DT)(DC)(DA)(DA) (DT)(DT)(DG)(DG)(DT)(DC)(DG)(DT)(DA)(DG) (DA) (DC)(DA)(DG)(DC)(DT)(DC)(DT)(DA) (DG)(DC)(DA)(DC)(DC)(DG)(DC)(DT)(DT)(DA) (DA)(DA) (DC)(DG)(DC)(DA)(DC)(DG)(DT) (DA)(DC)(DG)(DC)(DG)(DC)(DT)(DG)(DT)(DC) (DC)(DC)(DC) (DC)(DG)(DC)(DG)(DT)(DT) (DT)(DT)(DA)(DA)(DC)(DC)(DG)(DC)(DC)(DA) (DA)(DG)(DG)(DG) (DG)(DA)(DT)(DT)(DA) (DC)(DT)(DC)(DC)(DC)(DT)(DA)(DG)(DT)(DC) (DT)(DC)(DC)(DA)(DG) (DG)(DC)(DA)(DC) (DG)(DT)(DG)(DT)(DC)(DA)(DG)(DA)(DT)(DA) (DT)(DA)(DT)(DA)(DC)(DA) (DT)(DC)(DG) (DA)(DT) |
-Macromolecule #6: DNA (145-MER)
| Macromolecule | Name: DNA (145-MER) / type: dna / ID: 6 / Number of copies: 2 / Classification: DNA |
|---|---|
| Source (natural) | Organism: synthetic construct (others) |
| Molecular weight | Theoretical: 44.99166 KDa |
| Sequence | String: (DA)(DT)(DC)(DG)(DA)(DT)(DG)(DT)(DA)(DT) (DA)(DT)(DA)(DT)(DC)(DT)(DG)(DA)(DC)(DA) (DC)(DG)(DT)(DG)(DC)(DC)(DT)(DG)(DG) (DA)(DG)(DA)(DC)(DT)(DA)(DG)(DG)(DG)(DA) (DG) (DT)(DA)(DA)(DT)(DC)(DC) ...String: (DA)(DT)(DC)(DG)(DA)(DT)(DG)(DT)(DA)(DT) (DA)(DT)(DA)(DT)(DC)(DT)(DG)(DA)(DC)(DA) (DC)(DG)(DT)(DG)(DC)(DC)(DT)(DG)(DG) (DA)(DG)(DA)(DC)(DT)(DA)(DG)(DG)(DG)(DA) (DG) (DT)(DA)(DA)(DT)(DC)(DC)(DC)(DC) (DT)(DT)(DG)(DG)(DC)(DG)(DG)(DT)(DT)(DA) (DA)(DA) (DA)(DC)(DG)(DC)(DG)(DG)(DG) (DG)(DG)(DA)(DC)(DA)(DG)(DC)(DG)(DC)(DG) (DT)(DA)(DC) (DG)(DT)(DG)(DC)(DG)(DT) (DT)(DT)(DA)(DA)(DG)(DC)(DG)(DG)(DT)(DG) (DC)(DT)(DA)(DG) (DA)(DG)(DC)(DT)(DG) (DT)(DC)(DT)(DA)(DC)(DG)(DA)(DC)(DC)(DA) (DA)(DT)(DT)(DG)(DA) (DG)(DC)(DG)(DG) (DC)(DC)(DT)(DC)(DG)(DG)(DC)(DA)(DC)(DC) (DG)(DG)(DG)(DA)(DT)(DT) (DC)(DT)(DG) (DA)(DT) |
-Macromolecule #8: ZINC ION
| Macromolecule | Name: ZINC ION / type: ligand / ID: 8 / Number of copies: 2 / Formula: ZN |
|---|---|
| Molecular weight | Theoretical: 65.409 Da |
-Experimental details
-Structure determination
| Method | cryo EM |
|---|---|
 Processing Processing | single particle reconstruction |
| Aggregation state | particle |
- Sample preparation
Sample preparation
| Buffer | pH: 7.5 |
|---|---|
| Vitrification | Cryogen name: ETHANE |
- Electron microscopy
Electron microscopy
| Microscope | TFS KRIOS |
|---|---|
| Image recording | Film or detector model: GATAN K3 BIOQUANTUM (6k x 4k) / Average electron dose: 64.0 e/Å2 |
| Electron beam | Acceleration voltage: 300 kV / Electron source:  FIELD EMISSION GUN FIELD EMISSION GUN |
| Electron optics | Illumination mode: FLOOD BEAM / Imaging mode: BRIGHT FIELD |
| Experimental equipment |  Model: Titan Krios / Image courtesy: FEI Company |
 Movie
Movie Controller
Controller




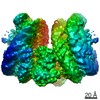
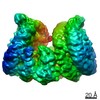
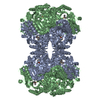











 Z (Sec.)
Z (Sec.) Y (Row.)
Y (Row.) X (Col.)
X (Col.)