[English] 日本語
 Yorodumi
Yorodumi- EMDB-20579: Cryo-EM structure of RET/GFRa3/ARTN extracellular complex. The 3D... -
+ Open data
Open data
- Basic information
Basic information
| Entry | Database: EMDB / ID: EMD-20579 | |||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
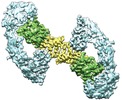
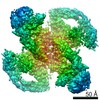
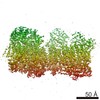
| Title | Cryo-EM structure of RET/GFRa3/ARTN extracellular complex. The 3D refinement was applied with C2 symmetry | |||||||||
 Map data Map data | Cryo-EM structure of RET/GFRa3/ARTN extracellular complex. The 3D refinement was applied with C2 symmetry. | |||||||||
 Sample Sample |
| |||||||||
 Keywords Keywords | RET / receptor tyrosine kinase / cryo-EM / SIGNALING PROTEIN | |||||||||
| Function / homology |  Function and homology information Function and homology informationglial cell-derived neurotrophic factor receptor activity / glial cell-derived neurotrophic factor receptor binding / Peyer's patch morphogenesis / GDF15-GFRAL signaling pathway / positive regulation of metanephric glomerulus development / ureter maturation / embryonic epithelial tube formation / glial cell-derived neurotrophic factor receptor signaling pathway / lymphocyte migration into lymphoid organs / posterior midgut development ...glial cell-derived neurotrophic factor receptor activity / glial cell-derived neurotrophic factor receptor binding / Peyer's patch morphogenesis / GDF15-GFRAL signaling pathway / positive regulation of metanephric glomerulus development / ureter maturation / embryonic epithelial tube formation / glial cell-derived neurotrophic factor receptor signaling pathway / lymphocyte migration into lymphoid organs / posterior midgut development / axon guidance receptor activity / Formation of the ureteric bud / membrane protein proteolysis / SUMO is conjugated to E1 (UBA2:SAE1) / SUMOylation of nuclear envelope proteins / SUMO is transferred from E1 to E2 (UBE2I, UBC9) / SUMO is proteolytically processed / SUMOylation of transcription factors / Formation of the nephric duct / Postmitotic nuclear pore complex (NPC) reformation / SUMOylation of transcription cofactors / neuron cell-cell adhesion / enteric nervous system development / septin ring / SUMOylation of DNA damage response and repair proteins / Transcriptional and post-translational regulation of MITF-M expression and activity / SUMOylation of DNA replication proteins / sympathetic nervous system development / induction of positive chemotaxis / peripheral nervous system development / SUMOylation of SUMOylation proteins / NCAM1 interactions / neuron maturation / plasma membrane protein complex / Recruitment and ATM-mediated phosphorylation of repair and signaling proteins at DNA double strand breaks / positive regulation of extrinsic apoptotic signaling pathway in absence of ligand / SUMOylation of RNA binding proteins / positive regulation of cell adhesion mediated by integrin / SUMOylation of chromatin organization proteins / neural crest cell migration / extrinsic component of membrane / ureteric bud development / response to pain / regulation of axonogenesis / homophilic cell-cell adhesion / ubiquitin-like protein ligase binding / RET signaling / protein sumoylation / neuroblast proliferation / positive regulation of cell size / regulation of cell adhesion / cellular response to retinoic acid / NPAS4 regulates expression of target genes / transmembrane receptor protein tyrosine kinase activity / axon guidance / cell surface receptor protein tyrosine kinase signaling pathway / condensed nuclear chromosome / growth factor activity / positive regulation of neuron projection development / receptor protein-tyrosine kinase / receptor tyrosine kinase binding / neuron migration / protein tag activity / nervous system development / signaling receptor activity / MAPK cascade / RAF/MAP kinase cascade / protein tyrosine kinase activity / positive regulation of phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase/protein kinase B signal transduction / receptor complex / positive regulation of MAPK cascade / endosome membrane / positive regulation of cell migration / signaling receptor binding / axon / external side of plasma membrane / calcium ion binding / positive regulation of gene expression / positive regulation of DNA-templated transcription / signal transduction / extracellular space / extracellular region / ATP binding / identical protein binding / nucleus / plasma membrane / cytosol Similarity search - Function | |||||||||
| Biological species |  Homo sapiens (human) Homo sapiens (human) | |||||||||
| Method | single particle reconstruction / cryo EM / Resolution: 3.8 Å | |||||||||
 Authors Authors | Li J / Shang GJ | |||||||||
 Citation Citation |  Journal: Elife / Year: 2019 Journal: Elife / Year: 2019Title: Cryo-EM analyses reveal the common mechanism and diversification in the activation of RET by different ligands. Authors: Jie Li / Guijun Shang / Yu-Ju Chen / Chad A Brautigam / Jen Liou / Xuewu Zhang / Xiao-Chen Bai /  Abstract: RET is a receptor tyrosine kinase (RTK) that plays essential roles in development and has been implicated in several human diseases. Different from most of RTKs, RET requires not only its cognate ...RET is a receptor tyrosine kinase (RTK) that plays essential roles in development and has been implicated in several human diseases. Different from most of RTKs, RET requires not only its cognate ligands but also co-receptors for activation, the mechanisms of which remain unclear due to lack of high-resolution structures of the ligand/co-receptor/receptor complexes. Here, we report cryo-EM structures of the extracellular region ternary complexes of GDF15/GFRAL/RET, GDNF/GFRα1/RET, NRTN/GFRα2/RET and ARTN/GFRα3/RET. These structures reveal that all the four ligand/co-receptor pairs, while using different atomic interactions, induce a specific dimerization mode of RET that is poised to bring the two kinase domains into close proximity for cross-phosphorylation. The NRTN/GFRα2/RET dimeric complex further pack into a tetrameric assembly, which is shown by our cell-based assays to regulate the endocytosis of RET. Our analyses therefore reveal both the common mechanism and diversification in the activation of RET by different ligands. | |||||||||
| History |
|
- Structure visualization
Structure visualization
| Movie |
 Movie viewer Movie viewer |
|---|---|
| Structure viewer | EM map:  SurfView SurfView Molmil Molmil Jmol/JSmol Jmol/JSmol |
| Supplemental images |
- Downloads & links
Downloads & links
-EMDB archive
| Map data |  emd_20579.map.gz emd_20579.map.gz | 49.2 MB |  EMDB map data format EMDB map data format | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Header (meta data) |  emd-20579-v30.xml emd-20579-v30.xml emd-20579.xml emd-20579.xml | 15.9 KB 15.9 KB | Display Display |  EMDB header EMDB header |
| Images |  emd_20579.png emd_20579.png | 240.6 KB | ||
| Filedesc metadata |  emd-20579.cif.gz emd-20579.cif.gz | 6.6 KB | ||
| Archive directory |  http://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/structures/EMD-20579 http://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/structures/EMD-20579 ftp://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/structures/EMD-20579 ftp://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/structures/EMD-20579 | HTTPS FTP |
-Related structure data
| Related structure data |  6q2sMC  6q2jC  6q2nC  6q2oC  6q2rC M: atomic model generated by this map C: citing same article ( |
|---|---|
| Similar structure data |
- Links
Links
| EMDB pages |  EMDB (EBI/PDBe) / EMDB (EBI/PDBe) /  EMDataResource EMDataResource |
|---|---|
| Related items in Molecule of the Month |
- Map
Map
| File |  Download / File: emd_20579.map.gz / Format: CCP4 / Size: 52.7 MB / Type: IMAGE STORED AS FLOATING POINT NUMBER (4 BYTES) Download / File: emd_20579.map.gz / Format: CCP4 / Size: 52.7 MB / Type: IMAGE STORED AS FLOATING POINT NUMBER (4 BYTES) | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Annotation | Cryo-EM structure of RET/GFRa3/ARTN extracellular complex. The 3D refinement was applied with C2 symmetry. | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Projections & slices | Image control
Images are generated by Spider. | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Voxel size | X=Y=Z: 1.07 Å | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Density |
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Symmetry | Space group: 1 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Details | EMDB XML:
CCP4 map header:
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
-Supplemental data
- Sample components
Sample components
-Entire : RET, GFRAL and GDF15 extracellular complex
| Entire | Name: RET, GFRAL and GDF15 extracellular complex |
|---|---|
| Components |
|
-Supramolecule #1: RET, GFRAL and GDF15 extracellular complex
| Supramolecule | Name: RET, GFRAL and GDF15 extracellular complex / type: complex / ID: 1 / Parent: 0 / Macromolecule list: #1-#3 |
|---|---|
| Source (natural) | Organism:  Homo sapiens (human) Homo sapiens (human) |
| Molecular weight | Theoretical: 200 kDa/nm |
-Macromolecule #1: Ubiquitin-like protein SMT3,Artemin
| Macromolecule | Name: Ubiquitin-like protein SMT3,Artemin / type: protein_or_peptide / ID: 1 Details: A SUMO protein was fused to the N-terminal of NRTN for the protein expression Number of copies: 2 / Enantiomer: LEVO |
|---|---|
| Source (natural) | Organism:  Homo sapiens (human) Homo sapiens (human) |
| Molecular weight | Theoretical: 25.793287 KDa |
| Recombinant expression | Organism:  |
| Sequence | String: MGSSHHHHHH SSGLVPRGSH MASMSDSEVN QEAKPEVKPE VKPETHINLK VSDGSSEIFF KIKKTTPLRR LMEAFAKRQG KEMDSLRFL YDGIRIQADQ TPEDLDMEDN DIIEAHREQI GGSAGGPGSR ARAAGARGCR LRSQLVPVRA LGLGHRSDEL V RFRFCSGS ...String: MGSSHHHHHH SSGLVPRGSH MASMSDSEVN QEAKPEVKPE VKPETHINLK VSDGSSEIFF KIKKTTPLRR LMEAFAKRQG KEMDSLRFL YDGIRIQADQ TPEDLDMEDN DIIEAHREQI GGSAGGPGSR ARAAGARGCR LRSQLVPVRA LGLGHRSDEL V RFRFCSGS CRRARSPHDL SLASLLGAGA LRPPPGSRPV SQPCCRPTRY EAVSFMDVNS TWRTVDRLSA TACGCLG UniProtKB: Ubiquitin-like protein SMT3, Artemin |
-Macromolecule #2: GDNF family receptor alpha-3
| Macromolecule | Name: GDNF family receptor alpha-3 / type: protein_or_peptide / ID: 2 / Number of copies: 2 / Enantiomer: LEVO |
|---|---|
| Source (natural) | Organism:  Homo sapiens (human) Homo sapiens (human) |
| Molecular weight | Theoretical: 38.370023 KDa |
| Recombinant expression | Organism:  Homo sapiens (human) Homo sapiens (human) |
| Sequence | String: DPLPTESRLM NSCLQARRKC QADPTCSAAY HHLDSCTSSI STPLPSEEPS VPADCLEAAQ QLRNSSLIGC MCHRRMKNQV ACLDIYWTV HRARSLGNYE LDVSPYEDTV TSKPWKMNLS KLNMLKPDSD LCLKFAMLCT LNDKCDRLRK AYGEACSGPH C QRHVCLRQ ...String: DPLPTESRLM NSCLQARRKC QADPTCSAAY HHLDSCTSSI STPLPSEEPS VPADCLEAAQ QLRNSSLIGC MCHRRMKNQV ACLDIYWTV HRARSLGNYE LDVSPYEDTV TSKPWKMNLS KLNMLKPDSD LCLKFAMLCT LNDKCDRLRK AYGEACSGPH C QRHVCLRQ LLTFFEKAAE PHAQGLLLCP CAPNDRGCGE RRRNTIAPNC ALPPVAPNCL ELRRLCFSDP LCRSRLVDFQ TH CHPMDIL GTCATEQSRC LRAYLGLIGT AMTPNFVSNV NTSVALSCTC RGSGNLQEEC EMLEGFFSHN PCLTEAIAAK MRF HSQLFS QDWPHPGTHH HHHHHH UniProtKB: GDNF family receptor alpha-3 |
-Macromolecule #3: Proto-oncogene tyrosine-protein kinase receptor Ret
| Macromolecule | Name: Proto-oncogene tyrosine-protein kinase receptor Ret / type: protein_or_peptide / ID: 3 / Number of copies: 2 / Enantiomer: LEVO / EC number: receptor protein-tyrosine kinase |
|---|---|
| Source (natural) | Organism:  Homo sapiens (human) Homo sapiens (human) |
| Molecular weight | Theoretical: 69.100812 KDa |
| Recombinant expression | Organism:  Homo sapiens (human) Homo sapiens (human) |
| Sequence | String: LYFSRDAYWE KLYVDQAAGT PLLYVHALRD APEEVPSFRL GQHLYGTYRT RLHENNWICI QEDTGLLYLN RSLDHSSWEK LSVRNHGFP LLTVYLKVFL SPTSLREGEC QWPGCARVYF SFFNTSFPAC SSLKPRELCF PETRPSFRIR ENRPPGTFHQ F RLLPVQFL ...String: LYFSRDAYWE KLYVDQAAGT PLLYVHALRD APEEVPSFRL GQHLYGTYRT RLHENNWICI QEDTGLLYLN RSLDHSSWEK LSVRNHGFP LLTVYLKVFL SPTSLREGEC QWPGCARVYF SFFNTSFPAC SSLKPRELCF PETRPSFRIR ENRPPGTFHQ F RLLPVQFL CPNISVAYRL LEGEGLPFRC APDSLEVSTR WALDREQREK YELVAVCTVH AGAREEVVMV PFPVTVYDED DS APTFPAG VDTASAVVEF KRKEDTVVAT LRVFDADVVP ASGELVRRYT STLLPGDTWA QQTFRVEHWP NETSVQANGS FVR ATVHDY RLVLNRNLSI SENRTMQLAV LVNDSDFQGP GAGVLLLHFN VSVLPVSLHL PSTYSLSVSR RARRFAQIGK VCVE NCQAF SGINVQYKLH SSGANCSTLG VVTSAEDTSG ILFVNDTKAL RRPKCAELHY MVVATDQQTS RQAQAQLLVT VEGSY VAEE AGCPLSCAVS KRRLECEECG GLGSPTGRCE WRQGDGKGIT RNFSTCSPST KTCPDGHCDV VETQDINICP QDCLRG SIV GGHEPGEPRG IKAGYGTCNC FPEEEKCFCE PEDIQDPLCD ELCRGTHHHH HHHH UniProtKB: Proto-oncogene tyrosine-protein kinase receptor Ret |
-Macromolecule #4: 2-acetamido-2-deoxy-beta-D-glucopyranose
| Macromolecule | Name: 2-acetamido-2-deoxy-beta-D-glucopyranose / type: ligand / ID: 4 / Number of copies: 14 / Formula: NAG |
|---|---|
| Molecular weight | Theoretical: 221.208 Da |
| Chemical component information |  ChemComp-NAG: |
-Macromolecule #5: CALCIUM ION
| Macromolecule | Name: CALCIUM ION / type: ligand / ID: 5 / Number of copies: 8 / Formula: CA |
|---|---|
| Molecular weight | Theoretical: 40.078 Da |
-Experimental details
-Structure determination
| Method | cryo EM |
|---|---|
 Processing Processing | single particle reconstruction |
| Aggregation state | particle |
- Sample preparation
Sample preparation
| Concentration | 1 mg/mL |
|---|---|
| Buffer | pH: 7.4 |
| Grid | Details: unspecified |
| Vitrification | Cryogen name: ETHANE / Chamber humidity: 100 % / Chamber temperature: 277 K / Instrument: FEI VITROBOT MARK IV |
- Electron microscopy
Electron microscopy
| Microscope | FEI TITAN KRIOS |
|---|---|
| Specialist optics | Energy filter - Name: GIF Quantum LS / Energy filter - Slit width: 20 eV |
| Image recording | Film or detector model: GATAN K2 QUANTUM (4k x 4k) / Detector mode: SUPER-RESOLUTION / Digitization - Frames/image: 1-30 / Number grids imaged: 1 / Average exposure time: 15.0 sec. / Average electron dose: 50.0 e/Å2 |
| Electron beam | Acceleration voltage: 300 kV / Electron source:  FIELD EMISSION GUN FIELD EMISSION GUN |
| Electron optics | C2 aperture diameter: 70.0 µm / Calibrated magnification: 46729 / Illumination mode: FLOOD BEAM / Imaging mode: BRIGHT FIELD / Cs: 2.7 mm |
| Sample stage | Specimen holder model: FEI TITAN KRIOS AUTOGRID HOLDER / Cooling holder cryogen: NITROGEN |
| Experimental equipment |  Model: Titan Krios / Image courtesy: FEI Company |
+ Image processing
Image processing
-Atomic model buiding 1
| Refinement | Space: REAL / Protocol: FLEXIBLE FIT / Overall B value: 190 |
|---|---|
| Output model |  PDB-6q2s: |
 Movie
Movie Controller
Controller























 Z (Sec.)
Z (Sec.) Y (Row.)
Y (Row.) X (Col.)
X (Col.)