+ Open data
Open data
- Basic information
Basic information
| Entry | Database: EMDB / ID: EMD-13159 | |||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
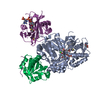
| Title | Structure of the V. vulnificus ExoY-G-actin-profilin complex | |||||||||
 Map data Map data | Main map, was used to build VvExoY and Actin | |||||||||
 Sample Sample |
| |||||||||
 Keywords Keywords | Bacterial toxin / G-actin / profilin / toxin | |||||||||
| Function / homology |  Function and homology information Function and homology informationcalcium- and calmodulin-responsive adenylate cyclase activity / synapse maturation / adenyl-nucleotide exchange factor activity / negative regulation of actin filament bundle assembly / modification of postsynaptic actin cytoskeleton / positive regulation of norepinephrine uptake / Regulation of CDH1 Function / Formation of the polybromo-BAF (pBAF) complex / Formation of the non-canonical BAF (ncBAF) complex / Formation of the canonical BAF (cBAF) complex ...calcium- and calmodulin-responsive adenylate cyclase activity / synapse maturation / adenyl-nucleotide exchange factor activity / negative regulation of actin filament bundle assembly / modification of postsynaptic actin cytoskeleton / positive regulation of norepinephrine uptake / Regulation of CDH1 Function / Formation of the polybromo-BAF (pBAF) complex / Formation of the non-canonical BAF (ncBAF) complex / Formation of the canonical BAF (cBAF) complex / Formation of the embryonic stem cell BAF (esBAF) complex / Formation of neuronal progenitor and neuronal BAF (npBAF and nBAF) / negative regulation of actin filament polymerization / positive regulation of actin filament bundle assembly / regulation of actin filament polymerization / bBAF complex / Signaling by ROBO receptors / cellular response to cytochalasin B / npBAF complex / nBAF complex / brahma complex / regulation of transepithelial transport / morphogenesis of a polarized epithelium / Formation of annular gap junctions / Formation of the dystrophin-glycoprotein complex (DGC) / positive regulation of ATP-dependent activity / structural constituent of postsynaptic actin cytoskeleton / GBAF complex / Gap junction degradation / Folding of actin by CCT/TriC / regulation of G0 to G1 transition / Cell-extracellular matrix interactions / protein localization to adherens junction / dense body / negative regulation of stress fiber assembly / Tat protein binding / postsynaptic actin cytoskeleton / Prefoldin mediated transfer of substrate to CCT/TriC / RSC-type complex / proline-rich region binding / PCP/CE pathway / regulation of double-strand break repair / regulation of nucleotide-excision repair / Adherens junctions interactions / RHOF GTPase cycle / adherens junction assembly / apical protein localization / positive regulation of ruffle assembly / Sensory processing of sound by inner hair cells of the cochlea / Sensory processing of sound by outer hair cells of the cochlea / Interaction between L1 and Ankyrins / tight junction / regulation of mitotic metaphase/anaphase transition / SWI/SNF complex / positive regulation of T cell differentiation / host cell cytosol / apical junction complex / positive regulation of double-strand break repair / detection of maltose stimulus / maintenance of blood-brain barrier / regulation of norepinephrine uptake / maltose transport complex / transporter regulator activity / nitric-oxide synthase binding / cortical cytoskeleton / positive regulation of stem cell population maintenance / positive regulation of actin filament polymerization / NuA4 histone acetyltransferase complex / establishment or maintenance of cell polarity / carbohydrate transport / Recycling pathway of L1 / Regulation of MITF-M-dependent genes involved in pigmentation / brush border / regulation of G1/S transition of mitotic cell cycle / positive regulation of epithelial cell migration / actin monomer binding / EPH-ephrin mediated repulsion of cells / carbohydrate transmembrane transporter activity / maltose binding / negative regulation of cell differentiation / kinesin binding / maltose transport / maltodextrin transmembrane transport / RHO GTPases Activate WASPs and WAVEs / regulation of synaptic vesicle endocytosis / positive regulation of myoblast differentiation / RHO GTPases activate IQGAPs / regulation of protein localization to plasma membrane / positive regulation of double-strand break repair via homologous recombination / ATP-binding cassette (ABC) transporter complex, substrate-binding subunit-containing / phosphotyrosine residue binding / phosphatidylinositol-4,5-bisphosphate binding / EPHB-mediated forward signaling / cytoskeleton organization / substantia nigra development / ATP-binding cassette (ABC) transporter complex / axonogenesis / calyx of Held / nitric-oxide synthase regulator activity / cell chemotaxis Similarity search - Function | |||||||||
| Biological species |  Vibrio vulnificus (bacteria) / Vibrio vulnificus (bacteria) /  Homo sapiens (human) Homo sapiens (human) | |||||||||
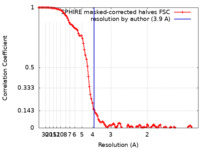
| Method | single particle reconstruction / cryo EM / Resolution: 3.9 Å | |||||||||
 Authors Authors | Belyy A / Merino F | |||||||||
| Funding support |  Germany, 1 items Germany, 1 items
| |||||||||
 Citation Citation |  Journal: Nat Commun / Year: 2021 Journal: Nat Commun / Year: 2021Title: Mechanism of actin-dependent activation of nucleotidyl cyclase toxins from bacterial human pathogens. Authors: Alexander Belyy / Felipe Merino / Undine Mechold / Stefan Raunser /   Abstract: Bacterial human pathogens secrete initially inactive nucleotidyl cyclases that become potent enzymes by binding to actin inside eukaryotic host cells. The underlying molecular mechanism of this ...Bacterial human pathogens secrete initially inactive nucleotidyl cyclases that become potent enzymes by binding to actin inside eukaryotic host cells. The underlying molecular mechanism of this activation is, however, unclear. Here, we report structures of ExoY from Pseudomonas aeruginosa and Vibrio vulnificus bound to their corresponding activators F-actin and profilin-G-actin. The structures reveal that in contrast to the apo-state, two flexible regions become ordered and interact strongly with actin. The specific stabilization of these regions results in an allosteric stabilization of the nucleotide binding pocket and thereby to an activation of the enzyme. Differences in the sequence and conformation of the actin-binding regions are responsible for the selective binding to either F- or G-actin. Other nucleotidyl cyclase toxins that bind to calmodulin rather than actin undergo a similar disordered-to-ordered transition during activation, suggesting that the allosteric activation-by-stabilization mechanism of ExoY is conserved in these enzymes, albeit the different activator. | |||||||||
| History |
|
- Structure visualization
Structure visualization
| Movie |
 Movie viewer Movie viewer |
|---|---|
| Structure viewer | EM map:  SurfView SurfView Molmil Molmil Jmol/JSmol Jmol/JSmol |
| Supplemental images |
- Downloads & links
Downloads & links
-EMDB archive
| Map data |  emd_13159.map.gz emd_13159.map.gz | 7.5 MB |  EMDB map data format EMDB map data format | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Header (meta data) |  emd-13159-v30.xml emd-13159-v30.xml emd-13159.xml emd-13159.xml | 21.1 KB 21.1 KB | Display Display |  EMDB header EMDB header |
| FSC (resolution estimation) |  emd_13159_fsc.xml emd_13159_fsc.xml | 12.4 KB | Display |  FSC data file FSC data file |
| Images |  emd_13159.png emd_13159.png | 117.9 KB | ||
| Filedesc metadata |  emd-13159.cif.gz emd-13159.cif.gz | 7.2 KB | ||
| Others |  emd_13159_additional_1.map.gz emd_13159_additional_1.map.gz | 7.3 MB | ||
| Archive directory |  http://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/structures/EMD-13159 http://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/structures/EMD-13159 ftp://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/structures/EMD-13159 ftp://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/structures/EMD-13159 | HTTPS FTP |
-Related structure data
| Related structure data |  7p1hMC  7p1gC M: atomic model generated by this map C: citing same article ( |
|---|---|
| Similar structure data |
- Links
Links
| EMDB pages |  EMDB (EBI/PDBe) / EMDB (EBI/PDBe) /  EMDataResource EMDataResource |
|---|---|
| Related items in Molecule of the Month |
- Map
Map
| File |  Download / File: emd_13159.map.gz / Format: CCP4 / Size: 125 MB / Type: IMAGE STORED AS FLOATING POINT NUMBER (4 BYTES) Download / File: emd_13159.map.gz / Format: CCP4 / Size: 125 MB / Type: IMAGE STORED AS FLOATING POINT NUMBER (4 BYTES) | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Annotation | Main map, was used to build VvExoY and Actin | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Projections & slices | Image control
Images are generated by Spider. | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Voxel size | X=Y=Z: 0.68 Å | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Density |
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Symmetry | Space group: 1 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Details | EMDB XML:
CCP4 map header:
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
-Supplemental data
-Additional map: Secondary map, was used to build actin-profilin interface
| File | emd_13159_additional_1.map | ||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Annotation | Secondary map, was used to build actin-profilin interface | ||||||||||||
| Projections & Slices |
| ||||||||||||
| Density Histograms |
- Sample components
Sample components
-Entire : Structure of the V. vulnificus ExoY-G-actin-profilin complex
| Entire | Name: Structure of the V. vulnificus ExoY-G-actin-profilin complex |
|---|---|
| Components |
|
-Supramolecule #1: Structure of the V. vulnificus ExoY-G-actin-profilin complex
| Supramolecule | Name: Structure of the V. vulnificus ExoY-G-actin-profilin complex type: complex / ID: 1 / Parent: 0 / Macromolecule list: #1-#3 |
|---|
-Macromolecule #1: Maltose/maltodextrin-binding periplasmic protein,RTX-toxin
| Macromolecule | Name: Maltose/maltodextrin-binding periplasmic protein,RTX-toxin type: protein_or_peptide / ID: 1 / Number of copies: 1 / Enantiomer: LEVO |
|---|---|
| Source (natural) | Organism:  Vibrio vulnificus (bacteria) Vibrio vulnificus (bacteria) |
| Molecular weight | Theoretical: 91.467539 KDa |
| Recombinant expression | Organism:  |
| Sequence | String: MGSSHHHHHH SSGLVPRGSH MKIEEGKLVI WINGDKGYNG LAEVGKKFEK DTGIKVTVEH PDKLEEKFPQ VAATGDGPDI IFWAHDRFG GYAQSGLLAE ITPDKAFQDK LYPFTWDAVR YNGKLIAYPI AVEALSLIYN KDLLPNPPKT WEEIPALDKE L KAKGKSAL ...String: MGSSHHHHHH SSGLVPRGSH MKIEEGKLVI WINGDKGYNG LAEVGKKFEK DTGIKVTVEH PDKLEEKFPQ VAATGDGPDI IFWAHDRFG GYAQSGLLAE ITPDKAFQDK LYPFTWDAVR YNGKLIAYPI AVEALSLIYN KDLLPNPPKT WEEIPALDKE L KAKGKSAL MFNLQEPYFT WPLIAADGGY AFKYENGKYD IKDVGVDNAG AKAGLTFLVD LIKNKHMNAD TDYSIAEAAF NK GETAMTI NGPWAWSNID TSKVNYGVTV LPTFKGQPSK PFVGVLSAGI NAASPNKELA KEFLENYLLT DEGLEAVNKD KPL GAVALK SYEEELVKDP RIAATMENAQ KGEIMPNIPQ MSAFWYAVRT AVINAASGRQ TVDEALKDAQ TNSGSSGSSV EASD TELGT NTDAPHKNYQ SRDLVLEPIV QPETIELGMP DSDQKILAEV AERENVIIGV RPVDEKSKSL IDSKLYSSKG LFVKA KSSD WGPMSGFIPV DQAFAKASAR RDLDKFNGYA EQSIESGNAV SADLYLNQVR IDELVSKYQS LTALEFDAES GMYKTT ATN GDQTVTFFLN KVTVDSKDLW QVHYIKDGKL APFKVIGDPV SKQPMTADYD LLTVMYSYSD LGPQDKLKQP LTWEQWK ES VTYEELTPKY KELYNSEVLY NKKDGASLGV VSDRLKALKD VINTSLGRTD GLEMVHHGAD DANPYAVMAD NFPATFFV P KSFFMEDGLG EGKGSIQTYF NVNEQGAVVI RDPQEFSNFQ QVAINVSYRA SLNDKWNVGL DDPLFTPKSK LSHDFLNAK EEVIKKLSGE VETNVRTTQL LTDNEGL UniProtKB: Maltose/maltodextrin-binding periplasmic protein, RTX-toxin |
-Macromolecule #2: Actin, cytoplasmic 1
| Macromolecule | Name: Actin, cytoplasmic 1 / type: protein_or_peptide / ID: 2 / Number of copies: 1 / Enantiomer: LEVO |
|---|---|
| Source (natural) | Organism:  Homo sapiens (human) Homo sapiens (human) |
| Molecular weight | Theoretical: 41.402242 KDa |
| Recombinant expression | Organism:  Trichoplusia ni (cabbage looper) Trichoplusia ni (cabbage looper) |
| Sequence | String: DIAALVVDNG SGMCKAGFAG DDAPRAVFPS IVGRPRHQGV MVGMGQKDSY VGDEAQSKRG ILTLKYPIE(HIC) GIVTNW DDM EKIWHHTFYN ELRVAPEEHP VLLTEAPLNP KANREKMTQI MFETFNTPAM YVAIQAVLSL YASGRTTGIV MDSGDGV TH TVPIYEGYAL ...String: DIAALVVDNG SGMCKAGFAG DDAPRAVFPS IVGRPRHQGV MVGMGQKDSY VGDEAQSKRG ILTLKYPIE(HIC) GIVTNW DDM EKIWHHTFYN ELRVAPEEHP VLLTEAPLNP KANREKMTQI MFETFNTPAM YVAIQAVLSL YASGRTTGIV MDSGDGV TH TVPIYEGYAL PHAILRLDLA GRDLTDYLMK ILTERGYSFT TTAEREIVRD IKEKLCYVAL DFEQEMATAA SSSSLEKS Y ELPDGQVITI GNERFRCPEA LFQPSFLGME SAGIHETTFN SIMKCDVDIR KDLYANTVLS GGTTMYPGIA DRMQKEITA LAPSTMKIKI IAPPERKYSV WIGGSILASL STFQQMWISK QEYDESGPSI VHRKCF UniProtKB: Actin, cytoplasmic 1 |
-Macromolecule #3: Profilin-1
| Macromolecule | Name: Profilin-1 / type: protein_or_peptide / ID: 3 / Number of copies: 1 / Enantiomer: LEVO |
|---|---|
| Source (natural) | Organism:  Homo sapiens (human) Homo sapiens (human) |
| Molecular weight | Theoretical: 15.071222 KDa |
| Recombinant expression | Organism:  |
| Sequence | String: MAGWNAYIDN LMADGTCQDA AIVGYKDSPS VWAAVPGKTF VNITPAEVGV LVGKDRSSFY VNGLTLGGQK CSVIRDSLLQ DGEFSMDLR TKSTGGAPTF NVTVTKTDKT LVLLMGKEGV HGGLINKKCY EMASHLRRSQ Y UniProtKB: Profilin-1 |
-Macromolecule #4: CALCIUM ION
| Macromolecule | Name: CALCIUM ION / type: ligand / ID: 4 / Number of copies: 1 / Formula: CA |
|---|---|
| Molecular weight | Theoretical: 40.078 Da |
-Macromolecule #5: ADENOSINE-5'-TRIPHOSPHATE
| Macromolecule | Name: ADENOSINE-5'-TRIPHOSPHATE / type: ligand / ID: 5 / Number of copies: 1 / Formula: ATP |
|---|---|
| Molecular weight | Theoretical: 507.181 Da |
| Chemical component information |  ChemComp-ATP: |
-Experimental details
-Structure determination
| Method | cryo EM |
|---|---|
 Processing Processing | single particle reconstruction |
| Aggregation state | particle |
- Sample preparation
Sample preparation
| Buffer | pH: 8 |
|---|---|
| Grid | Model: Quantifoil R2/1 / Material: COPPER / Mesh: 300 |
| Vitrification | Cryogen name: ETHANE / Chamber humidity: 100 % / Instrument: FEI VITROBOT MARK III |
- Electron microscopy
Electron microscopy
| Microscope | FEI TITAN KRIOS |
|---|---|
| Image recording | Film or detector model: GATAN K3 (6k x 4k) / Detector mode: SUPER-RESOLUTION / Number grids imaged: 1 / Number real images: 6879 / Average exposure time: 2.0 sec. / Average electron dose: 60.0 e/Å2 |
| Electron beam | Acceleration voltage: 300 kV / Electron source:  FIELD EMISSION GUN FIELD EMISSION GUN |
| Electron optics | Illumination mode: SPOT SCAN / Imaging mode: BRIGHT FIELD / Nominal defocus max: 2.5 µm / Nominal defocus min: 1.2 µm |
| Experimental equipment |  Model: Titan Krios / Image courtesy: FEI Company |
 Movie
Movie Controller
Controller



























 Z (Sec.)
Z (Sec.) Y (Row.)
Y (Row.) X (Col.)
X (Col.)