[English] 日本語
 Yorodumi
Yorodumi- EMDB-11891: Bacillus subtilis ribosome-associated quality control complex sta... -
+ Open data
Open data
- Basic information
Basic information
| Entry | Database: EMDB / ID: EMD-11891 | ||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
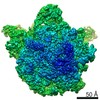
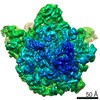
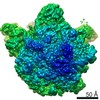
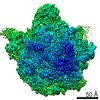
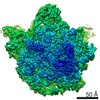
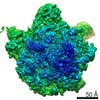
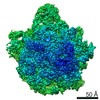
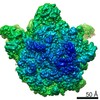
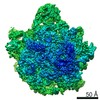
| Title | Bacillus subtilis ribosome-associated quality control complex state B, multibody refinement focussed on RqcH. Ribosomal 50S subunit with P-tRNA, RqcH, and RqcP/YabO | ||||||||||||||||||
 Map data Map data | Bacillus subtilis 50S ribosme-associated quality control complex state B. in complex P-tRNA, RqcH and RqcP/YabO | ||||||||||||||||||
 Sample Sample |
| ||||||||||||||||||
 Keywords Keywords | 50S / tRNA / RQC / RqcH / peptidyl-tRNA / translation / RqcP / YabO / alanine tailing | ||||||||||||||||||
| Function / homology |  Function and homology information Function and homology informationRQC complex / ribosomal large subunit binding / rescue of stalled cytosolic ribosome / large ribosomal subunit rRNA binding / cytosolic large ribosomal subunit / tRNA binding / rRNA binding / structural constituent of ribosome / translation / response to antibiotic Similarity search - Function | ||||||||||||||||||
| Biological species |   | ||||||||||||||||||
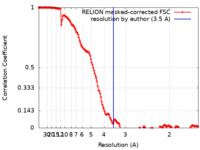
| Method | single particle reconstruction / cryo EM / Resolution: 3.5 Å | ||||||||||||||||||
 Authors Authors | Crowe-McAuliffe C / Wilson DN | ||||||||||||||||||
| Funding support |  Germany, Germany,  Sweden, 5 items Sweden, 5 items
| ||||||||||||||||||
 Citation Citation |  Journal: Mol Cell / Year: 2021 Journal: Mol Cell / Year: 2021Title: Structural Basis for Bacterial Ribosome-Associated Quality Control by RqcH and RqcP. Authors: Caillan Crowe-McAuliffe / Hiraku Takada / Victoriia Murina / Christine Polte / Sergo Kasvandik / Tanel Tenson / Zoya Ignatova / Gemma C Atkinson / Daniel N Wilson / Vasili Hauryliuk /    Abstract: In all branches of life, stalled translation intermediates are recognized and processed by ribosome-associated quality control (RQC) pathways. RQC begins with the splitting of stalled ribosomes, ...In all branches of life, stalled translation intermediates are recognized and processed by ribosome-associated quality control (RQC) pathways. RQC begins with the splitting of stalled ribosomes, leaving an unfinished polypeptide still attached to the large subunit. Ancient and conserved NEMF family RQC proteins target these incomplete proteins for degradation by the addition of C-terminal "tails." How such tailing can occur without the regular suite of translational components is, however, unclear. Using single-particle cryo-electron microscopy (EM) of native complexes, we show that C-terminal tailing in Bacillus subtilis is mediated by NEMF protein RqcH in concert with RqcP, an Hsp15 family protein. Our structures reveal how these factors mediate tRNA movement across the ribosomal 50S subunit to synthesize polypeptides in the absence of mRNA or the small subunit. | ||||||||||||||||||
| History |
|
- Structure visualization
Structure visualization
| Movie |
 Movie viewer Movie viewer |
|---|---|
| Structure viewer | EM map:  SurfView SurfView Molmil Molmil Jmol/JSmol Jmol/JSmol |
| Supplemental images |
- Downloads & links
Downloads & links
-EMDB archive
| Map data |  emd_11891.map.gz emd_11891.map.gz | 13.4 MB |  EMDB map data format EMDB map data format | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Header (meta data) |  emd-11891-v30.xml emd-11891-v30.xml emd-11891.xml emd-11891.xml | 18.9 KB 18.9 KB | Display Display |  EMDB header EMDB header |
| FSC (resolution estimation) |  emd_11891_fsc.xml emd_11891_fsc.xml | 14.9 KB | Display |  FSC data file FSC data file |
| Images |  emd_11891.png emd_11891.png | 39.4 KB | ||
| Filedesc metadata |  emd-11891.cif.gz emd-11891.cif.gz | 7.4 KB | ||
| Archive directory |  http://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/structures/EMD-11891 http://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/structures/EMD-11891 ftp://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/structures/EMD-11891 ftp://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/structures/EMD-11891 | HTTPS FTP |
-Related structure data
| Related structure data |  7asaMC  7as8C  7as9C C: citing same article ( M: atomic model generated by this map |
|---|---|
| Similar structure data | |
| EM raw data |  EMPIAR-10540 (Title: Affinity-purified RqcH-ribosome-associated quality control complexes from Bacillus subtilis EMPIAR-10540 (Title: Affinity-purified RqcH-ribosome-associated quality control complexes from Bacillus subtilisData size: 514.6 Data #1: Unaligned multi-frame micrographs of affinity-purified RqcH ribosome-associated quality control complexes from Bacillus subtilis [micrographs - multiframe])  EMPIAR-10541 (Title: Affinity-purified RqcP/YabO-ribosome-associated quality control complexes from Bacillus subtilis EMPIAR-10541 (Title: Affinity-purified RqcP/YabO-ribosome-associated quality control complexes from Bacillus subtilisData size: 358.1 Data #1: Unaligned multiframe micrographs of an affinity-purified RqcP/YabO sample [micrographs - multiframe]) |
- Links
Links
| EMDB pages |  EMDB (EBI/PDBe) / EMDB (EBI/PDBe) /  EMDataResource EMDataResource |
|---|---|
| Related items in Molecule of the Month |
- Map
Map
| File |  Download / File: emd_11891.map.gz / Format: CCP4 / Size: 282.6 MB / Type: IMAGE STORED AS FLOATING POINT NUMBER (4 BYTES) Download / File: emd_11891.map.gz / Format: CCP4 / Size: 282.6 MB / Type: IMAGE STORED AS FLOATING POINT NUMBER (4 BYTES) | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Annotation | Bacillus subtilis 50S ribosme-associated quality control complex state B. in complex P-tRNA, RqcH and RqcP/YabO | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Projections & slices | Image control
Images are generated by Spider. | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Voxel size | X=Y=Z: 0.82 Å | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
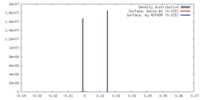
| Density |
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Symmetry | Space group: 1 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Details | EMDB XML:
CCP4 map header:
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
-Supplemental data
- Sample components
Sample components
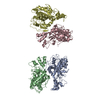
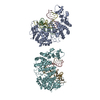
-Entire : 50S ribosomal subunit in complex with RqcH, P-tRNA, and YabO/RqcP
| Entire | Name: 50S ribosomal subunit in complex with RqcH, P-tRNA, and YabO/RqcP |
|---|---|
| Components |
|
-Supramolecule #1: 50S ribosomal subunit in complex with RqcH, P-tRNA, and YabO/RqcP
| Supramolecule | Name: 50S ribosomal subunit in complex with RqcH, P-tRNA, and YabO/RqcP type: complex / ID: 1 / Parent: 0 / Macromolecule list: #1-#5 |
|---|---|
| Molecular weight | Theoretical: 1.6 MDa |
-Supramolecule #2: RqcH
| Supramolecule | Name: RqcH / type: complex / ID: 2 / Parent: 1 / Macromolecule list: #1 |
|---|---|
| Source (natural) | Organism:  |
-Supramolecule #3: P-tRNA, and YabO/RqcP
| Supramolecule | Name: P-tRNA, and YabO/RqcP / type: complex / ID: 3 / Parent: 1 / Macromolecule list: #2-#5 |
|---|---|
| Source (natural) | Organism:  |
-Macromolecule #1: Rqc2 homolog RqcH
| Macromolecule | Name: Rqc2 homolog RqcH / type: protein_or_peptide / ID: 1 / Number of copies: 1 / Enantiomer: LEVO |
|---|---|
| Source (natural) | Organism:  |
| Molecular weight | Theoretical: 68.341391 KDa |
| Recombinant expression | Organism:  |
| Sequence | String: MSFDGMFTYG MTHELNEKIM GGRITKIHQP YKHDVIFHIR AKGKNQKLLL SAHPSYSRVH ITAQAYENPS EPPMFCMLLR KHIEGGFIE KIEQAGLDRI MIFHIKSRNE IGDETVRKLY VEIMGRHSNI ILTDAAENVI IDGLKHLSPS MNSYRTVLPG Q DYKLPPAQ ...String: MSFDGMFTYG MTHELNEKIM GGRITKIHQP YKHDVIFHIR AKGKNQKLLL SAHPSYSRVH ITAQAYENPS EPPMFCMLLR KHIEGGFIE KIEQAGLDRI MIFHIKSRNE IGDETVRKLY VEIMGRHSNI ILTDAAENVI IDGLKHLSPS MNSYRTVLPG Q DYKLPPAQ DKISPLEASE DDILRHLSFQ EGRLDKQIVD HFSGVSPLFA KEAVHRAGLA NKVTLPKALL ALFAEVKEHR FI PNITTVN GKEYFYLLEL THLKGEARRF DSLSELLDRF YFGKAERDRV KQQAQDLERF VVNERKKNAN KIKKLEKTLE YSE NAKEFQ LYGELLTANL YMLKKGDKQA EVINYYDEES PTITIPLNPN KTPSENAQAY FTKYQKAKNS VAVVEEQIRL AQEE IEYFD QLIQQLSSAS PRDISEIREE LVEGKYLRPK QQKGQKKQKP HNPVLETYES TSGLTILVGK NNRQNEYLTT RVAAR DDIW LHTKDIPGSH VVIRSSEPDE QTIMEAATIA AYFSKAKDSS SVPVDYTKIR HVKKPNGAKP GFVTYDSQHT VFVTPD ADT VIKLKKSGSG GDYKDHDGDY KDHDIDYKDD DDKG UniProtKB: Rqc2 homolog RqcH |
-Macromolecule #2: Uncharacterized protein YabO
| Macromolecule | Name: Uncharacterized protein YabO / type: protein_or_peptide / ID: 2 / Number of copies: 1 / Enantiomer: LEVO |
|---|---|
| Source (natural) | Organism:  |
| Molecular weight | Theoretical: 9.737266 KDa |
| Sequence | String: MRLDKFLKVS RLIKRRTLAK EVADQGRISI NGNQAKASSD VKPGDELTVR FGQKLVTVQV NELKDTTKKE EAANMYTILK EEKLGE UniProtKB: RQC P-site tRNA stabilizing factor |
-Macromolecule #5: 50S ribosomal protein L11
| Macromolecule | Name: 50S ribosomal protein L11 / type: protein_or_peptide / ID: 5 / Number of copies: 1 / Enantiomer: LEVO |
|---|---|
| Source (natural) | Organism:  |
| Molecular weight | Theoretical: 14.951442 KDa |
| Sequence | String: MAKKVVKVVK LQIPAGKANP APPVGPALGQ AGVNIMGFCK EFNARTADQA GLIIPVEISV YEDRSFTFIT KTPPAAVLLK KAAGIESGS GEPNRNKVAT VKRDKVREIA ETKMPDLNAA DVEAAMRMVE GTARSMGIVI ED UniProtKB: Large ribosomal subunit protein uL11 |
-Macromolecule #3: tRNA-Ala-1-1
| Macromolecule | Name: tRNA-Ala-1-1 / type: rna / ID: 3 / Number of copies: 1 |
|---|---|
| Source (natural) | Organism:  Strain: 168 |
| Molecular weight | Theoretical: 24.491547 KDa |
| Sequence | String: GGGGCCUUAG CUCAGCUGGG AGAGCGCCUG CUUUGCACGC AGGAGGUCAG CGGUUCGAUC CCGCUAGGCU CCACCA |
-Macromolecule #4: 23S rRNA
| Macromolecule | Name: 23S rRNA / type: rna / ID: 4 / Number of copies: 1 |
|---|---|
| Source (natural) | Organism:  Strain: 168 |
| Molecular weight | Theoretical: 949.010938 KDa |
| Sequence | String: GGUUAAGUUA GAAAGGGCGC ACGGUGGAUG CCUUGGCACU AGGAGCCGAU GAAGGACGGG ACGAACACCG AUAUGCUUCG GGGAGCUGU AAGCAAGCUU UGAUCCGGAG AUUUCCGAAU GGGGAAACCC ACCACUCGUA AUGGAGUGGU AUCCAUAUCU G AAUUCAUA ...String: GGUUAAGUUA GAAAGGGCGC ACGGUGGAUG CCUUGGCACU AGGAGCCGAU GAAGGACGGG ACGAACACCG AUAUGCUUCG GGGAGCUGU AAGCAAGCUU UGAUCCGGAG AUUUCCGAAU GGGGAAACCC ACCACUCGUA AUGGAGUGGU AUCCAUAUCU G AAUUCAUA GGAUAUGAGA AGGCAGACCC GGGGAACUGA AACAUCUAAG UACCCGGAGG AAGAGAAAGC AAAUGCGAUU CC CUGAGUA GCGGCGAGCG AAACGGGAUC AGCCCAAACC AAGAGGCUUG CCUCUUGGGG UUGUAGGACA CUCUGUACGG AGU UACAAA GGAACGAGGU AGAUGAAGAG GUCUGGAAAG GCCCGCCAUA GGAGGUAACA GCCCUGUAGU CAAAACUUCG UUCU CUCCU GAGUGGAUCC UGAGUACGGC GGAACACGUG AAAUUCCGUC GGAAUCCGGG AGGACCAUCU CCCAAGGCUA AAUAC UCCC UAGUGACCGA UAGUGAACCA GUACCGUGAG GGAAAGGUGA AAAGCACCCC GGAAGGGGAG UGAAAGAGAU CCUGAA ACC GUGUGCCUAC AAGUAGUCAG AGCCCGUUAA CGGGUGAUGG CGUGCCUUUU GUAGAAUGAA CCGGCGAGUU ACGAUCU CG UGCAAGGUUA AGCAGAAGAU GCGGAGCCGC AGCGAAAGCG AGUCUGAAUA GGGCGCAUGA GUACGUGGUC GUAGACCC G AAACCAGGUG AUCUACCCAU GUCCAGGGUG AAGUUCAGGU AACACUGAAU GGAGGCCCGA ACCCACGCAC GUUGAAAAG UGCGGGGAUG AGGUGUGGGU AGGGGUGAAA UGCCAAUCGA ACCUGGAGAU AGCUGGUUCU CUCCGAAAUA GCUUUAGGGC UAGCCUCAA GGUAAGAGUC UUGGAGGUAG AGCACUGAUU GGACUAGGGG CCCCUACCGG GUUACCGAAU UCAGUCAAAC U CCGAAUGC CAAUGACUUA UCCUUGGGAG UCAGACUGCG AGUGAUAAGA UCCGUAGUCG AAAGGGAAAC AGCCCAGACC GC CAGCUAA GGUCCCAAAG UAUACGUUAA GUGGAAAAGG AUGUGGAGUU GCUUAGACAA CCAGGAUGUU GGCUUAGAAG CAG CCACCA UUUAAAGAGU GCGUAAUAGC UCACUGGUCG AGUGACUCUG CGCCGAAAAU GUACCGGGGC UAAACGUAUC ACCG AAGCU GCGGACUGUU CUUCGAACAG UGGUAGGAGA GCGUUCUAAG GGCUGUGAAG CCAGACCGGA AGGACUGGUG GAGCG CUUA GAAGUGAGAA UGCCGGUAUG AGUAGCGAAA GAGGGGUGAG AAUCCCCUCC ACCGAAUGCC UAAGGUUUCC UGAGGA AGG CUCGUCCGCU CAGGGUUAGU CGGGACCUAA GCCGAGGCCG AAAGGCGUAG GCGAUGGACA ACAGGUUGAU AUUCCUG UA CCACCUCCUC ACCAUUUGAG CAAUGGGGGG ACGCAGGAGG AUAGGGUAAG CGCGGUAUUG GAUAUCCGCG UCCAAGCA G UUAGGCUGGG AAAUAGGCAA AUCCGUUUCC CAUAAGGCUG AGCUGUGAUG GCGAGCGAAA UAUAGUAGCG AAGUUCCUG AUUCCACACU GCCAAGAAAA GCCUCUAGCG AGGUGAGAGG UGCCCGUACC GCAAACCGAC ACAGGUAGGC GAGGAGAGAA UCCUAAGGU GAUCGAGAGA ACUCUCGUUA AGGAACUCGG CAAAAUGACC CCGUAACUUC GGGAGAAGGG GUGCUCUGUU A GGGUGCAA GCCCGAGAGA GCCGCAGUGA AUAGGCCCAG GCGACUGUUU AGCAAAAACA CAGGUCUCUG CGAAGCCGUA AG GCGAAGU AUAGGGGCUG ACGCCUGCCC GGUGCUGGAA GGUUAAGAGG AGCGCUUAGC GUAAGCGAAG GUGCGAAUUG AAG CCCCAG UAAACGGCGG CCGUAACUAU AACGGUCCUA AGGUAGCGAA AUUCCUUGUC GGGUAAGUUC CGACCCGCAC GAAA GGCGC AACGAUCUGG GCACUGUCUC AACGAGAGAC UCGGUGAAAU UAUAGUACCU GUGAAGAUGC AGGUUACCCG CGACA GGAC GGAAAGACCC CGUGGAGCUU UACUGCAGCC UGAUAUUGAA UGUUGGUACA GCUUGUACAG GAUAGGUAGG AGCCUU GGA AACCGGAGCG CCAGCUUCGG UGGAGGCAUC GGUGGGAUAC UACCCUGGCU GUAUUGACCU UCUAACCCGC CGCCCUU AU CGGGCGGGGA GACAGUGUCA GGUGGGCAGU UUGACUGGGG CGGUCGCCUC CUAAAAGGUA ACGGAGGCGC CCAAAGGU U CCCUCAGAAU GGUUGGAAAU CAUUCGCAGA GUGUAAAGGC ACAAGGGAGC UUGACUGCGA GACCUACAAG UCGAGCAGG GACGAAAGUC GGGCUUAGUG AUCCGGUGGU UCCGCAUGGA AGGGCCAUCG CUCAACGGAU AAAAGCUACC CCGGGGAUAA CAGGCUUAU CUCCCCCAAG AGUCCACAUC GACGGGGAGG UUUGGCACCU CGAUGUCGGC UCAUCGCAUC CUGGGGCUGU A GUCGGUCC CAAGGGUUGG GCUGUUCGCC CAUUAAAGCG GUACGCGAGC UGGGUUCAGA ACGUCGUGAG ACAGUUCGGU CC CUAUCCG UCGCGGGCGC AGGAAAUUUG AGAGGAGCUG UCCUUAGUAC GAGAGGACCG GGAUGGACGC ACCGCUGGUG UAC CAGUUG UUCUGCCAAG GGCAUCGCUG GGUAGCUAUG UGCGGACGGG AUAAGUGCUG AAAGCAUCUA AGCAUGAAGC CCCC CUCAA GAUGAGAUUU CCCAUUCCGC AAGGAAGUAA GAUCCCUGAA AGAUGAUCAG GUUGAUAGGU CUGAGGUGGA AGUGU GGCG ACACAUGGAG CUGACAGAUA CUAAUCGAUC GAGGACUUAA CC |
-Experimental details
-Structure determination
| Method | cryo EM |
|---|---|
 Processing Processing | single particle reconstruction |
| Aggregation state | particle |
- Sample preparation
Sample preparation
| Buffer | pH: 7.5 |
|---|---|
| Vitrification | Cryogen name: ETHANE |
- Electron microscopy
Electron microscopy
| Microscope | FEI TITAN KRIOS |
|---|---|
| Image recording | Film or detector model: GATAN K2 SUMMIT (4k x 4k) / Detector mode: COUNTING / Number grids imaged: 2 / Average electron dose: 29.0 e/Å2 |
| Electron beam | Acceleration voltage: 300 kV / Electron source:  FIELD EMISSION GUN FIELD EMISSION GUN |
| Electron optics | Illumination mode: FLOOD BEAM / Imaging mode: BRIGHT FIELD |
| Experimental equipment |  Model: Titan Krios / Image courtesy: FEI Company |
 Movie
Movie Controller
Controller











 Z (Sec.)
Z (Sec.) Y (Row.)
Y (Row.) X (Col.)
X (Col.)