[English] 日本語
 Yorodumi
Yorodumi- PDB-7as9: Bacillus subtilis ribosome-associated quality control complex sta... -
+ Open data
Open data
- Basic information
Basic information
| Entry | Database: PDB / ID: 7as9 | ||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
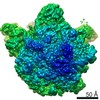
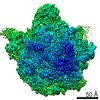
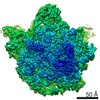
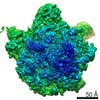
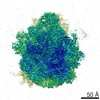
| Title | Bacillus subtilis ribosome-associated quality control complex state A. Ribosomal 50S subunit with peptidyl tRNA in the A/P position and RqcH. | ||||||||||||||||||
 Components Components |
| ||||||||||||||||||
 Keywords Keywords | TRANSLATION / 50S / tRNA / RQC / RqcH / peptidyl-tRNA | ||||||||||||||||||
| Function / homology |  Function and homology information Function and homology informationRQC complex / positive regulation of rRNA processing / nucleoid / ribosomal large subunit binding / rescue of stalled cytosolic ribosome / rRNA processing / large ribosomal subunit / transferase activity / ribosomal large subunit assembly / 5S rRNA binding ...RQC complex / positive regulation of rRNA processing / nucleoid / ribosomal large subunit binding / rescue of stalled cytosolic ribosome / rRNA processing / large ribosomal subunit / transferase activity / ribosomal large subunit assembly / 5S rRNA binding / large ribosomal subunit rRNA binding / cytosolic large ribosomal subunit / cytoplasmic translation / tRNA binding / negative regulation of translation / rRNA binding / structural constituent of ribosome / ribosome / translation / ribonucleoprotein complex / response to antibiotic / mRNA binding / DNA binding / RNA binding / cytoplasm Similarity search - Function | ||||||||||||||||||
| Biological species |   | ||||||||||||||||||
| Method | ELECTRON MICROSCOPY / single particle reconstruction / cryo EM / Resolution: 3.5 Å | ||||||||||||||||||
 Authors Authors | Crowe-McAuliffe, C. / Wilson, D.N. | ||||||||||||||||||
| Funding support |  Germany, Germany,  Sweden, 5items Sweden, 5items
| ||||||||||||||||||
 Citation Citation |  Journal: Mol Cell / Year: 2021 Journal: Mol Cell / Year: 2021Title: Structural Basis for Bacterial Ribosome-Associated Quality Control by RqcH and RqcP. Authors: Caillan Crowe-McAuliffe / Hiraku Takada / Victoriia Murina / Christine Polte / Sergo Kasvandik / Tanel Tenson / Zoya Ignatova / Gemma C Atkinson / Daniel N Wilson / Vasili Hauryliuk /    Abstract: In all branches of life, stalled translation intermediates are recognized and processed by ribosome-associated quality control (RQC) pathways. RQC begins with the splitting of stalled ribosomes, ...In all branches of life, stalled translation intermediates are recognized and processed by ribosome-associated quality control (RQC) pathways. RQC begins with the splitting of stalled ribosomes, leaving an unfinished polypeptide still attached to the large subunit. Ancient and conserved NEMF family RQC proteins target these incomplete proteins for degradation by the addition of C-terminal "tails." How such tailing can occur without the regular suite of translational components is, however, unclear. Using single-particle cryo-electron microscopy (EM) of native complexes, we show that C-terminal tailing in Bacillus subtilis is mediated by NEMF protein RqcH in concert with RqcP, an Hsp15 family protein. Our structures reveal how these factors mediate tRNA movement across the ribosomal 50S subunit to synthesize polypeptides in the absence of mRNA or the small subunit. | ||||||||||||||||||
| History |
|
- Structure visualization
Structure visualization
| Movie |
 Movie viewer Movie viewer |
|---|---|
| Structure viewer | Molecule:  Molmil Molmil Jmol/JSmol Jmol/JSmol |
- Downloads & links
Downloads & links
- Download
Download
| PDBx/mmCIF format |  7as9.cif.gz 7as9.cif.gz | 2 MB | Display |  PDBx/mmCIF format PDBx/mmCIF format |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| PDB format |  pdb7as9.ent.gz pdb7as9.ent.gz | 1.6 MB | Display |  PDB format PDB format |
| PDBx/mmJSON format |  7as9.json.gz 7as9.json.gz | Tree view |  PDBx/mmJSON format PDBx/mmJSON format | |
| Others |  Other downloads Other downloads |
-Validation report
| Arichive directory |  https://data.pdbj.org/pub/pdb/validation_reports/as/7as9 https://data.pdbj.org/pub/pdb/validation_reports/as/7as9 ftp://data.pdbj.org/pub/pdb/validation_reports/as/7as9 ftp://data.pdbj.org/pub/pdb/validation_reports/as/7as9 | HTTPS FTP |
|---|
-Related structure data
| Related structure data |  11890MC  7as8C  7asaC M: map data used to model this data C: citing same article ( |
|---|---|
| Similar structure data | |
| EM raw data |  EMPIAR-10540 (Title: Affinity-purified RqcH-ribosome-associated quality control complexes from Bacillus subtilis EMPIAR-10540 (Title: Affinity-purified RqcH-ribosome-associated quality control complexes from Bacillus subtilisData size: 514.6 Data #1: Unaligned multi-frame micrographs of affinity-purified RqcH ribosome-associated quality control complexes from Bacillus subtilis [micrographs - multiframe]) |
- Links
Links
- Assembly
Assembly
| Deposited unit | 
|
|---|---|
| 1 |
|
- Components
Components
-Protein , 1 types, 1 molecules 0
| #1: Protein | Mass: 68341.391 Da / Num. of mol.: 1 Source method: isolated from a genetically manipulated source Source: (gene. exp.)  Strain: 168 / Gene: rqcH, yloA, BSU15640 / Production host:  |
|---|
-RNA chain , 3 types, 3 molecules 2AB
| #2: RNA chain | Mass: 24491.547 Da / Num. of mol.: 1 / Source method: isolated from a natural source Source: (natural)  |
|---|---|
| #3: RNA chain | Mass: 949010.938 Da / Num. of mol.: 1 / Source method: isolated from a natural source Source: (natural)  |
| #4: RNA chain | Mass: 38423.863 Da / Num. of mol.: 1 / Source method: isolated from a natural source Source: (natural)  |
+50S ribosomal protein ... , 28 types, 28 molecules EFGHIKLNOPQRSTUVWXYabcdfghij
-Details
| Has protein modification | Y |
|---|
-Experimental details
-Experiment
| Experiment | Method: ELECTRON MICROSCOPY |
|---|---|
| EM experiment | Aggregation state: PARTICLE / 3D reconstruction method: single particle reconstruction |
- Sample preparation
Sample preparation
| Component |
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Molecular weight | Value: 1.6 MDa / Experimental value: NO | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Source (natural) |
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Source (recombinant) | Organism:  | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Buffer solution | pH: 7.5 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Specimen | Embedding applied: NO / Shadowing applied: NO / Staining applied: NO / Vitrification applied: YES | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Vitrification | Cryogen name: ETHANE |
- Electron microscopy imaging
Electron microscopy imaging
| Experimental equipment |  Model: Titan Krios / Image courtesy: FEI Company |
|---|---|
| Microscopy | Model: FEI TITAN KRIOS |
| Electron gun | Electron source:  FIELD EMISSION GUN / Accelerating voltage: 300 kV / Illumination mode: FLOOD BEAM FIELD EMISSION GUN / Accelerating voltage: 300 kV / Illumination mode: FLOOD BEAM |
| Electron lens | Mode: BRIGHT FIELD |
| Image recording | Electron dose: 29 e/Å2 / Detector mode: COUNTING / Film or detector model: GATAN K2 SUMMIT (4k x 4k) / Num. of grids imaged: 2 |
- Processing
Processing
| CTF correction | Type: PHASE FLIPPING AND AMPLITUDE CORRECTION |
|---|---|
| 3D reconstruction | Resolution: 3.5 Å / Resolution method: FSC 0.143 CUT-OFF / Num. of particles: 10703 / Symmetry type: POINT |
 Movie
Movie Controller
Controller






 PDBj
PDBj





























