+ Open data
Open data
- Basic information
Basic information
| Entry | Database: PDB / ID: 7r7s | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
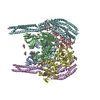
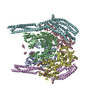
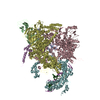
| Title | p47-bound p97-R155H mutant with ATPgammaS | ||||||
 Components Components |
| ||||||
 Keywords Keywords | HYDROLASE/Lipid Binding Protein / AAA+ ATPase / MOTOR PROTEIN / HYDROLASE / HYDROLASE-Lipid Binding Protein complex | ||||||
| Function / homology |  Function and homology information Function and homology informationnegative regulation of protein localization to centrosome / RHOH GTPase cycle / positive regulation of mitotic centrosome separation / nuclear membrane reassembly / Golgi stack / positive regulation of Lys63-specific deubiquitinase activity / spindle pole centrosome / flavin adenine dinucleotide catabolic process / positive regulation of oxidative phosphorylation / VCP-NSFL1C complex ...negative regulation of protein localization to centrosome / RHOH GTPase cycle / positive regulation of mitotic centrosome separation / nuclear membrane reassembly / Golgi stack / positive regulation of Lys63-specific deubiquitinase activity / spindle pole centrosome / flavin adenine dinucleotide catabolic process / positive regulation of oxidative phosphorylation / VCP-NSFL1C complex / cytoplasm protein quality control / endosome to lysosome transport via multivesicular body sorting pathway / endoplasmic reticulum stress-induced pre-emptive quality control / cellular response to arsenite ion / Derlin-1 retrotranslocation complex / BAT3 complex binding / protein-DNA covalent cross-linking repair / positive regulation of protein K63-linked deubiquitination / deubiquitinase activator activity / ubiquitin-modified protein reader activity / regulation of protein localization to chromatin / aggresome assembly / NADH metabolic process / mitotic spindle disassembly / VCP-NPL4-UFD1 AAA ATPase complex / vesicle-fusing ATPase / cellular response to misfolded protein / stress granule disassembly / negative regulation of protein localization to chromatin / positive regulation of mitochondrial membrane potential / retrograde protein transport, ER to cytosol / K48-linked polyubiquitin modification-dependent protein binding / regulation of aerobic respiration / regulation of synapse organization / positive regulation of ATP biosynthetic process / ATPase complex / ubiquitin-specific protease binding / Golgi organization / MHC class I protein binding / ubiquitin-like protein ligase binding / establishment of mitotic spindle orientation / RHOH GTPase cycle / autophagosome assembly / polyubiquitin modification-dependent protein binding / autophagosome maturation / HSF1 activation / negative regulation of hippo signaling / endoplasmic reticulum to Golgi vesicle-mediated transport / translesion synthesis / proteasomal protein catabolic process / Protein methylation / interstrand cross-link repair / ATP metabolic process / negative regulation of smoothened signaling pathway / endoplasmic reticulum unfolded protein response / ERAD pathway / Attachment and Entry / proteasome complex / viral genome replication / lipid droplet / Josephin domain DUBs / N-glycan trimming in the ER and Calnexin/Calreticulin cycle / ubiquitin binding / Hh mutants are degraded by ERAD / macroautophagy / Hedgehog ligand biogenesis / Defective CFTR causes cystic fibrosis / positive regulation of protein-containing complex assembly / ADP binding / Translesion Synthesis by POLH / establishment of protein localization / ABC-family proteins mediated transport / : / autophagy / Aggrephagy / cytoplasmic stress granule / positive regulation of non-canonical NF-kappaB signal transduction / positive regulation of protein catabolic process / azurophil granule lumen / KEAP1-NFE2L2 pathway / positive regulation of canonical Wnt signaling pathway / Ovarian tumor domain proteases / double-strand break repair / positive regulation of proteasomal ubiquitin-dependent protein catabolic process / E3 ubiquitin ligases ubiquitinate target proteins / site of double-strand break / Neddylation / chromosome / cellular response to heat / ATPase binding / ubiquitin-dependent protein catabolic process / protein phosphatase binding / secretory granule lumen / regulation of apoptotic process / proteasome-mediated ubiquitin-dependent protein catabolic process / ficolin-1-rich granule lumen / membrane fusion / Attachment and Entry / protein ubiquitination / protein domain specific binding Similarity search - Function | ||||||
| Biological species |  Homo sapiens (human) Homo sapiens (human) | ||||||
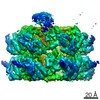
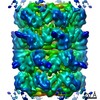
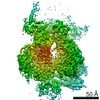
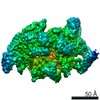
| Method | ELECTRON MICROSCOPY / single particle reconstruction / cryo EM / Resolution: 4.23 Å | ||||||
 Authors Authors | Nandi, P. / Li, S. / Coulmbres, R.C.A. / Wang, F. / Williams, D.R. / Malyutin, A.G. / Poh, Y.-P. / Chou, T.-F. / Chiu, P.-L. | ||||||
| Funding support |  United States, 1items United States, 1items
| ||||||
 Citation Citation |  Journal: Int J Mol Sci / Year: 2021 Journal: Int J Mol Sci / Year: 2021Title: Structural and Functional Analysis of Disease-Linked p97 ATPase Mutant Complexes. Authors: Purbasha Nandi / Shan Li / Rod Carlo A Columbres / Feng Wang / Dewight R Williams / Yu-Ping Poh / Tsui-Fen Chou / Po-Lin Chiu /  Abstract: IBMPFD/ALS is a genetic disorder caused by a single amino acid mutation on the p97 ATPase, promoting ATPase activity and cofactor dysregulation. The disease mechanism underlying p97 ATPase ...IBMPFD/ALS is a genetic disorder caused by a single amino acid mutation on the p97 ATPase, promoting ATPase activity and cofactor dysregulation. The disease mechanism underlying p97 ATPase malfunction remains unclear. To understand how the mutation alters the ATPase regulation, we assembled a full-length p97 with its p47 cofactor and first visualized their structures using single-particle cryo-EM. More than one-third of the population was the dodecameric form. Nucleotide presence dissociates the dodecamer into two hexamers for its highly elevated function. The N-domains of the p97 mutant all show up configurations in ADP- or ATPS-bound states. Our functional and structural analyses showed that the p47 binding is likely to impact the p97 ATPase activities via changing the conformations of arginine fingers. These functional and structural analyses underline the ATPase dysregulation with the miscommunication between the functional modules of the p97. | ||||||
| History |
|
- Structure visualization
Structure visualization
| Movie |
 Movie viewer Movie viewer |
|---|---|
| Structure viewer | Molecule:  Molmil Molmil Jmol/JSmol Jmol/JSmol |
- Downloads & links
Downloads & links
- Download
Download
| PDBx/mmCIF format |  7r7s.cif.gz 7r7s.cif.gz | 728.7 KB | Display |  PDBx/mmCIF format PDBx/mmCIF format |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| PDB format |  pdb7r7s.ent.gz pdb7r7s.ent.gz | 603.4 KB | Display |  PDB format PDB format |
| PDBx/mmJSON format |  7r7s.json.gz 7r7s.json.gz | Tree view |  PDBx/mmJSON format PDBx/mmJSON format | |
| Others |  Other downloads Other downloads |
-Validation report
| Summary document |  7r7s_validation.pdf.gz 7r7s_validation.pdf.gz | 1.6 MB | Display |  wwPDB validaton report wwPDB validaton report |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Full document |  7r7s_full_validation.pdf.gz 7r7s_full_validation.pdf.gz | 1.7 MB | Display | |
| Data in XML |  7r7s_validation.xml.gz 7r7s_validation.xml.gz | 108.5 KB | Display | |
| Data in CIF |  7r7s_validation.cif.gz 7r7s_validation.cif.gz | 165.1 KB | Display | |
| Arichive directory |  https://data.pdbj.org/pub/pdb/validation_reports/r7/7r7s https://data.pdbj.org/pub/pdb/validation_reports/r7/7r7s ftp://data.pdbj.org/pub/pdb/validation_reports/r7/7r7s ftp://data.pdbj.org/pub/pdb/validation_reports/r7/7r7s | HTTPS FTP |
-Related structure data
| Related structure data |  24302MC  7l5wC  7l5xC  7r7tC  7r7uC M: map data used to model this data C: citing same article ( |
|---|---|
| Similar structure data | |
| EM raw data |  EMPIAR-10920 (Title: Cryo-EM dataset of mutant p97R155H-p47 in presence of ATPγS collected using Thermo Fisher/FEI Titan Krios TEM Gatan K2 Summit DED camera EMPIAR-10920 (Title: Cryo-EM dataset of mutant p97R155H-p47 in presence of ATPγS collected using Thermo Fisher/FEI Titan Krios TEM Gatan K2 Summit DED cameraData size: 280.3 Data #1: Motion corrected dose-weighted micrographs for the cryo-EM dataset of disease mutant p97R155H-p47 in presence of ADP. [micrographs - single frame]) |
- Links
Links
- Assembly
Assembly
| Deposited unit | 
|
|---|---|
| 1 |
|
- Components
Components
| #1: Protein | Mass: 89417.773 Da / Num. of mol.: 6 Source method: isolated from a genetically manipulated source Source: (gene. exp.)  Homo sapiens (human) / Gene: VCP / Production host: Homo sapiens (human) / Gene: VCP / Production host:  #2: Protein | Mass: 40731.855 Da / Num. of mol.: 2 Source method: isolated from a genetically manipulated source Source: (gene. exp.)   #3: Chemical | ChemComp-AGS / Has ligand of interest | Y | |
|---|
-Experimental details
-Experiment
| Experiment | Method: ELECTRON MICROSCOPY |
|---|---|
| EM experiment | Aggregation state: PARTICLE / 3D reconstruction method: single particle reconstruction |
- Sample preparation
Sample preparation
| Component | Name: p47-bound p97-R155H mutant with ATPgammaS / Type: COMPLEX / Details: p47-bound p97-R155H mutant with ATPgammaS / Entity ID: #1-#2 / Source: RECOMBINANT | ||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Molecular weight | Value: 0.723 MDa / Experimental value: NO | ||||||||||||||||||||
| Source (natural) | Organism:  Homo sapiens (human) Homo sapiens (human) | ||||||||||||||||||||
| Source (recombinant) | Organism: Escherichia virus LL11 / Strain: BL21 | ||||||||||||||||||||
| Buffer solution | pH: 7.4 | ||||||||||||||||||||
| Buffer component |
| ||||||||||||||||||||
| Specimen | Conc.: 0.2 mg/ml / Embedding applied: NO / Shadowing applied: NO / Staining applied: NO / Vitrification applied: YES / Details: The protein sample was monodisperse. | ||||||||||||||||||||
| Specimen support | Grid type: C-flat-2/1 | ||||||||||||||||||||
| Vitrification | Instrument: FEI VITROBOT MARK IV / Cryogen name: ETHANE / Humidity: 100 % / Chamber temperature: 292 K / Details: The grid was blotted for 6 seconds. |
- Electron microscopy imaging
Electron microscopy imaging
| Experimental equipment |  Model: Titan Krios / Image courtesy: FEI Company |
|---|---|
| Microscopy | Model: FEI TITAN KRIOS |
| Electron gun | Electron source:  FIELD EMISSION GUN / Accelerating voltage: 300 kV / Illumination mode: FLOOD BEAM FIELD EMISSION GUN / Accelerating voltage: 300 kV / Illumination mode: FLOOD BEAM |
| Electron lens | Mode: BRIGHT FIELD / Nominal magnification: 48077 X / Nominal defocus max: -2500 nm / Nominal defocus min: -800 nm / Cs: 2.7 mm / C2 aperture diameter: 50 µm / Alignment procedure: COMA FREE |
| Specimen holder | Cryogen: NITROGEN / Specimen holder model: FEI TITAN KRIOS AUTOGRID HOLDER / Residual tilt: 0.001 mradians |
| Image recording | Electron dose: 44.4 e/Å2 / Detector mode: SUPER-RESOLUTION / Film or detector model: GATAN K2 SUMMIT (4k x 4k) / Num. of real images: 2796 |
| Image scans | Sampling size: 5 µm |
- Processing
Processing
| Software | Name: PHENIX / Version: 1.18.2_3874: / Classification: refinement | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| EM software |
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| CTF correction | Type: PHASE FLIPPING AND AMPLITUDE CORRECTION | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Particle selection | Num. of particles selected: 401303 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
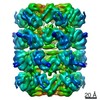
| 3D reconstruction | Resolution: 4.23 Å / Resolution method: FSC 0.143 CUT-OFF / Num. of particles: 63353 / Algorithm: BACK PROJECTION / Symmetry type: POINT | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Atomic model building | B value: 124.8 / Protocol: OTHER / Space: REAL / Target criteria: CC | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Atomic model building | PDB-ID: 5FTN Accession code: 5FTN / Source name: PDB / Type: experimental model | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Refine LS restraints |
|
 Movie
Movie Controller
Controller








 PDBj
PDBj