[English] 日本語
 Yorodumi
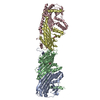
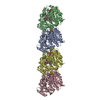
Yorodumi- PDB-7mta: Rhodopsin kinase (GRK1)-S5E/S488E/T489E in complex with rhodopsin... -
+ Open data
Open data
- Basic information
Basic information
| Entry | Database: PDB / ID: 7mta | |||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Title | Rhodopsin kinase (GRK1)-S5E/S488E/T489E in complex with rhodopsin and Fab1 | |||||||||||||||
 Components Components |
| |||||||||||||||
 Keywords Keywords | MEMBRANE / Signaling protein/Immune System / GPCR / signal desensitization / Kinase / MEMBRANE PROTEIN / Signaling protein-Immune System complex | |||||||||||||||
| Function / homology |  Function and homology information Function and homology informationrhodopsin kinase / rhodopsin kinase activity / Opsins / VxPx cargo-targeting to cilium / regulation of opsin-mediated signaling pathway / rod bipolar cell differentiation / sperm head plasma membrane / absorption of visible light / opsin binding / The canonical retinoid cycle in rods (twilight vision) ...rhodopsin kinase / rhodopsin kinase activity / Opsins / VxPx cargo-targeting to cilium / regulation of opsin-mediated signaling pathway / rod bipolar cell differentiation / sperm head plasma membrane / absorption of visible light / opsin binding / The canonical retinoid cycle in rods (twilight vision) / G protein-coupled opsin signaling pathway / 11-cis retinal binding / podosome assembly / G protein-coupled photoreceptor activity / photoreceptor inner segment membrane / cellular response to light stimulus / rod photoreceptor outer segment / G protein-coupled receptor complex / Inactivation, recovery and regulation of the phototransduction cascade / thermotaxis / Activation of the phototransduction cascade / outer membrane / detection of temperature stimulus involved in thermoception / response to light intensity / photoreceptor cell maintenance / arrestin family protein binding / photoreceptor outer segment membrane / G alpha (i) signalling events / response to light stimulus / phototransduction, visible light / phototransduction / G-protein alpha-subunit binding / regulation of signal transduction / photoreceptor outer segment / visual perception / guanyl-nucleotide exchange factor activity / microtubule cytoskeleton organization / cell-cell junction / photoreceptor disc membrane / sperm midpiece / protein autophosphorylation / gene expression / G protein-coupled receptor signaling pathway / Golgi membrane / signal transduction / zinc ion binding / ATP binding / identical protein binding / membrane / plasma membrane / cytoplasm Similarity search - Function | |||||||||||||||
| Biological species |   Homo sapiens (human) Homo sapiens (human) | |||||||||||||||
| Method | ELECTRON MICROSCOPY / single particle reconstruction / cryo EM / Resolution: 4.1 Å | |||||||||||||||
 Authors Authors | Chen, Q. / Chen, C.-L. / Tesmer, J.J.G. | |||||||||||||||
| Funding support |  United States, 4items United States, 4items
| |||||||||||||||
 Citation Citation |  Journal: Nature / Year: 2021 Journal: Nature / Year: 2021Title: Structures of rhodopsin in complex with G-protein-coupled receptor kinase 1. Authors: Qiuyan Chen / Manolo Plasencia / Zhuang Li / Somnath Mukherjee / Dhabaleswar Patra / Chun-Liang Chen / Thomas Klose / Xin-Qiu Yao / Anthony A Kossiakoff / Leifu Chang / Philip C Andrews / John J G Tesmer /  Abstract: G-protein-coupled receptor (GPCR) kinases (GRKs) selectively phosphorylate activated GPCRs, thereby priming them for desensitization. Although it is unclear how GRKs recognize these receptors, a ...G-protein-coupled receptor (GPCR) kinases (GRKs) selectively phosphorylate activated GPCRs, thereby priming them for desensitization. Although it is unclear how GRKs recognize these receptors, a conserved region at the GRK N terminus is essential for this process. Here we report a series of cryo-electron microscopy single-particle reconstructions of light-activated rhodopsin (Rho*) bound to rhodopsin kinase (GRK1), wherein the N terminus of GRK1 forms a helix that docks into the open cytoplasmic cleft of Rho*. The helix also packs against the GRK1 kinase domain and stabilizes it in an active configuration. The complex is further stabilized by electrostatic interactions between basic residues that are conserved in most GPCRs and acidic residues that are conserved in GRKs. We did not observe any density for the regulator of G-protein signalling homology domain of GRK1 or the C terminus of rhodopsin. Crosslinking with mass spectrometry analysis confirmed these results and revealed dynamic behaviour in receptor-bound GRK1 that would allow the phosphorylation of multiple sites in the receptor tail. We have identified GRK1 residues whose mutation augments kinase activity and crosslinking with Rho*, as well as residues that are involved in activation by acidic phospholipids. From these data, we present a general model for how a small family of protein kinases can recognize and be activated by hundreds of different GPCRs. | |||||||||||||||
| History |
|
- Structure visualization
Structure visualization
| Movie |
 Movie viewer Movie viewer |
|---|---|
| Structure viewer | Molecule:  Molmil Molmil Jmol/JSmol Jmol/JSmol |
- Downloads & links
Downloads & links
- Download
Download
| PDBx/mmCIF format |  7mta.cif.gz 7mta.cif.gz | 1 MB | Display |  PDBx/mmCIF format PDBx/mmCIF format |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| PDB format |  pdb7mta.ent.gz pdb7mta.ent.gz | 876.4 KB | Display |  PDB format PDB format |
| PDBx/mmJSON format |  7mta.json.gz 7mta.json.gz | Tree view |  PDBx/mmJSON format PDBx/mmJSON format | |
| Others |  Other downloads Other downloads |
-Validation report
| Arichive directory |  https://data.pdbj.org/pub/pdb/validation_reports/mt/7mta https://data.pdbj.org/pub/pdb/validation_reports/mt/7mta ftp://data.pdbj.org/pub/pdb/validation_reports/mt/7mta ftp://data.pdbj.org/pub/pdb/validation_reports/mt/7mta | HTTPS FTP |
|---|
-Related structure data
| Related structure data |  23979MC  7mt8C  7mt9C 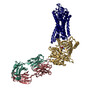 7mtbC M: map data used to model this data C: citing same article ( |
|---|---|
| Similar structure data |
- Links
Links
- Assembly
Assembly
| Deposited unit | 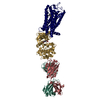
|
|---|---|
| 1 |
|
| Number of models | 6 |
- Components
Components
-Protein , 2 types, 2 molecules GR
| #1: Protein | Mass: 61542.012 Da / Num. of mol.: 1 / Mutation: S5E, S488E, T489E Source method: isolated from a genetically manipulated source Source: (gene. exp.)   |
|---|---|
| #4: Protein | Mass: 39031.457 Da / Num. of mol.: 1 / Source method: isolated from a natural source / Source: (natural)  |
-Antibody , 2 types, 2 molecules HL
| #2: Antibody | Mass: 24999.779 Da / Num. of mol.: 1 Source method: isolated from a genetically manipulated source Source: (gene. exp.)  Homo sapiens (human) / Production host: Homo sapiens (human) / Production host:  |
|---|---|
| #3: Antibody | Mass: 23786.396 Da / Num. of mol.: 1 Source method: isolated from a genetically manipulated source Source: (gene. exp.)  Homo sapiens (human) / Production host: Homo sapiens (human) / Production host:  |
-Non-polymers , 2 types, 2 molecules 
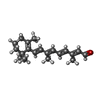

| #5: Chemical | ChemComp-SGV / |
|---|---|
| #6: Chemical | ChemComp-RET / |
-Details
| Has ligand of interest | N |
|---|---|
| Has protein modification | Y |
-Experimental details
-Experiment
| Experiment | Method: ELECTRON MICROSCOPY |
|---|---|
| EM experiment | Aggregation state: PARTICLE / 3D reconstruction method: single particle reconstruction |
- Sample preparation
Sample preparation
| Component |
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Source (natural) |
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Buffer solution | pH: 8 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Specimen | Embedding applied: NO / Shadowing applied: NO / Staining applied: NO / Vitrification applied: YES | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Vitrification | Cryogen name: ETHANE |
- Electron microscopy imaging
Electron microscopy imaging
| Experimental equipment |  Model: Titan Krios / Image courtesy: FEI Company |
|---|---|
| Microscopy | Model: FEI TITAN KRIOS |
| Electron gun | Electron source:  FIELD EMISSION GUN / Accelerating voltage: 300 kV / Illumination mode: FLOOD BEAM FIELD EMISSION GUN / Accelerating voltage: 300 kV / Illumination mode: FLOOD BEAM |
| Electron lens | Mode: BRIGHT FIELD |
| Image recording | Electron dose: 54 e/Å2 / Film or detector model: GATAN K3 BIOQUANTUM (6k x 4k) |
- Processing
Processing
| CTF correction | Type: PHASE FLIPPING AND AMPLITUDE CORRECTION |
|---|---|
| 3D reconstruction | Resolution: 4.1 Å / Resolution method: FSC 0.143 CUT-OFF / Num. of particles: 310363 / Symmetry type: POINT |
 Movie
Movie Controller
Controller







 PDBj
PDBj
















