+Search query
-Structure paper
| Title | Structures of rhodopsin in complex with G-protein-coupled receptor kinase 1. |
|---|---|
| Journal, issue, pages | Nature, Vol. 595, Issue 7868, Page 600-605, Year 2021 |
| Publish date | Jul 14, 2021 |
 Authors Authors | Qiuyan Chen / Manolo Plasencia / Zhuang Li / Somnath Mukherjee / Dhabaleswar Patra / Chun-Liang Chen / Thomas Klose / Xin-Qiu Yao / Anthony A Kossiakoff / Leifu Chang / Philip C Andrews / John J G Tesmer /  |
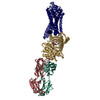
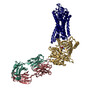
| PubMed Abstract | G-protein-coupled receptor (GPCR) kinases (GRKs) selectively phosphorylate activated GPCRs, thereby priming them for desensitization. Although it is unclear how GRKs recognize these receptors, a ...G-protein-coupled receptor (GPCR) kinases (GRKs) selectively phosphorylate activated GPCRs, thereby priming them for desensitization. Although it is unclear how GRKs recognize these receptors, a conserved region at the GRK N terminus is essential for this process. Here we report a series of cryo-electron microscopy single-particle reconstructions of light-activated rhodopsin (Rho*) bound to rhodopsin kinase (GRK1), wherein the N terminus of GRK1 forms a helix that docks into the open cytoplasmic cleft of Rho*. The helix also packs against the GRK1 kinase domain and stabilizes it in an active configuration. The complex is further stabilized by electrostatic interactions between basic residues that are conserved in most GPCRs and acidic residues that are conserved in GRKs. We did not observe any density for the regulator of G-protein signalling homology domain of GRK1 or the C terminus of rhodopsin. Crosslinking with mass spectrometry analysis confirmed these results and revealed dynamic behaviour in receptor-bound GRK1 that would allow the phosphorylation of multiple sites in the receptor tail. We have identified GRK1 residues whose mutation augments kinase activity and crosslinking with Rho*, as well as residues that are involved in activation by acidic phospholipids. From these data, we present a general model for how a small family of protein kinases can recognize and be activated by hundreds of different GPCRs. |
 External links External links |  Nature / Nature /  PubMed:34262173 / PubMed:34262173 /  PubMed Central PubMed Central |
| Methods | EM (single particle) |
| Resolution | 4.0 - 7.0 Å |
| Structure data | EMDB-23977, PDB-7mt8: EMDB-23978, PDB-7mt9: EMDB-23979, PDB-7mta: EMDB-23980, PDB-7mtb: |
| Chemicals |  ChemComp-SGV: 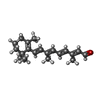 ChemComp-RET: |
| Source |
|
 Keywords Keywords | MEMBRANE PROTEIN / Signaling protein / GPCR / signal desensitization / Kinase / MEMBRANE PROTEIN/Signaling protein / MEMBRANE PROTEIN-Signaling protein complex / MEMBRANE / Signaling protein/Immune System / Signaling protein-Immune System complex / MEMBRANE PROTEIN-Immune System complex |
 Movie
Movie Controller
Controller Structure viewers
Structure viewers About Yorodumi Papers
About Yorodumi Papers









 homo sapiens (human)
homo sapiens (human)