+ データを開く
データを開く
- 基本情報
基本情報
| 登録情報 | データベース: PDB / ID: 7krj | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
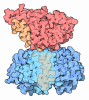
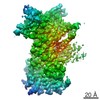
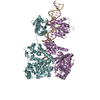
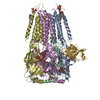
| タイトル | The GR-Maturation Complex: Glucocorticoid Receptor in complex with Hsp90 and co-chaperone p23 | ||||||
 要素 要素 |
| ||||||
 キーワード キーワード | CHAPERONE / ligand binding / ATP binding / protein folding / cryo-EM | ||||||
| 機能・相同性 |  機能・相同性情報 機能・相同性情報prostaglandin-E synthase / prostaglandin-E synthase activity / Regulation of NPAS4 gene transcription / regulation of glucocorticoid biosynthetic process / nuclear glucocorticoid receptor activity / prostanoid biosynthetic process / telomerase activity / Aryl hydrocarbon receptor signalling / steroid hormone binding / glucocorticoid metabolic process ...prostaglandin-E synthase / prostaglandin-E synthase activity / Regulation of NPAS4 gene transcription / regulation of glucocorticoid biosynthetic process / nuclear glucocorticoid receptor activity / prostanoid biosynthetic process / telomerase activity / Aryl hydrocarbon receptor signalling / steroid hormone binding / glucocorticoid metabolic process / response to cortisol / PTK6 Expression / neuroinflammatory response / Synthesis of Prostaglandins (PG) and Thromboxanes (TX) / mammary gland duct morphogenesis / microglia differentiation / maternal behavior / astrocyte differentiation / telomerase holoenzyme complex / prostaglandin biosynthetic process / protein folding chaperone complex / adrenal gland development / regulation of gluconeogenesis / cellular response to glucocorticoid stimulus / sperm mitochondrial sheath / sulfonylurea receptor binding / dATP binding / CTP binding / positive regulation of protein polymerization / Scavenging by Class F Receptors / vRNP Assembly / UTP binding / cellular response to steroid hormone stimulus / sperm plasma membrane / chaperone-mediated autophagy / Rho GDP-dissociation inhibitor binding / Respiratory syncytial virus genome replication / telomerase holoenzyme complex assembly / mitochondrial transport / Uptake and function of diphtheria toxin / Drug-mediated inhibition of ERBB2 signaling / Resistance of ERBB2 KD mutants to trastuzumab / Resistance of ERBB2 KD mutants to sapitinib / Resistance of ERBB2 KD mutants to tesevatinib / Resistance of ERBB2 KD mutants to neratinib / Resistance of ERBB2 KD mutants to osimertinib / Resistance of ERBB2 KD mutants to afatinib / Resistance of ERBB2 KD mutants to AEE788 / Resistance of ERBB2 KD mutants to lapatinib / Drug resistance in ERBB2 TMD/JMD mutants / protein import into mitochondrial matrix / TPR domain binding / dendritic growth cone / motor behavior / Assembly and release of respiratory syncytial virus (RSV) virions / PIWI-interacting RNA (piRNA) biogenesis / non-chaperonin molecular chaperone ATPase / : / Sema3A PAK dependent Axon repulsion / protein unfolding / regulation of protein ubiquitination / positive regulation of cell size / HSF1-dependent transactivation / estrogen response element binding / response to unfolded protein / enzyme-substrate adaptor activity / cellular response to dexamethasone stimulus / HSF1 activation / skeletal muscle contraction / nuclear receptor-mediated steroid hormone signaling pathway / regulation of protein-containing complex assembly / FOXO-mediated transcription of oxidative stress, metabolic and neuronal genes / telomere maintenance via telomerase / Attenuation phase / chaperone-mediated protein complex assembly / regulation of postsynaptic membrane neurotransmitter receptor levels / cellular response to transforming growth factor beta stimulus / axonal growth cone / neurofibrillary tangle assembly / RHOBTB2 GTPase cycle / core promoter sequence-specific DNA binding / positive regulation of lamellipodium assembly / nitric oxide metabolic process / eNOS activation / Tetrahydrobiopterin (BH4) synthesis, recycling, salvage and regulation / DNA polymerase binding / positive regulation of defense response to virus by host / response to salt stress / steroid binding / Signaling by ERBB2 / positive regulation of telomere maintenance via telomerase / cardiac muscle cell apoptotic process / endocytic vesicle lumen / positive regulation of cardiac muscle contraction / Loss of Nlp from mitotic centrosomes / Loss of proteins required for interphase microtubule organization from the centrosome / Recruitment of mitotic centrosome proteins and complexes / telomere maintenance / activation of innate immune response / lysosomal lumen 類似検索 - 分子機能 | ||||||
| 生物種 |  Homo sapiens (ヒト) Homo sapiens (ヒト) | ||||||
| 手法 | 電子顕微鏡法 / 単粒子再構成法 / クライオ電子顕微鏡法 / 解像度: 2.56 Å | ||||||
 データ登録者 データ登録者 | Noddings, C.M. / Wang, Y.-R. / Agard, D.A. | ||||||
| 資金援助 |  米国, 1件 米国, 1件
| ||||||
 引用 引用 |  ジャーナル: Nature / 年: 2022 ジャーナル: Nature / 年: 2022タイトル: Structure of Hsp90-p23-GR reveals the Hsp90 client-remodelling mechanism. 著者: Chari M Noddings / Ray Yu-Ruei Wang / Jill L Johnson / David A Agard /  要旨: Hsp90 is a conserved and essential molecular chaperone responsible for the folding and activation of hundreds of 'client' proteins. The glucocorticoid receptor (GR) is a model client that constantly ...Hsp90 is a conserved and essential molecular chaperone responsible for the folding and activation of hundreds of 'client' proteins. The glucocorticoid receptor (GR) is a model client that constantly depends on Hsp90 for activity. GR ligand binding was previously shown to nr inhibited by Hsp70 and restored by Hsp90, aided by the co-chaperone p23. However, a molecular understanding of the chaperone-mediated remodelling that occurs between the inactive Hsp70-Hsp90 'client-loading complex' and an activated Hsp90-p23 'client-maturation complex' is lacking for any client, including GR. Here we present a cryo-electron microscopy (cryo-EM) structure of the human GR-maturation complex (GR-Hsp90-p23), revealing that the GR ligand-binding domain is restored to a folded, ligand-bound conformation, while being simultaneously threaded through the Hsp90 lumen. In addition, p23 directly stabilizes native GR using a C-terminal helix, resulting in enhanced ligand binding. This structure of a client bound to Hsp90 in a native conformation contrasts sharply with the unfolded kinase-Hsp90 structure. Thus, aided by direct co-chaperone-client interactions, Hsp90 can directly dictate client-specific folding outcomes. Together with the GR-loading complex structure, we present the molecular mechanism of chaperone-mediated GR remodelling, establishing the first, to our knowledge, complete chaperone cycle for any Hsp90 client. | ||||||
| 履歴 |
|
- 構造の表示
構造の表示
| ムービー |
 ムービービューア ムービービューア |
|---|---|
| 構造ビューア | 分子:  Molmil Molmil Jmol/JSmol Jmol/JSmol |
- ダウンロードとリンク
ダウンロードとリンク
- ダウンロード
ダウンロード
| PDBx/mmCIF形式 |  7krj.cif.gz 7krj.cif.gz | 630.5 KB | 表示 |  PDBx/mmCIF形式 PDBx/mmCIF形式 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| PDB形式 |  pdb7krj.ent.gz pdb7krj.ent.gz | 522.1 KB | 表示 |  PDB形式 PDB形式 |
| PDBx/mmJSON形式 |  7krj.json.gz 7krj.json.gz | ツリー表示 |  PDBx/mmJSON形式 PDBx/mmJSON形式 | |
| その他 |  その他のダウンロード その他のダウンロード |
-検証レポート
| 文書・要旨 |  7krj_validation.pdf.gz 7krj_validation.pdf.gz | 1.4 MB | 表示 |  wwPDB検証レポート wwPDB検証レポート |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 文書・詳細版 |  7krj_full_validation.pdf.gz 7krj_full_validation.pdf.gz | 1.4 MB | 表示 | |
| XML形式データ |  7krj_validation.xml.gz 7krj_validation.xml.gz | 57.7 KB | 表示 | |
| CIF形式データ |  7krj_validation.cif.gz 7krj_validation.cif.gz | 87.3 KB | 表示 | |
| アーカイブディレクトリ |  https://data.pdbj.org/pub/pdb/validation_reports/kr/7krj https://data.pdbj.org/pub/pdb/validation_reports/kr/7krj ftp://data.pdbj.org/pub/pdb/validation_reports/kr/7krj ftp://data.pdbj.org/pub/pdb/validation_reports/kr/7krj | HTTPS FTP |
-関連構造データ
| 関連構造データ | 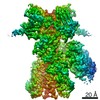 23004MC M: このデータのモデリングに利用したマップデータ C: 同じ文献を引用 ( |
|---|---|
| 類似構造データ | |
| 電子顕微鏡画像生データ |  EMPIAR-11028 (タイトル: Cryo-EM Structures of Glucocorticoid Receptor-Hsp90-p23 [the GR Maturation Complex], Hsp90-p23, and MBP-Hsp90-p23 EMPIAR-11028 (タイトル: Cryo-EM Structures of Glucocorticoid Receptor-Hsp90-p23 [the GR Maturation Complex], Hsp90-p23, and MBP-Hsp90-p23Data size: 494.1 Data #1: MotionCor2 aligned frames of GR-Hsp90-p23 collected on Gatan K3 [micrographs - single frame] Data #2: Processed subsets [picked particles - single frame - processed]) |
- リンク
リンク
- 集合体
集合体
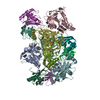
| 登録構造単位 | 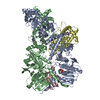
|
|---|---|
| 1 |
|
- 要素
要素
-タンパク質 , 3種, 4分子 ABCD
| #1: タンパク質 | 分子量: 84781.727 Da / 分子数: 2 / 由来タイプ: 組換発現 / 由来: (組換発現)  Homo sapiens (ヒト) / 遺伝子: HSP90AA1, HSP90A, HSPC1, HSPCA / 発現宿主: Homo sapiens (ヒト) / 遺伝子: HSP90AA1, HSP90A, HSPC1, HSPCA / 発現宿主:  #2: タンパク質 | | 分子量: 18720.395 Da / 分子数: 1 / 由来タイプ: 組換発現 / 由来: (組換発現)  Homo sapiens (ヒト) / 遺伝子: PTGES3, P23, TEBP / 発現宿主: Homo sapiens (ヒト) / 遺伝子: PTGES3, P23, TEBP / 発現宿主:  #3: タンパク質 | | 分子量: 29924.867 Da / 分子数: 1 / Mutation: F602S / 由来タイプ: 組換発現 / 由来: (組換発現)  Homo sapiens (ヒト) / 遺伝子: NR3C1, GRL / 発現宿主: Homo sapiens (ヒト) / 遺伝子: NR3C1, GRL / 発現宿主:  |
|---|
-非ポリマー , 3種, 5分子 




| #4: 化合物 | | #5: 化合物 | #6: 化合物 | ChemComp-DEX / | |
|---|
-詳細
| 研究の焦点であるリガンドがあるか | N |
|---|
-実験情報
-実験
| 実験 | 手法: 電子顕微鏡法 |
|---|---|
| EM実験 | 試料の集合状態: PARTICLE / 3次元再構成法: 単粒子再構成法 |
- 試料調製
試料調製
| 構成要素 | 名称: Complex of the Glucocorticoid Receptor ligand binding domain, Hsp90 alpha dimer, and the co-chaperone p23 タイプ: COMPLEX / Entity ID: #1-#3 / 由来: RECOMBINANT |
|---|---|
| 分子量 | 値: 0.263 MDa / 実験値: NO |
| 由来(天然) | 生物種:  Homo sapiens (ヒト) Homo sapiens (ヒト) |
| 由来(組換発現) | 生物種:  |
| 緩衝液 | pH: 7.5 |
| 試料 | 包埋: NO / シャドウイング: NO / 染色: NO / 凍結: YES |
| 試料支持 | グリッドの材料: COPPER / グリッドのサイズ: 400 divisions/in. / グリッドのタイプ: Quantifoil R1.2/1.3 |
| 急速凍結 | 装置: FEI VITROBOT MARK IV / 凍結剤: ETHANE / 湿度: 100 % / 凍結前の試料温度: 283 K |
- 電子顕微鏡撮影
電子顕微鏡撮影
| 実験機器 |  モデル: Titan Krios / 画像提供: FEI Company |
|---|---|
| 顕微鏡 | モデル: FEI TITAN KRIOS |
| 電子銃 | 電子線源:  FIELD EMISSION GUN / 加速電圧: 300 kV / 照射モード: FLOOD BEAM FIELD EMISSION GUN / 加速電圧: 300 kV / 照射モード: FLOOD BEAM |
| 電子レンズ | モード: BRIGHT FIELD / 倍率(公称値): 105000 X / 最大 デフォーカス(公称値): 2000 nm / 最小 デフォーカス(公称値): 800 nm / Cs: 2.7 mm / アライメント法: COMA FREE |
| 試料ホルダ | 凍結剤: NITROGEN 試料ホルダーモデル: FEI TITAN KRIOS AUTOGRID HOLDER |
| 撮影 | 平均露光時間: 5.9 sec. / 電子線照射量: 60 e/Å2 フィルム・検出器のモデル: GATAN K3 BIOQUANTUM (6k x 4k) 実像数: 5608 |
| 電子光学装置 | エネルギーフィルター名称: GIF Bioquantum / エネルギーフィルタースリット幅: 20 eV |
- 解析
解析
| EMソフトウェア |
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| CTF補正 | タイプ: PHASE FLIPPING AND AMPLITUDE CORRECTION | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 粒子像の選択 | 選択した粒子像数: 6062152 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 対称性 | 点対称性: C1 (非対称) | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 3次元再構成 | 解像度: 2.56 Å / 解像度の算出法: FSC 0.143 CUT-OFF / 粒子像の数: 140217 / 対称性のタイプ: POINT | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 原子モデル構築 | 3D fitting-ID: 1 / Source name: PDB / タイプ: experimental model
|
 ムービー
ムービー コントローラー
コントローラー








 PDBj
PDBj