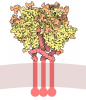
+ Open data
Open data
- Basic information
Basic information
| Entry | Database: PDB / ID: 7fdc | ||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
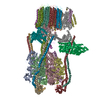
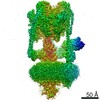
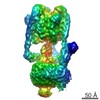
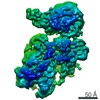
| Title | CryoEM Structures of Reconstituted V-ATPase, state3 | ||||||||||||
 Components Components |
| ||||||||||||
 Keywords Keywords | MOTOR PROTEIN / ATPase / proton pump / rotary motor enzyme / membrane protein | ||||||||||||
| Function / homology |  Function and homology information Function and homology informationBlockage of phagosome acidification / Ion channel transport / Regulation of MITF-M-dependent genes involved in lysosome biogenesis and autophagy / vacuole-mitochondrion membrane contact site / intracellular pH reduction / Nef Mediated CD8 Down-regulation / cell wall mannoprotein biosynthetic process / ATPase-coupled ion transmembrane transporter activity / cellular response to alkaline pH / protein localization to vacuolar membrane ...Blockage of phagosome acidification / Ion channel transport / Regulation of MITF-M-dependent genes involved in lysosome biogenesis and autophagy / vacuole-mitochondrion membrane contact site / intracellular pH reduction / Nef Mediated CD8 Down-regulation / cell wall mannoprotein biosynthetic process / ATPase-coupled ion transmembrane transporter activity / cellular response to alkaline pH / protein localization to vacuolar membrane / Insulin receptor recycling / Transferrin endocytosis and recycling / polyphosphate metabolic process / ROS and RNS production in phagocytes / Amino acids regulate mTORC1 / Golgi lumen acidification / proteasome storage granule assembly / P-type proton-exporting transporter activity / vacuolar transport / extrinsic component of synaptic vesicle membrane / Transferrin endocytosis and recycling / vacuolar proton-transporting V-type ATPase, V1 domain / vacuolar proton-transporting V-type ATPase, V0 domain / clathrin-coated vesicle membrane / lysosomal lumen acidification / endosomal lumen acidification / vacuole organization / protein targeting to vacuole / proton-transporting V-type ATPase complex / Amino acids regulate mTORC1 / pexophagy / fungal-type vacuole / vacuolar proton-transporting V-type ATPase complex / Nef Mediated CD4 Down-regulation / ROS and RNS production in phagocytes / cellular hyperosmotic response / vacuolar acidification / fungal-type vacuole membrane / phosphatidylinositol-3,5-bisphosphate binding / proton transmembrane transporter activity / proton-transporting ATPase activity, rotational mechanism / intracellular copper ion homeostasis / regulation of macroautophagy / ATP metabolic process / Insulin receptor recycling / enzyme regulator activity / Neutrophil degranulation / RNA endonuclease activity / proton transmembrane transport / cell periphery / transmembrane transport / endocytosis / intracellular calcium ion homeostasis / cytoplasmic stress granule / ATPase binding / protein-containing complex assembly / intracellular iron ion homeostasis / endosome membrane / membrane raft / Golgi membrane / lysosomal membrane / endoplasmic reticulum membrane / extracellular exosome / ATP binding / membrane / plasma membrane / cytoplasm / cytosol Similarity search - Function | ||||||||||||
| Biological species |   Homo sapiens (human) Homo sapiens (human) | ||||||||||||
| Method | ELECTRON MICROSCOPY / single particle reconstruction / cryo EM / Resolution: 6.6 Å | ||||||||||||
 Authors Authors | Khan, M.M. / Lee, S. / Oot, R.A. / Couoh-Cardel, S. / KIm, H. / Wilkens, S. / Roh, S.H. | ||||||||||||
| Funding support |  United States, 3items United States, 3items
| ||||||||||||
 Citation Citation |  Journal: EMBO J / Year: 2022 Journal: EMBO J / Year: 2022Title: Oxidative stress protein Oxr1 promotes V-ATPase holoenzyme disassembly in catalytic activity-independent manner. Authors: Md Murad Khan / Seowon Lee / Sergio Couoh-Cardel / Rebecca A Oot / Hyunmin Kim / Stephan Wilkens / Soung-Hun Roh /   Abstract: The vacuolar ATPase (V-ATPase) is a rotary motor proton pump that is regulated by an assembly equilibrium between active holoenzyme and autoinhibited V -ATPase and V proton channel subcomplexes. ...The vacuolar ATPase (V-ATPase) is a rotary motor proton pump that is regulated by an assembly equilibrium between active holoenzyme and autoinhibited V -ATPase and V proton channel subcomplexes. Here, we report cryo-EM structures of yeast V-ATPase assembled in vitro from lipid nanodisc reconstituted V and mutant V . Our analysis identified holoenzymes in three active rotary states, indicating that binding of V to V provides sufficient free energy to overcome V autoinhibition. Moreover, the structures suggest that the unequal spacing of V 's proton-carrying glutamic acid residues serves to alleviate the symmetry mismatch between V and V motors, a notion that is supported by mutagenesis experiments. We also uncover a structure of free V bound to Oxr1, a conserved but poorly characterized factor involved in the oxidative stress response. Biochemical experiments show that Oxr1 inhibits V -ATPase and causes disassembly of the holoenzyme, suggesting that Oxr1 plays a direct role in V-ATPase regulation. | ||||||||||||
| History |
|
- Structure visualization
Structure visualization
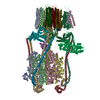
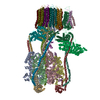
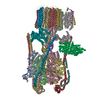
| Movie |
 Movie viewer Movie viewer |
|---|---|
| Structure viewer | Molecule:  Molmil Molmil Jmol/JSmol Jmol/JSmol |
- Downloads & links
Downloads & links
- Download
Download
| PDBx/mmCIF format |  7fdc.cif.gz 7fdc.cif.gz | 1.4 MB | Display |  PDBx/mmCIF format PDBx/mmCIF format |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| PDB format |  pdb7fdc.ent.gz pdb7fdc.ent.gz | 1.1 MB | Display |  PDB format PDB format |
| PDBx/mmJSON format |  7fdc.json.gz 7fdc.json.gz | Tree view |  PDBx/mmJSON format PDBx/mmJSON format | |
| Others |  Other downloads Other downloads |
-Validation report
| Arichive directory |  https://data.pdbj.org/pub/pdb/validation_reports/fd/7fdc https://data.pdbj.org/pub/pdb/validation_reports/fd/7fdc ftp://data.pdbj.org/pub/pdb/validation_reports/fd/7fdc ftp://data.pdbj.org/pub/pdb/validation_reports/fd/7fdc | HTTPS FTP |
|---|
-Related structure data
| Related structure data |  31540MC  7fdaC  7fdbC  7fdeC M: map data used to model this data C: citing same article ( |
|---|---|
| Similar structure data |
- Links
Links
- Assembly
Assembly
| Deposited unit | 
|
|---|---|
| 1 |
|
- Components
Components
-Yeast Vacuolar ATPase ... , 3 types, 5 molecules ACEQf
| #1: Protein | Mass: 67796.508 Da / Num. of mol.: 3 / Source method: isolated from a natural source / Source: (natural)  #9: Protein | | Mass: 95625.484 Da / Num. of mol.: 1 / Source method: isolated from a natural source / Source: (natural)  #16: Protein | | Mass: 9369.934 Da / Num. of mol.: 1 / Source method: isolated from a natural source / Source: (natural)  |
|---|
-V-type proton ATPase subunit ... , 11 types, 24 molecules BDFGIKHJLMNOSTUVWXYZabcd
| #2: Protein | Mass: 57815.023 Da / Num. of mol.: 3 / Source method: isolated from a natural source / Source: (natural)  #3: Protein | Mass: 26508.393 Da / Num. of mol.: 3 / Source method: isolated from a natural source / Source: (natural)  #4: Protein | Mass: 13735.680 Da / Num. of mol.: 3 / Source method: isolated from a natural source / Source: (natural)  #5: Protein | | Mass: 29235.023 Da / Num. of mol.: 1 / Source method: isolated from a natural source / Source: (natural)  #6: Protein | | Mass: 13479.170 Da / Num. of mol.: 1 / Source method: isolated from a natural source / Source: (natural)  #7: Protein | | Mass: 44241.352 Da / Num. of mol.: 1 Source method: isolated from a genetically manipulated source Source: (gene. exp.)   #10: Protein | | Mass: 39822.484 Da / Num. of mol.: 1 / Source method: isolated from a natural source / Source: (natural)  #11: Protein | | Mass: 22610.641 Da / Num. of mol.: 1 / Source method: isolated from a natural source / Source: (natural)  #12: Protein | | Mass: 17046.361 Da / Num. of mol.: 1 / Source method: isolated from a natural source / Source: (natural)  #13: Protein | Mass: 16357.501 Da / Num. of mol.: 8 / Source method: isolated from a natural source / Source: (natural)  #14: Protein | | Mass: 8387.065 Da / Num. of mol.: 1 / Source method: isolated from a natural source / Source: (natural)  |
|---|
-Protein , 2 types, 2 molecules Pe
| #8: Protein | Mass: 53885.984 Da / Num. of mol.: 1 Source method: isolated from a genetically manipulated source Source: (gene. exp.)   Homo sapiens (human) Homo sapiens (human)Strain: S288c / Production host:  |
|---|---|
| #15: Protein | Mass: 29694.885 Da / Num. of mol.: 1 / Source method: isolated from a natural source / Source: (natural)  |
-Experimental details
-Experiment
| Experiment | Method: ELECTRON MICROSCOPY |
|---|---|
| EM experiment | Aggregation state: PARTICLE / 3D reconstruction method: single particle reconstruction |
- Sample preparation
Sample preparation
| Component |
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Molecular weight | Value: 1 MDa / Experimental value: NO | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Source (natural) |
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Source (recombinant) |
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Buffer solution | pH: 7.4 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Specimen | Conc.: 1 mg/ml / Embedding applied: NO / Shadowing applied: NO / Staining applied: NO / Vitrification applied: YES | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Specimen support | Grid material: GOLD / Grid type: UltrAuFoil | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Vitrification | Instrument: HOMEMADE PLUNGER / Cryogen name: ETHANE / Humidity: 90 % / Chamber temperature: 277 K |
- Electron microscopy imaging
Electron microscopy imaging
| Experimental equipment |  Model: Titan Krios / Image courtesy: FEI Company |
|---|---|
| Microscopy | Model: TFS KRIOS |
| Electron gun | Electron source:  FIELD EMISSION GUN / Accelerating voltage: 300 kV / Illumination mode: FLOOD BEAM FIELD EMISSION GUN / Accelerating voltage: 300 kV / Illumination mode: FLOOD BEAM |
| Electron lens | Mode: BRIGHT FIELD |
| Image recording | Average exposure time: 10 sec. / Electron dose: 50 e/Å2 / Detector mode: COUNTING / Film or detector model: GATAN K2 SUMMIT (4k x 4k) / Num. of real images: 15741 |
| EM imaging optics | Energyfilter name: GIF Bioquantum / Energyfilter slit width: 20 eV |
- Processing
Processing
| Software | Name: PHENIX / Version: 1.19rc6_4061: / Classification: refinement | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| EM software |
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||
| CTF correction | Type: PHASE FLIPPING AND AMPLITUDE CORRECTION | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 3D reconstruction | Resolution: 6.6 Å / Resolution method: FSC 0.143 CUT-OFF / Num. of particles: 15741 / Algorithm: BACK PROJECTION / Symmetry type: POINT | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Atomic model building | Protocol: FLEXIBLE FIT / Space: REAL | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Refine LS restraints |
|
 Movie
Movie Controller
Controller








 PDBj
PDBj