[English] 日本語
 Yorodumi
Yorodumi- PDB-5l9u: Model of human Anaphase-promoting complex/Cyclosome (APC/C-CDH1) ... -
+ Open data
Open data
- Basic information
Basic information
| Entry | Database: PDB / ID: 5l9u | ||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Title | Model of human Anaphase-promoting complex/Cyclosome (APC/C-CDH1) with a cross linked Ubiquitin variant-substrate-UBE2C (UBCH10) complex representing key features of multiubiquitination | ||||||||||||||||||
 Components Components |
| ||||||||||||||||||
 Keywords Keywords | SIGNALING PROTEIN / ubiquitination / multi-protein complex / cell division | ||||||||||||||||||
| Function / homology |  Function and homology information Function and homology informationTranslesion synthesis by REV1 / Recognition of DNA damage by PCNA-containing replication complex / APC/C:Cdc20 mediated degradation of Cyclin B / APC-Cdc20 mediated degradation of Nek2A / Activated NOTCH1 Transmits Signal to the Nucleus / Downregulation of TGF-beta receptor signaling / Regulation of FZD by ubiquitination / Regulation of TNFR1 signaling / TNFR1-induced NF-kappa-B signaling pathway / Translesion synthesis by POLK ...Translesion synthesis by REV1 / Recognition of DNA damage by PCNA-containing replication complex / APC/C:Cdc20 mediated degradation of Cyclin B / APC-Cdc20 mediated degradation of Nek2A / Activated NOTCH1 Transmits Signal to the Nucleus / Downregulation of TGF-beta receptor signaling / Regulation of FZD by ubiquitination / Regulation of TNFR1 signaling / TNFR1-induced NF-kappa-B signaling pathway / Translesion synthesis by POLK / Translesion synthesis by POLI / Termination of translesion DNA synthesis / Gap-filling DNA repair synthesis and ligation in GG-NER / Formation of TC-NER Pre-Incision Complex / Dual incision in TC-NER / Gap-filling DNA repair synthesis and ligation in TC-NER / Fanconi Anemia Pathway / Regulation of TP53 Degradation / Regulation of TP53 Activity through Methylation / Cyclin D associated events in G1 / Stabilization of p53 / PTK6 Regulates RTKs and Their Effectors AKT1 and DOK1 / Synthesis of active ubiquitin: roles of E1 and E2 enzymes / ER Quality Control Compartment (ERQC) / Interferon alpha/beta signaling / Endosomal Sorting Complex Required For Transport (ESCRT) / Negative regulators of DDX58/IFIH1 signaling / Activation of IRF3, IRF7 mediated by TBK1, IKKε (IKBKE) / IKK complex recruitment mediated by RIP1 / IRAK2 mediated activation of TAK1 complex / TRAF6-mediated induction of TAK1 complex within TLR4 complex / Alpha-protein kinase 1 signaling pathway / Inactivation of CSF3 (G-CSF) signaling / IRAK2 mediated activation of TAK1 complex upon TLR7/8 or 9 stimulation / Regulation of NF-kappa B signaling / Regulation of TBK1, IKKε (IKBKE)-mediated activation of IRF3, IRF7 / NOD1/2 Signaling Pathway / activated TAK1 mediates p38 MAPK activation / JNK (c-Jun kinases) phosphorylation and activation mediated by activated human TAK1 / Formation of Incision Complex in GG-NER / Dual Incision in GG-NER / E3 ubiquitin ligases ubiquitinate target proteins / Translesion Synthesis by POLH / Downregulation of ERBB2:ERBB3 signaling / TCF dependent signaling in response to WNT / Regulation of innate immune responses to cytosolic DNA / HDR through Homologous Recombination (HRR) / Downregulation of ERBB2 signaling / Regulation of signaling by CBL / Ovarian tumor domain proteases / Recruitment and ATM-mediated phosphorylation of repair and signaling proteins at DNA double strand breaks / DNA Damage Recognition in GG-NER / NOTCH3 Activation and Transmission of Signal to the Nucleus / Interleukin-1 signaling / negative regulation of diacylglycerol biosynthetic process / protein localization to septin ring / Downregulation of ERBB4 signaling / Deactivation of the beta-catenin transactivating complex / Negative regulation of MET activity / Regulation of PTEN localization / Josephin domain DUBs / mitotic morphogenesis checkpoint signaling / Pexophagy / Stimuli-sensing channels / N-glycan trimming in the ER and Calnexin/Calreticulin cycle / Metalloprotease DUBs / Regulation of necroptotic cell death / Oxygen-dependent proline hydroxylation of Hypoxia-inducible Factor Alpha / Autodegradation of Cdh1 by Cdh1:APC/C / SCF-beta-TrCP mediated degradation of Emi1 / APC/C:Cdc20 mediated degradation of Securin / APC/C:Cdh1 mediated degradation of Cdc20 and other APC/C:Cdh1 targeted proteins in late mitosis/early G1 / Cdc20:Phospho-APC/C mediated degradation of Cyclin A / SCF(Skp2)-mediated degradation of p27/p21 / NRIF signals cell death from the nucleus / NF-kB is activated and signals survival / Autodegradation of the E3 ubiquitin ligase COP1 / Asymmetric localization of PCP proteins / Degradation of DVL / Hedgehog ligand biogenesis / Dectin-1 mediated noncanonical NF-kB signaling / Degradation of GLI1 by the proteasome / Hedgehog 'on' state / TNFR2 non-canonical NF-kB pathway / NIK-->noncanonical NF-kB signaling / Assembly of the pre-replicative complex / CDK-mediated phosphorylation and removal of Cdc6 / G2/M Checkpoints / Ubiquitin-Mediated Degradation of Phosphorylated Cdc25A / Ubiquitin-dependent degradation of Cyclin D / The role of GTSE1 in G2/M progression after G2 checkpoint / FBXL7 down-regulates AURKA during mitotic entry and in early mitosis / RUNX1 regulates transcription of genes involved in differentiation of HSCs / Regulation of RUNX3 expression and activity / Aggrephagy / GSK3B and BTRC:CUL1-mediated-degradation of NFE2L2 / p75NTR recruits signalling complexes / TGF-beta receptor signaling in EMT (epithelial to mesenchymal transition) / GLI3 is processed to GLI3R by the proteasome / Activation of NF-kappaB in B cells Similarity search - Function | ||||||||||||||||||
| Biological species |  Homo sapiens (human) Homo sapiens (human)  | ||||||||||||||||||
| Method | ELECTRON MICROSCOPY / single particle reconstruction / cryo EM / Resolution: 6.4 Å | ||||||||||||||||||
 Authors Authors | Brown, N.G. / VanderLinden, R. / Dube, P. / Haselbach, D. / Peters, J.M. / Stark, H. / Schulman, B.A. | ||||||||||||||||||
| Funding support |  United States, United States,  Germany, 5items Germany, 5items
| ||||||||||||||||||
 Citation Citation |  Journal: Cell / Year: 2016 Journal: Cell / Year: 2016Title: Dual RING E3 Architectures Regulate Multiubiquitination and Ubiquitin Chain Elongation by APC/C. Authors: Nicholas G Brown / Ryan VanderLinden / Edmond R Watson / Florian Weissmann / Alban Ordureau / Kuen-Phon Wu / Wei Zhang / Shanshan Yu / Peter Y Mercredi / Joseph S Harrison / Iain F Davidson ...Authors: Nicholas G Brown / Ryan VanderLinden / Edmond R Watson / Florian Weissmann / Alban Ordureau / Kuen-Phon Wu / Wei Zhang / Shanshan Yu / Peter Y Mercredi / Joseph S Harrison / Iain F Davidson / Renping Qiao / Ying Lu / Prakash Dube / Michael R Brunner / Christy R R Grace / Darcie J Miller / David Haselbach / Marc A Jarvis / Masaya Yamaguchi / David Yanishevski / Georg Petzold / Sachdev S Sidhu / Brian Kuhlman / Marc W Kirschner / J Wade Harper / Jan-Michael Peters / Holger Stark / Brenda A Schulman /     Abstract: Protein ubiquitination involves E1, E2, and E3 trienzyme cascades. E2 and RING E3 enzymes often collaborate to first prime a substrate with a single ubiquitin (UB) and then achieve different forms of ...Protein ubiquitination involves E1, E2, and E3 trienzyme cascades. E2 and RING E3 enzymes often collaborate to first prime a substrate with a single ubiquitin (UB) and then achieve different forms of polyubiquitination: multiubiquitination of several sites and elongation of linkage-specific UB chains. Here, cryo-EM and biochemistry show that the human E3 anaphase-promoting complex/cyclosome (APC/C) and its two partner E2s, UBE2C (aka UBCH10) and UBE2S, adopt specialized catalytic architectures for these two distinct forms of polyubiquitination. The APC/C RING constrains UBE2C proximal to a substrate and simultaneously binds a substrate-linked UB to drive processive multiubiquitination. Alternatively, during UB chain elongation, the RING does not bind UBE2S but rather lures an evolving substrate-linked UB to UBE2S positioned through a cullin interaction to generate a Lys11-linked chain. Our findings define mechanisms of APC/C regulation, and establish principles by which specialized E3-E2-substrate-UB architectures control different forms of polyubiquitination. | ||||||||||||||||||
| History |
|
- Structure visualization
Structure visualization
| Movie |
 Movie viewer Movie viewer |
|---|---|
| Structure viewer | Molecule:  Molmil Molmil Jmol/JSmol Jmol/JSmol |
- Downloads & links
Downloads & links
- Download
Download
| PDBx/mmCIF format |  5l9u.cif.gz 5l9u.cif.gz | 366.5 KB | Display |  PDBx/mmCIF format PDBx/mmCIF format |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| PDB format |  pdb5l9u.ent.gz pdb5l9u.ent.gz | 203.5 KB | Display |  PDB format PDB format |
| PDBx/mmJSON format |  5l9u.json.gz 5l9u.json.gz | Tree view |  PDBx/mmJSON format PDBx/mmJSON format | |
| Others |  Other downloads Other downloads |
-Validation report
| Arichive directory |  https://data.pdbj.org/pub/pdb/validation_reports/l9/5l9u https://data.pdbj.org/pub/pdb/validation_reports/l9/5l9u ftp://data.pdbj.org/pub/pdb/validation_reports/l9/5l9u ftp://data.pdbj.org/pub/pdb/validation_reports/l9/5l9u | HTTPS FTP |
|---|
-Related structure data
| Related structure data |  3432MC 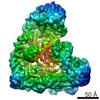 3433C  5jg6C 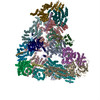 5l9tC M: map data used to model this data C: citing same article ( |
|---|---|
| Similar structure data |
- Links
Links
- Assembly
Assembly
| Deposited unit | 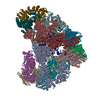
|
|---|---|
| 1 |
|
- Components
Components
-Anaphase-promoting complex subunit ... , 11 types, 13 molecules ABDEGWILMNOXY
| #1: Protein | Mass: 216725.469 Da / Num. of mol.: 1 Source method: isolated from a genetically manipulated source Source: (gene. exp.)  Homo sapiens (human) / Gene: ANAPC1, TSG24 / Production host: Homo sapiens (human) / Gene: ANAPC1, TSG24 / Production host:  Trichoplusia ni (cabbage looper) / References: UniProt: Q9H1A4 Trichoplusia ni (cabbage looper) / References: UniProt: Q9H1A4 | ||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| #2: Protein | Mass: 9854.647 Da / Num. of mol.: 1 Source method: isolated from a genetically manipulated source Source: (gene. exp.)  Homo sapiens (human) / Gene: ANAPC11, HSPC214 / Production host: Homo sapiens (human) / Gene: ANAPC11, HSPC214 / Production host:  Trichoplusia ni (cabbage looper) / References: UniProt: Q9NYG5 Trichoplusia ni (cabbage looper) / References: UniProt: Q9NYG5 | ||||||||||||
| #4: Protein | Mass: 14286.727 Da / Num. of mol.: 1 Source method: isolated from a genetically manipulated source Source: (gene. exp.)  Homo sapiens (human) / Gene: ANAPC15, C11orf51, HSPC020 / Production host: Homo sapiens (human) / Gene: ANAPC15, C11orf51, HSPC020 / Production host:  Trichoplusia ni (cabbage looper) / References: UniProt: P60006 Trichoplusia ni (cabbage looper) / References: UniProt: P60006 | ||||||||||||
| #5: Protein | Mass: 11677.995 Da / Num. of mol.: 1 Source method: isolated from a genetically manipulated source Source: (gene. exp.)  Homo sapiens (human) / Gene: ANAPC16, C10orf104, CENP-27 / Production host: Homo sapiens (human) / Gene: ANAPC16, C10orf104, CENP-27 / Production host:  Trichoplusia ni (cabbage looper) / References: UniProt: Q96DE5 Trichoplusia ni (cabbage looper) / References: UniProt: Q96DE5 | ||||||||||||
| #7: Protein | Mass: 9793.999 Da / Num. of mol.: 2 Source method: isolated from a genetically manipulated source Source: (gene. exp.)  Homo sapiens (human) / Gene: CDC26, ANAPC12, C9orf17 / Production host: Homo sapiens (human) / Gene: CDC26, ANAPC12, C9orf17 / Production host:  Trichoplusia ni (cabbage looper) / References: UniProt: Q8NHZ8 Trichoplusia ni (cabbage looper) / References: UniProt: Q8NHZ8#8: Protein | | Mass: 93207.328 Da / Num. of mol.: 1 Source method: isolated from a genetically manipulated source Details: Construct contains the remnant of PreScission Protease site at C-terminus. Source: (gene. exp.)  Homo sapiens (human) / Gene: ANAPC4, APC4 / Production host: Homo sapiens (human) / Gene: ANAPC4, APC4 / Production host:  Trichoplusia ni (cabbage looper) / References: UniProt: Q9UJX5 Trichoplusia ni (cabbage looper) / References: UniProt: Q9UJX5#10: Protein | | Mass: 21282.143 Da / Num. of mol.: 1 Source method: isolated from a genetically manipulated source Source: (gene. exp.)  Homo sapiens (human) / Gene: ANAPC10, APC10 / Production host: Homo sapiens (human) / Gene: ANAPC10, APC10 / Production host:  Trichoplusia ni (cabbage looper) / References: UniProt: Q9UM13 Trichoplusia ni (cabbage looper) / References: UniProt: Q9UM13#11: Protein | | Mass: 8528.309 Da / Num. of mol.: 1 Source method: isolated from a genetically manipulated source Source: (gene. exp.)  Homo sapiens (human) / Gene: ANAPC13 / Production host: Homo sapiens (human) / Gene: ANAPC13 / Production host:  Trichoplusia ni (cabbage looper) / References: UniProt: Q9BS18 Trichoplusia ni (cabbage looper) / References: UniProt: Q9BS18#12: Protein | | Mass: 93938.977 Da / Num. of mol.: 1 Source method: isolated from a genetically manipulated source Source: (gene. exp.)  Homo sapiens (human) / Gene: ANAPC2, APC2, KIAA1406 / Production host: Homo sapiens (human) / Gene: ANAPC2, APC2, KIAA1406 / Production host:  Trichoplusia ni (cabbage looper) / References: UniProt: Q9UJX6 Trichoplusia ni (cabbage looper) / References: UniProt: Q9UJX6#13: Protein | | Mass: 85179.766 Da / Num. of mol.: 1 Source method: isolated from a genetically manipulated source Source: (gene. exp.)  Homo sapiens (human) / Gene: ANAPC5, APC5 / Production host: Homo sapiens (human) / Gene: ANAPC5, APC5 / Production host:  Trichoplusia ni (cabbage looper) / References: UniProt: Q9UJX4 Trichoplusia ni (cabbage looper) / References: UniProt: Q9UJX4#17: Protein | Mass: 63204.020 Da / Num. of mol.: 2 Source method: isolated from a genetically manipulated source Source: (gene. exp.)  Homo sapiens (human) / Gene: ANAPC7, APC7 / Production host: Homo sapiens (human) / Gene: ANAPC7, APC7 / Production host:  Trichoplusia ni (cabbage looper) / References: UniProt: Q9UJX3 Trichoplusia ni (cabbage looper) / References: UniProt: Q9UJX3 |
-Cell division cycle protein ... , 3 types, 6 molecules CPFHJK
| #3: Protein | Mass: 68921.031 Da / Num. of mol.: 2 Source method: isolated from a genetically manipulated source Source: (gene. exp.)  Homo sapiens (human) / Gene: CDC23, ANAPC8 / Production host: Homo sapiens (human) / Gene: CDC23, ANAPC8 / Production host:  Trichoplusia ni (cabbage looper) / References: UniProt: Q9UJX2 Trichoplusia ni (cabbage looper) / References: UniProt: Q9UJX2#6: Protein | Mass: 91973.125 Da / Num. of mol.: 2 Source method: isolated from a genetically manipulated source Source: (gene. exp.)  Homo sapiens (human) / Gene: CDC27, ANAPC3, D0S1430E, D17S978E / Production host: Homo sapiens (human) / Gene: CDC27, ANAPC3, D0S1430E, D17S978E / Production host:  Trichoplusia ni (cabbage looper) / References: UniProt: P30260 Trichoplusia ni (cabbage looper) / References: UniProt: P30260#9: Protein | Mass: 71747.516 Da / Num. of mol.: 2 Source method: isolated from a genetically manipulated source Source: (gene. exp.)  Homo sapiens (human) / Gene: CDC16, ANAPC6 / Production host: Homo sapiens (human) / Gene: CDC16, ANAPC6 / Production host:  Trichoplusia ni (cabbage looper) / References: UniProt: Q13042 Trichoplusia ni (cabbage looper) / References: UniProt: Q13042 |
|---|
-Protein , 3 types, 3 molecules RSU
| #14: Protein | Mass: 54838.688 Da / Num. of mol.: 1 Source method: isolated from a genetically manipulated source Source: (gene. exp.)  Homo sapiens (human) / Gene: FZR1, CDH1, FYR, FZR, KIAA1242 / Production host: Homo sapiens (human) / Gene: FZR1, CDH1, FYR, FZR, KIAA1242 / Production host:  Trichoplusia ni (cabbage looper) / References: UniProt: Q9UM11 Trichoplusia ni (cabbage looper) / References: UniProt: Q9UM11 |
|---|---|
| #15: Protein | Mass: 17057.281 Da / Num. of mol.: 1 / Mutation: K788C,K788C,K788C Source method: isolated from a genetically manipulated source Details: This construct comprises 768-842 of HSL1 with an N-terminal Gemini-IM motif and linker and a C-terminal UB variant (CHAIN V). K788C of this construct is cross-linked to UBE2C C115 (CHAIN U) ...Details: This construct comprises 768-842 of HSL1 with an N-terminal Gemini-IM motif and linker and a C-terminal UB variant (CHAIN V). K788C of this construct is cross-linked to UBE2C C115 (CHAIN U) and to UbG75C (not visible) via TMEA. Source: (gene. exp.)   Gene: HSL1, YKL101W, YKL453 / Production host:  References: UniProt: P34244, UniProt: Q63429, non-specific serine/threonine protein kinase |
| #16: Protein | Mass: 20768.289 Da / Num. of mol.: 1 / Mutation: C102A Source method: isolated from a genetically manipulated source Source: (gene. exp.)  Homo sapiens (human) / Gene: UBE2C, UBCH10 / Production host: Homo sapiens (human) / Gene: UBE2C, UBCH10 / Production host:  Trichoplusia ni (cabbage looper) Trichoplusia ni (cabbage looper)References: UniProt: O00762, E2 ubiquitin-conjugating enzyme, (E3-independent) E2 ubiquitin-conjugating enzyme |
-Details
| Has protein modification | N |
|---|
-Experimental details
-Experiment
| Experiment | Method: ELECTRON MICROSCOPY |
|---|---|
| EM experiment | Aggregation state: PARTICLE / 3D reconstruction method: single particle reconstruction |
- Sample preparation
Sample preparation
| Component | Name: Multi-protein complex of APC/C, coactivator CDH1, and cross-linked complex of UBE2C, Ubiquitin, and Substrate-UB_variant fusion. Type: COMPLEX / Entity ID: all |
|---|---|
| Molecular weight | Value: 1.28 MDa / Experimental value: NO |
| Buffer solution | pH: 8 |
| Specimen | Conc.: 0.1 mg/ml / Embedding applied: NO / Shadowing applied: NO / Staining applied: NO / Vitrification applied: YES |
| Vitrification | Cryogen name: ETHANE |
- Electron microscopy imaging
Electron microscopy imaging
| Experimental equipment |  Model: Titan Krios / Image courtesy: FEI Company |
|---|---|
| Microscopy | Model: FEI TITAN KRIOS |
| Electron gun | Electron source:  FIELD EMISSION GUN / Accelerating voltage: 300 kV / Illumination mode: SPOT SCAN FIELD EMISSION GUN / Accelerating voltage: 300 kV / Illumination mode: SPOT SCAN |
| Electron lens | Mode: BRIGHT FIELD |
| Image recording | Electron dose: 40 e/Å2 / Film or detector model: FEI FALCON II (4k x 4k) |
- Processing
Processing
| EM software | Name: RELION / Version: 1.2 / Category: 3D reconstruction |
|---|---|
| CTF correction | Type: PHASE FLIPPING AND AMPLITUDE CORRECTION |
| 3D reconstruction | Resolution: 6.4 Å / Resolution method: FSC 0.143 CUT-OFF / Num. of particles: 135578 / Symmetry type: POINT |
 Movie
Movie Controller
Controller






 PDBj
PDBj





















