[English] 日本語
 Yorodumi
Yorodumi- EMDB-4318: Structure of the chromatin remodelling enzyme Chd1 bound to a ubi... -
+ Open data
Open data
- Basic information
Basic information
| Entry | Database: EMDB / ID: EMD-4318 | |||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
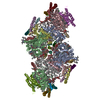
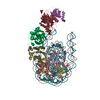
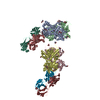
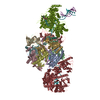
| Title | Structure of the chromatin remodelling enzyme Chd1 bound to a ubiquitinylated nucleosome | |||||||||
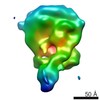
 Map data Map data | CryoEM reconstruction for a S.cerevisiae chromatin remodeller bound to 601 nucleosome. | |||||||||
 Sample Sample |
| |||||||||
 Keywords Keywords | Chromatin remodellers / MOTOR PROTEIN | |||||||||
| Function / homology |  Function and homology information Function and homology informationregulation of transcriptional start site selection at RNA polymerase II promoter / nucleolar chromatin / negative regulation of DNA-templated DNA replication / regulation of chromatin organization / rDNA binding / SLIK (SAGA-like) complex / DNA double-strand break processing / nucleosome organization / ATP-dependent chromatin remodeler activity / hypothalamus gonadotrophin-releasing hormone neuron development ...regulation of transcriptional start site selection at RNA polymerase II promoter / nucleolar chromatin / negative regulation of DNA-templated DNA replication / regulation of chromatin organization / rDNA binding / SLIK (SAGA-like) complex / DNA double-strand break processing / nucleosome organization / ATP-dependent chromatin remodeler activity / hypothalamus gonadotrophin-releasing hormone neuron development / female meiosis I / SAGA complex / positive regulation of protein monoubiquitination / fat pad development / mitochondrion transport along microtubule / sister chromatid cohesion / termination of RNA polymerase II transcription / : / female gonad development / seminiferous tubule development / termination of RNA polymerase I transcription / male meiosis I / positive regulation of intrinsic apoptotic signaling pathway by p53 class mediator / ATP-dependent activity, acting on DNA / energy homeostasis / neuron projection morphogenesis / regulation of proteasomal protein catabolic process / Maturation of protein E / Maturation of protein E / ER Quality Control Compartment (ERQC) / Myoclonic epilepsy of Lafora / FLT3 signaling by CBL mutants / Constitutive Signaling by NOTCH1 HD Domain Mutants / IRAK2 mediated activation of TAK1 complex / Prevention of phagosomal-lysosomal fusion / Alpha-protein kinase 1 signaling pathway / Glycogen synthesis / IRAK1 recruits IKK complex / IRAK1 recruits IKK complex upon TLR7/8 or 9 stimulation / Endosomal Sorting Complex Required For Transport (ESCRT) / Membrane binding and targetting of GAG proteins / Negative regulation of FLT3 / Regulation of TBK1, IKKε (IKBKE)-mediated activation of IRF3, IRF7 / PTK6 Regulates RTKs and Their Effectors AKT1 and DOK1 / Regulation of TBK1, IKKε-mediated activation of IRF3, IRF7 upon TLR3 ligation / IRAK2 mediated activation of TAK1 complex upon TLR7/8 or 9 stimulation / NOTCH2 Activation and Transmission of Signal to the Nucleus / TICAM1,TRAF6-dependent induction of TAK1 complex / TICAM1-dependent activation of IRF3/IRF7 / APC/C:Cdc20 mediated degradation of Cyclin B / Regulation of FZD by ubiquitination / Downregulation of ERBB4 signaling / APC-Cdc20 mediated degradation of Nek2A / p75NTR recruits signalling complexes / InlA-mediated entry of Listeria monocytogenes into host cells / TRAF6 mediated IRF7 activation in TLR7/8 or 9 signaling / Regulation of pyruvate metabolism / TRAF6-mediated induction of TAK1 complex within TLR4 complex / regulation of neuron apoptotic process / NF-kB is activated and signals survival / Regulation of innate immune responses to cytosolic DNA / Pexophagy / Downregulation of ERBB2:ERBB3 signaling / NRIF signals cell death from the nucleus / Activated NOTCH1 Transmits Signal to the Nucleus / Regulation of PTEN localization / VLDLR internalisation and degradation / Synthesis of active ubiquitin: roles of E1 and E2 enzymes / Translesion synthesis by REV1 / Regulation of BACH1 activity / TICAM1, RIP1-mediated IKK complex recruitment / positive regulation of protein ubiquitination / MAP3K8 (TPL2)-dependent MAPK1/3 activation / Translesion synthesis by POLK / InlB-mediated entry of Listeria monocytogenes into host cell / Degradation of CDH1 / JNK (c-Jun kinases) phosphorylation and activation mediated by activated human TAK1 / Activation of IRF3, IRF7 mediated by TBK1, IKKε (IKBKE) / Josephin domain DUBs / Downregulation of TGF-beta receptor signaling / Translesion synthesis by POLI / Gap-filling DNA repair synthesis and ligation in GG-NER / Degradation of CRY and PER proteins / IKK complex recruitment mediated by RIP1 / Regulation of activated PAK-2p34 by proteasome mediated degradation / PINK1-PRKN Mediated Mitophagy / TGF-beta receptor signaling in EMT (epithelial to mesenchymal transition) / regulation of mitochondrial membrane potential / TNFR1-induced NF-kappa-B signaling pathway / Autodegradation of Cdh1 by Cdh1:APC/C / TCF dependent signaling in response to WNT / APC/C:Cdc20 mediated degradation of Securin / Regulation of NF-kappa B signaling / N-glycan trimming in the ER and Calnexin/Calreticulin cycle / activated TAK1 mediates p38 MAPK activation / Asymmetric localization of PCP proteins / Ubiquitin-dependent degradation of Cyclin D / SCF-beta-TrCP mediated degradation of Emi1 / NIK-->noncanonical NF-kB signaling / TNFR2 non-canonical NF-kB pathway Similarity search - Function | |||||||||
| Biological species |   Homo sapiens (human) / Homo sapiens (human) /  | |||||||||
| Method | single particle reconstruction / cryo EM / Resolution: 4.5 Å | |||||||||
 Authors Authors | Sundaramoorthy R / Owen-hughes T | |||||||||
| Funding support |  United Kingdom, 1 items United Kingdom, 1 items
| |||||||||
 Citation Citation |  Journal: Elife / Year: 2018 Journal: Elife / Year: 2018Title: Structure of the chromatin remodelling enzyme Chd1 bound to a ubiquitinylated nucleosome. Authors: Ramasubramanian Sundaramoorthy / Amanda L Hughes / Hassane El-Mkami / David G Norman / Helder Ferreira / Tom Owen-Hughes /  Abstract: ATP-dependent chromatin remodelling proteins represent a diverse family of proteins that share ATPase domains that are adapted to regulate protein-DNA interactions. Here, we present structures of the ...ATP-dependent chromatin remodelling proteins represent a diverse family of proteins that share ATPase domains that are adapted to regulate protein-DNA interactions. Here, we present structures of the Chd1 protein engaged with nucleosomes in the presence of the transition state mimic ADP-beryllium fluoride. The path of DNA strands through the ATPase domains indicates the presence of contacts conserved with single strand translocases and additional contacts with both strands that are unique to Snf2 related proteins. The structure provides connectivity between rearrangement of ATPase lobes to a closed, nucleotide bound state and the sensing of linker DNA. Two turns of linker DNA are prised off the surface of the histone octamer as a result of Chd1 binding, and both the histone H3 tail and ubiquitin conjugated to lysine 120 are re-orientated towards the unravelled DNA. This indicates how changes to nucleosome structure can alter the way in which histone epitopes are presented. | |||||||||
| History |
|
- Structure visualization
Structure visualization
| Movie |
 Movie viewer Movie viewer |
|---|---|
| Structure viewer | EM map:  SurfView SurfView Molmil Molmil Jmol/JSmol Jmol/JSmol |
| Supplemental images |
- Downloads & links
Downloads & links
-EMDB archive
| Map data |  emd_4318.map.gz emd_4318.map.gz | 4.5 MB |  EMDB map data format EMDB map data format | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Header (meta data) |  emd-4318-v30.xml emd-4318-v30.xml emd-4318.xml emd-4318.xml | 27.6 KB 27.6 KB | Display Display |  EMDB header EMDB header |
| FSC (resolution estimation) |  emd_4318_fsc.xml emd_4318_fsc.xml | 8.4 KB | Display |  FSC data file FSC data file |
| Images |  emd_4318.png emd_4318.png | 33.9 KB | ||
| Filedesc metadata |  emd-4318.cif.gz emd-4318.cif.gz | 7.8 KB | ||
| Archive directory |  http://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/structures/EMD-4318 http://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/structures/EMD-4318 ftp://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/structures/EMD-4318 ftp://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/structures/EMD-4318 | HTTPS FTP |
-Related structure data
| Related structure data |  6ftxMC  4336C  6g0lC M: atomic model generated by this map C: citing same article ( |
|---|---|
| Similar structure data |
- Links
Links
| EMDB pages |  EMDB (EBI/PDBe) / EMDB (EBI/PDBe) /  EMDataResource EMDataResource |
|---|---|
| Related items in Molecule of the Month |
- Map
Map
| File |  Download / File: emd_4318.map.gz / Format: CCP4 / Size: 52.7 MB / Type: IMAGE STORED AS FLOATING POINT NUMBER (4 BYTES) Download / File: emd_4318.map.gz / Format: CCP4 / Size: 52.7 MB / Type: IMAGE STORED AS FLOATING POINT NUMBER (4 BYTES) | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Annotation | CryoEM reconstruction for a S.cerevisiae chromatin remodeller bound to 601 nucleosome. | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Projections & slices | Image control
Images are generated by Spider. | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Voxel size | X=Y=Z: 1.4 Å | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Density |
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Symmetry | Space group: 1 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Details | EMDB XML:
CCP4 map header:
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
-Supplemental data
- Sample components
Sample components
+Entire : X. laevis nucleosome pn 601 DNA with S.cerevisiae remodeller Chd1
+Supramolecule #1: X. laevis nucleosome pn 601 DNA with S.cerevisiae remodeller Chd1
+Supramolecule #2: X. laevis nucleosome pn 601 DNA with S.cerevisiae remodeller Chd1
+Supramolecule #3: X. laevis nucleosome pn 601 DNA with S.cerevisiae remodeller Chd1
+Supramolecule #4: X. laevis nucleosome pn 601 DNA with S.cerevisiae remodeller Chd1
+Supramolecule #5: X. laevis nucleosome pn 601 DNA with S.cerevisiae remodeller Chd1
+Macromolecule #1: Histone H3
+Macromolecule #2: Histone H4
+Macromolecule #3: Histone H2A type 1
+Macromolecule #4: Histone H2B
+Macromolecule #5: Histone H3.3C
+Macromolecule #8: Polyubiquitin-B
+Macromolecule #9: Chromatin-remodeling ATPase
+Macromolecule #6: DNA (159-MER)
+Macromolecule #7: DNA (160-MER)
+Macromolecule #10: BERYLLIUM TRIFLUORIDE ION
+Macromolecule #11: ADENOSINE-5'-DIPHOSPHATE
-Experimental details
-Structure determination
| Method | cryo EM |
|---|---|
 Processing Processing | single particle reconstruction |
| Aggregation state | particle |
- Sample preparation
Sample preparation
| Concentration | 1 mg/mL | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Buffer | pH: 7.5 / Component:
| ||||||
| Grid | Model: C-flat-1.2/1.3 4C / Material: COPPER / Mesh: 400 / Pretreatment - Type: GLOW DISCHARGE / Pretreatment - Time: 60 sec. / Pretreatment - Atmosphere: OTHER | ||||||
| Vitrification | Cryogen name: ETHANE / Chamber humidity: 100 % / Chamber temperature: 277 K / Instrument: FEI VITROBOT MARK III | ||||||
| Details | Sample was gel filtration purified and it is monodisperse |
- Electron microscopy
Electron microscopy
| Microscope | FEI TITAN KRIOS |
|---|---|
| Temperature | Min: 170.0 K / Max: 170.0 K |
| Specialist optics | Energy filter - Name: GIF Quantum LS |
| Image recording | Film or detector model: GATAN K2 QUANTUM (4k x 4k) / Detector mode: COUNTING / Digitization - Dimensions - Width: 3870 pixel / Digitization - Dimensions - Height: 3870 pixel / Digitization - Frames/image: 5-28 / Number grids imaged: 1 / Number real images: 1300 / Average exposure time: 0.32 sec. / Average electron dose: 1.25 e/Å2 |
| Electron beam | Acceleration voltage: 300 kV / Electron source:  FIELD EMISSION GUN FIELD EMISSION GUN |
| Electron optics | C2 aperture diameter: 70.0 µm / Calibrated defocus max: 4.0 µm / Calibrated defocus min: 1.5 µm / Calibrated magnification: 35714 / Illumination mode: FLOOD BEAM / Imaging mode: BRIGHT FIELD / Cs: 2.7 mm / Nominal defocus max: 4.0 µm / Nominal defocus min: 1.5 µm / Nominal magnification: 35714 |
| Sample stage | Specimen holder model: FEI TITAN KRIOS AUTOGRID HOLDER / Cooling holder cryogen: NITROGEN |
| Experimental equipment |  Model: Titan Krios / Image courtesy: FEI Company |
+ Image processing
Image processing
-Atomic model buiding 1
| Refinement | Space: RECIPROCAL / Protocol: FLEXIBLE FIT / Overall B value: 204 / Target criteria: Cross-correlation coefficient |
|---|---|
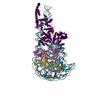
| Output model |  PDB-6ftx: |
 Movie
Movie Controller
Controller

























 Z (Sec.)
Z (Sec.) Y (Row.)
Y (Row.) X (Col.)
X (Col.)

























