[English] 日本語
 Yorodumi
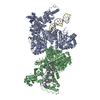
Yorodumi- EMDB-20524: Cryo-EM structure of full-length IGF1R-IGF1 complex. Only the ext... -
+ Open data
Open data
- Basic information
Basic information
| Entry | Database: EMDB / ID: EMD-20524 | |||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Title | Cryo-EM structure of full-length IGF1R-IGF1 complex. Only the extracellular region of the complex is resolved. | |||||||||
 Map data Map data | full-length IGF1R-IGF1 complex | |||||||||
 Sample Sample |
| |||||||||
 Keywords Keywords | IGF1R / IGF1 / SIGNALING PROTEIN-HORMONE complex | |||||||||
| Function / homology |  Function and homology information Function and homology informationnegative regulation of cholangiocyte apoptotic process / Signaling by Type 1 Insulin-like Growth Factor 1 Receptor (IGF1R) / IRS-related events triggered by IGF1R / SHC-related events triggered by IGF1R / positive regulation of steroid hormone biosynthetic process / glycolate metabolic process / muscle hypertrophy / negative regulation of oocyte development / insulin-like growth factor binding protein complex / insulin-like growth factor ternary complex ...negative regulation of cholangiocyte apoptotic process / Signaling by Type 1 Insulin-like Growth Factor 1 Receptor (IGF1R) / IRS-related events triggered by IGF1R / SHC-related events triggered by IGF1R / positive regulation of steroid hormone biosynthetic process / glycolate metabolic process / muscle hypertrophy / negative regulation of oocyte development / insulin-like growth factor binding protein complex / insulin-like growth factor ternary complex / positive regulation of trophectodermal cell proliferation / negative regulation of muscle cell apoptotic process / prostate gland stromal morphogenesis / positive regulation of type B pancreatic cell proliferation / type II pneumocyte differentiation / neuronal dense core vesicle lumen / positive regulation of glycoprotein biosynthetic process / proteoglycan biosynthetic process / regulation of establishment or maintenance of cell polarity / chondroitin sulfate proteoglycan biosynthetic process / positive regulation of transcription regulatory region DNA binding / insulin-like growth factor receptor activity / myotube cell development / positive regulation of DNA metabolic process / protein kinase complex / Extra-nuclear estrogen signaling / negative regulation of neuroinflammatory response / insulin-like growth factor binding / Signaling by Type 1 Insulin-like Growth Factor 1 Receptor (IGF1R) / skeletal muscle satellite cell maintenance involved in skeletal muscle regeneration / bone mineralization involved in bone maturation / positive regulation of cell growth involved in cardiac muscle cell development / IRS-related events triggered by IGF1R / negative regulation of vascular associated smooth muscle cell apoptotic process / positive regulation of cerebellar granule cell precursor proliferation / protein transporter activity / lung vasculature development / exocytic vesicle / cerebellar granule cell precursor proliferation / positive regulation of myoblast proliferation / transcytosis / positive regulation of meiotic cell cycle / positive regulation of axon regeneration / lung lobe morphogenesis / positive regulation of myelination / cell activation / negative regulation of hepatocyte apoptotic process / glial cell differentiation / negative regulation of androgen receptor signaling pathway / positive regulation of developmental growth / prostate gland epithelium morphogenesis / positive regulation of calcineurin-NFAT signaling cascade / transmembrane receptor protein tyrosine kinase activator activity / prostate gland growth / male sex determination / insulin receptor complex / positive regulation of protein-containing complex disassembly / insulin-like growth factor I binding / type B pancreatic cell proliferation / insulin receptor activity / mammary gland development / exocrine pancreas development / alphav-beta3 integrin-IGF-1-IGF1R complex / myoblast differentiation / cell surface receptor signaling pathway via STAT / positive regulation of insulin-like growth factor receptor signaling pathway / regulation of nitric oxide biosynthetic process / positive regulation of Ras protein signal transduction / response to L-glutamate / dendritic spine maintenance / activation of protein kinase B activity / positive regulation of smooth muscle cell migration / regulation of JNK cascade / growth hormone receptor signaling pathway / insulin binding / positive regulation of DNA binding / adrenal gland development / negative regulation of interleukin-1 beta production / lung alveolus development / muscle organ development / cellular response to insulin-like growth factor stimulus / branching morphogenesis of an epithelial tube / androgen receptor signaling pathway / prostate epithelial cord arborization involved in prostate glandular acinus morphogenesis / positive regulation of osteoblast proliferation / positive regulation of cardiac muscle hypertrophy / negative regulation of release of cytochrome c from mitochondria / positive regulation of cytokinesis / type I pneumocyte differentiation / establishment of cell polarity / negative regulation of amyloid-beta formation / inner ear development / negative regulation of smooth muscle cell apoptotic process / amyloid-beta clearance / myoblast proliferation / insulin receptor substrate binding / positive regulation of activated T cell proliferation / epithelial to mesenchymal transition / negative regulation of tumor necrosis factor production / Synthesis, secretion, and deacylation of Ghrelin Similarity search - Function | |||||||||
| Biological species |   Homo sapiens (human) Homo sapiens (human) | |||||||||
| Method | single particle reconstruction / cryo EM / Resolution: 4.3 Å | |||||||||
 Authors Authors | Li J / Choi E | |||||||||
 Citation Citation |  Journal: Nat Commun / Year: 2019 Journal: Nat Commun / Year: 2019Title: Structural basis of the activation of type 1 insulin-like growth factor receptor. Authors: Jie Li / Eunhee Choi / Hongtao Yu / Xiao-Chen Bai /  Abstract: Type 1 insulin-like growth factor receptor (IGF1R) is a receptor tyrosine kinase that regulates cell growth and proliferation, and can be activated by IGF1, IGF2, and insulin. Here, we report the ...Type 1 insulin-like growth factor receptor (IGF1R) is a receptor tyrosine kinase that regulates cell growth and proliferation, and can be activated by IGF1, IGF2, and insulin. Here, we report the cryo-EM structure of full-length IGF1R-IGF1 complex in the active state. This structure reveals that only one IGF1 molecule binds the Γ-shaped asymmetric IGF1R dimer. The IGF1-binding site is formed by the L1 and CR domains of one IGF1R protomer and the α-CT and FnIII-1 domains of the other. The liganded α-CT forms a rigid beam-like structure with the unliganded α-CT, which hinders the conformational change of the unliganded α-CT required for binding of a second IGF1 molecule. We further identify an L1-FnIII-2 interaction that mediates the dimerization of membrane-proximal domains of IGF1R. This interaction is required for optimal receptor activation. Our study identifies a source of the negative cooperativity in IGF1 binding to IGF1R and reveals the structural basis of IGF1R activation. | |||||||||
| History |
|
- Structure visualization
Structure visualization
| Movie |
 Movie viewer Movie viewer |
|---|---|
| Structure viewer | EM map:  SurfView SurfView Molmil Molmil Jmol/JSmol Jmol/JSmol |
| Supplemental images |
- Downloads & links
Downloads & links
-EMDB archive
| Map data |  emd_20524.map.gz emd_20524.map.gz | 77.7 MB |  EMDB map data format EMDB map data format | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Header (meta data) |  emd-20524-v30.xml emd-20524-v30.xml emd-20524.xml emd-20524.xml | 14 KB 14 KB | Display Display |  EMDB header EMDB header |
| Images |  emd_20524.png emd_20524.png | 178.7 KB | ||
| Filedesc metadata |  emd-20524.cif.gz emd-20524.cif.gz | 6.1 KB | ||
| Archive directory |  http://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/structures/EMD-20524 http://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/structures/EMD-20524 ftp://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/structures/EMD-20524 ftp://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/structures/EMD-20524 | HTTPS FTP |
-Related structure data
| Related structure data |  6pyhMC M: atomic model generated by this map C: citing same article ( |
|---|---|
| Similar structure data |
- Links
Links
| EMDB pages |  EMDB (EBI/PDBe) / EMDB (EBI/PDBe) /  EMDataResource EMDataResource |
|---|---|
| Related items in Molecule of the Month |
- Map
Map
| File |  Download / File: emd_20524.map.gz / Format: CCP4 / Size: 83.7 MB / Type: IMAGE STORED AS FLOATING POINT NUMBER (4 BYTES) Download / File: emd_20524.map.gz / Format: CCP4 / Size: 83.7 MB / Type: IMAGE STORED AS FLOATING POINT NUMBER (4 BYTES) | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Annotation | full-length IGF1R-IGF1 complex | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Projections & slices | Image control
Images are generated by Spider. | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Voxel size | X=Y=Z: 1.07 Å | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Density |
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Symmetry | Space group: 1 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Details | EMDB XML:
CCP4 map header:
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
-Supplemental data
- Sample components
Sample components
-Entire : Full-length MmIGF1R-HsIGF1 complex
| Entire | Name: Full-length MmIGF1R-HsIGF1 complex |
|---|---|
| Components |
|
-Supramolecule #1: Full-length MmIGF1R-HsIGF1 complex
| Supramolecule | Name: Full-length MmIGF1R-HsIGF1 complex / type: complex / ID: 1 / Parent: 0 / Macromolecule list: all |
|---|---|
| Molecular weight | Theoretical: 336 KDa |
-Supramolecule #2: MmIGF1R
| Supramolecule | Name: MmIGF1R / type: complex / ID: 2 / Parent: 1 / Macromolecule list: #1 |
|---|---|
| Source (natural) | Organism:  |
-Supramolecule #3: HsIGF1
| Supramolecule | Name: HsIGF1 / type: complex / ID: 3 / Parent: 1 / Macromolecule list: #2 |
|---|---|
| Source (natural) | Organism:  Homo sapiens (human) Homo sapiens (human) |
-Macromolecule #1: Insulin-like growth factor 1 receptor
| Macromolecule | Name: Insulin-like growth factor 1 receptor / type: protein_or_peptide / ID: 1 / Number of copies: 2 / Enantiomer: LEVO / EC number: receptor protein-tyrosine kinase |
|---|---|
| Source (natural) | Organism:  |
| Molecular weight | Theoretical: 145.279906 KDa |
| Recombinant expression | Organism:  Homo sapiens (human) Homo sapiens (human) |
| Sequence | String: EICGPGIDIR NDYQQLKRLE NCTVIEGFLH ILLISKAEDY RSYRFPKLTV ITEYLLLFRV AGLESLGDLF PNLTVIRGWK LFYNYALVI FEMTNLKDIG LYNLRNITRG AIRIEKNADL CYLSTIDWSL ILDAVSNNYI VGNKPPKECG DLCPGTLEEK P MCEKTTIN ...String: EICGPGIDIR NDYQQLKRLE NCTVIEGFLH ILLISKAEDY RSYRFPKLTV ITEYLLLFRV AGLESLGDLF PNLTVIRGWK LFYNYALVI FEMTNLKDIG LYNLRNITRG AIRIEKNADL CYLSTIDWSL ILDAVSNNYI VGNKPPKECG DLCPGTLEEK P MCEKTTIN NEYNYRCWTT NRCQKMCPSV CGKRACTENN ECCHPECLGS CHTPDDNTTC VACRHYYYKG VCVPACPPGT YR FEGWRCV DRDFCANIPN AESSDSDGFV IHDDECMQEC PSGFIRNSTQ SMYCIPCEGP CPKVCGDEEK KTKTIDSVTS AQM LQGCTI LKGNLLINIR RGNNIASELE NFMGLIEVVT GYVKIRHSHA LVSLSFLKNL RLILGEEQLE GNYSFYVLDN QNLQ QLWDW NHRNLTVRSG KMYFAFNPKL CVSEIYRMEE VTGTKGRQSK GDINTRNNGE RASCESDVLR FTSTTTWKNR IIITW HRYR PPDYRDLISF TVYYKEAPFK NVTEYDGQDA CGSNSWNMVD VDLPPNKEGE PGILLHGLKP WTQYAVYVKA VTLTMV END HIRGAKSEIL YIRTNASVPS IPLDVLSASN SSSQLIVKWN PPTLPNGNLS YYIVRWQRQP QDGYLYRHNY CSKDKIP IR KYADGTIDVE EVTENPKTEV CGGDKGPCCA CPKTEAEKQA EKEEAEYRKV FENFLHNSIF VPRPERRRRD VMQVANTT M SSRSRNTTVA DTYNITDPEE FETEYPFFES RVDNKERTVI SNLRPFTLYR IDIHSCNHEA EKLGCSASNF VFARTMPAE GADDIPGPVT WEPRPENSIF LKWPEPENPN GLILMYEIKY GSQVEDQREC VSRQEYRKYG GAKLNRLNPG NYTARIQATS LSGNGSWTD PVFFYVPAKT TYENFMHLII ALPVAILLIV GGLVIMLYVF HRKRNNSRLG NGVLYASVNP EAFSAADVYV P DEWEVARE KITMNRELGQ GSFGMVYEGV AKGVVKDEPE TRVAIKTVNE AASMRERIEF LNEASVMKEF NCHHVVRLLG VV SQGQPTL VIMELMTRGD LKSYLRSLRP EVEQNNLVLI PPSLSKMIQM AGEIADGMAY LNANKFVHRN LAARNCMVAE DFT VKIGDF GMTRDIYETD YYRKGGKGLL PVRWMSPESL KDGVFTTHSD VWSFGVVLWE IATLAEQPYQ GLSNEQVLRF VMEG GLLDK PDNCPDMLFE LMRMCWQYNP KMRPSFLEII GSIKDEMEPS FQEVSFYYSE ENKPPEPGTS SGLEVLFQ UniProtKB: Insulin-like growth factor 1 receptor |
-Macromolecule #2: Insulin-like growth factor I
| Macromolecule | Name: Insulin-like growth factor I / type: protein_or_peptide / ID: 2 / Number of copies: 1 / Enantiomer: LEVO |
|---|---|
| Source (natural) | Organism:  Homo sapiens (human) Homo sapiens (human) |
| Molecular weight | Theoretical: 7.663752 KDa |
| Recombinant expression | Organism:  |
| Sequence | String: GPETLCGAEL VDALQFVCGD RGFYFNKPTG YGSSSRRAPQ TGIVDECCFR SCDLRRLEMY CAPLKPAKSA UniProtKB: Insulin-like growth factor 1 |
-Experimental details
-Structure determination
| Method | cryo EM |
|---|---|
 Processing Processing | single particle reconstruction |
| Aggregation state | particle |
- Sample preparation
Sample preparation
| Concentration | 7 mg/mL |
|---|---|
| Buffer | pH: 7.5 |
| Grid | Details: unspecified |
| Vitrification | Cryogen name: ETHANE / Chamber humidity: 100 % / Instrument: FEI VITROBOT MARK IV |
- Electron microscopy
Electron microscopy
| Microscope | FEI TITAN KRIOS |
|---|---|
| Image recording | Film or detector model: GATAN K2 IS (4k x 4k) / Average exposure time: 15.0 sec. / Average electron dose: 50.0 e/Å2 |
| Electron beam | Acceleration voltage: 300 kV / Electron source:  FIELD EMISSION GUN FIELD EMISSION GUN |
| Electron optics | C2 aperture diameter: 70.0 µm / Illumination mode: FLOOD BEAM / Imaging mode: BRIGHT FIELD / Cs: 2.7 mm |
| Sample stage | Specimen holder model: FEI TITAN KRIOS AUTOGRID HOLDER / Cooling holder cryogen: NITROGEN |
| Experimental equipment |  Model: Titan Krios / Image courtesy: FEI Company |
+ Image processing
Image processing
-Atomic model buiding 1
| Refinement | Space: REAL / Protocol: FLEXIBLE FIT |
|---|---|
| Output model |  PDB-6pyh: |
 Movie
Movie Controller
Controller
























 Z (Sec.)
Z (Sec.) Y (Row.)
Y (Row.) X (Col.)
X (Col.)





















