[English] 日本語
 Yorodumi
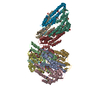
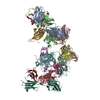
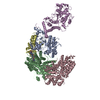
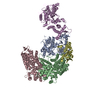
Yorodumi- PDB-6pyh: Cryo-EM structure of full-length IGF1R-IGF1 complex. Only the ext... -
+ Open data
Open data
- Basic information
Basic information
| Entry | Database: PDB / ID: 6pyh | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
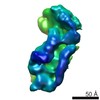
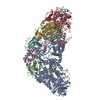
| Title | Cryo-EM structure of full-length IGF1R-IGF1 complex. Only the extracellular region of the complex is resolved. | ||||||
 Components Components |
| ||||||
 Keywords Keywords | SIGNALING PROTEIN/HORMONE / IGF1R / IGF1 / SIGNALING PROTEIN-HORMONE complex | ||||||
| Function / homology |  Function and homology information Function and homology informationnegative regulation of cholangiocyte apoptotic process / Signaling by Type 1 Insulin-like Growth Factor 1 Receptor (IGF1R) / IRS-related events triggered by IGF1R / SHC-related events triggered by IGF1R / positive regulation of steroid hormone biosynthetic process / glycolate metabolic process / muscle hypertrophy / negative regulation of oocyte development / insulin-like growth factor binding protein complex / insulin-like growth factor ternary complex ...negative regulation of cholangiocyte apoptotic process / Signaling by Type 1 Insulin-like Growth Factor 1 Receptor (IGF1R) / IRS-related events triggered by IGF1R / SHC-related events triggered by IGF1R / positive regulation of steroid hormone biosynthetic process / glycolate metabolic process / muscle hypertrophy / negative regulation of oocyte development / insulin-like growth factor binding protein complex / insulin-like growth factor ternary complex / positive regulation of trophectodermal cell proliferation / negative regulation of muscle cell apoptotic process / prostate gland stromal morphogenesis / positive regulation of type B pancreatic cell proliferation / type II pneumocyte differentiation / neuronal dense core vesicle lumen / positive regulation of glycoprotein biosynthetic process / proteoglycan biosynthetic process / regulation of establishment or maintenance of cell polarity / chondroitin sulfate proteoglycan biosynthetic process / positive regulation of transcription regulatory region DNA binding / insulin-like growth factor receptor activity / myotube cell development / positive regulation of DNA metabolic process / protein kinase complex / Extra-nuclear estrogen signaling / negative regulation of neuroinflammatory response / insulin-like growth factor binding / Signaling by Type 1 Insulin-like Growth Factor 1 Receptor (IGF1R) / skeletal muscle satellite cell maintenance involved in skeletal muscle regeneration / bone mineralization involved in bone maturation / positive regulation of cell growth involved in cardiac muscle cell development / IRS-related events triggered by IGF1R / negative regulation of vascular associated smooth muscle cell apoptotic process / positive regulation of cerebellar granule cell precursor proliferation / protein transporter activity / lung vasculature development / exocytic vesicle / cerebellar granule cell precursor proliferation / positive regulation of myoblast proliferation / transcytosis / positive regulation of meiotic cell cycle / positive regulation of axon regeneration / lung lobe morphogenesis / positive regulation of myelination / cell activation / negative regulation of hepatocyte apoptotic process / glial cell differentiation / negative regulation of androgen receptor signaling pathway / positive regulation of developmental growth / prostate gland epithelium morphogenesis / positive regulation of calcineurin-NFAT signaling cascade / transmembrane receptor protein tyrosine kinase activator activity / prostate gland growth / male sex determination / insulin receptor complex / positive regulation of protein-containing complex disassembly / insulin-like growth factor I binding / type B pancreatic cell proliferation / insulin receptor activity / mammary gland development / exocrine pancreas development / alphav-beta3 integrin-IGF-1-IGF1R complex / myoblast differentiation / cell surface receptor signaling pathway via STAT / positive regulation of insulin-like growth factor receptor signaling pathway / regulation of nitric oxide biosynthetic process / positive regulation of Ras protein signal transduction / response to L-glutamate / dendritic spine maintenance / activation of protein kinase B activity / positive regulation of smooth muscle cell migration / regulation of JNK cascade / growth hormone receptor signaling pathway / insulin binding / positive regulation of DNA binding / adrenal gland development / negative regulation of interleukin-1 beta production / lung alveolus development / muscle organ development / cellular response to insulin-like growth factor stimulus / branching morphogenesis of an epithelial tube / androgen receptor signaling pathway / prostate epithelial cord arborization involved in prostate glandular acinus morphogenesis / positive regulation of osteoblast proliferation / positive regulation of cardiac muscle hypertrophy / negative regulation of release of cytochrome c from mitochondria / positive regulation of cytokinesis / type I pneumocyte differentiation / establishment of cell polarity / negative regulation of amyloid-beta formation / inner ear development / negative regulation of smooth muscle cell apoptotic process / amyloid-beta clearance / myoblast proliferation / insulin receptor substrate binding / positive regulation of activated T cell proliferation / epithelial to mesenchymal transition / negative regulation of tumor necrosis factor production / Synthesis, secretion, and deacylation of Ghrelin Similarity search - Function | ||||||
| Biological species |   Homo sapiens (human) Homo sapiens (human) | ||||||
| Method | ELECTRON MICROSCOPY / single particle reconstruction / cryo EM / Resolution: 4.3 Å | ||||||
 Authors Authors | Li, J. / Choi, E. / Yu, H.T. / Bai, X.C. | ||||||
 Citation Citation |  Journal: Nat Commun / Year: 2019 Journal: Nat Commun / Year: 2019Title: Structural basis of the activation of type 1 insulin-like growth factor receptor. Authors: Jie Li / Eunhee Choi / Hongtao Yu / Xiao-Chen Bai /  Abstract: Type 1 insulin-like growth factor receptor (IGF1R) is a receptor tyrosine kinase that regulates cell growth and proliferation, and can be activated by IGF1, IGF2, and insulin. Here, we report the ...Type 1 insulin-like growth factor receptor (IGF1R) is a receptor tyrosine kinase that regulates cell growth and proliferation, and can be activated by IGF1, IGF2, and insulin. Here, we report the cryo-EM structure of full-length IGF1R-IGF1 complex in the active state. This structure reveals that only one IGF1 molecule binds the Γ-shaped asymmetric IGF1R dimer. The IGF1-binding site is formed by the L1 and CR domains of one IGF1R protomer and the α-CT and FnIII-1 domains of the other. The liganded α-CT forms a rigid beam-like structure with the unliganded α-CT, which hinders the conformational change of the unliganded α-CT required for binding of a second IGF1 molecule. We further identify an L1-FnIII-2 interaction that mediates the dimerization of membrane-proximal domains of IGF1R. This interaction is required for optimal receptor activation. Our study identifies a source of the negative cooperativity in IGF1 binding to IGF1R and reveals the structural basis of IGF1R activation. | ||||||
| History |
|
- Structure visualization
Structure visualization
| Movie |
 Movie viewer Movie viewer |
|---|---|
| Structure viewer | Molecule:  Molmil Molmil Jmol/JSmol Jmol/JSmol |
- Downloads & links
Downloads & links
- Download
Download
| PDBx/mmCIF format |  6pyh.cif.gz 6pyh.cif.gz | 318 KB | Display |  PDBx/mmCIF format PDBx/mmCIF format |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| PDB format |  pdb6pyh.ent.gz pdb6pyh.ent.gz | 246.2 KB | Display |  PDB format PDB format |
| PDBx/mmJSON format |  6pyh.json.gz 6pyh.json.gz | Tree view |  PDBx/mmJSON format PDBx/mmJSON format | |
| Others |  Other downloads Other downloads |
-Validation report
| Arichive directory |  https://data.pdbj.org/pub/pdb/validation_reports/py/6pyh https://data.pdbj.org/pub/pdb/validation_reports/py/6pyh ftp://data.pdbj.org/pub/pdb/validation_reports/py/6pyh ftp://data.pdbj.org/pub/pdb/validation_reports/py/6pyh | HTTPS FTP |
|---|
-Related structure data
| Related structure data |  20524MC M: map data used to model this data C: citing same article ( |
|---|---|
| Similar structure data |
- Links
Links
- Assembly
Assembly
| Deposited unit | 
|
|---|---|
| 1 |
|
- Components
Components
| #1: Protein | Mass: 145279.906 Da / Num. of mol.: 2 Source method: isolated from a genetically manipulated source Source: (gene. exp.)   Homo sapiens (human) Homo sapiens (human)References: UniProt: Q60751, receptor protein-tyrosine kinase #2: Protein | | Mass: 7663.752 Da / Num. of mol.: 1 Source method: isolated from a genetically manipulated source Source: (gene. exp.)  Homo sapiens (human) / Gene: IGF1, IBP1 / Production host: Homo sapiens (human) / Gene: IGF1, IBP1 / Production host:  Has protein modification | Y | |
|---|
-Experimental details
-Experiment
| Experiment | Method: ELECTRON MICROSCOPY |
|---|---|
| EM experiment | Aggregation state: PARTICLE / 3D reconstruction method: single particle reconstruction |
- Sample preparation
Sample preparation
| Component |
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Molecular weight | Value: 0.336 MDa / Experimental value: NO | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Source (natural) |
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Source (recombinant) |
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Buffer solution | pH: 7.5 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Specimen | Conc.: 7 mg/ml / Embedding applied: NO / Shadowing applied: NO / Staining applied: NO / Vitrification applied: YES | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Specimen support | Details: unspecified | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Vitrification | Instrument: FEI VITROBOT MARK IV / Cryogen name: ETHANE / Humidity: 100 % |
- Electron microscopy imaging
Electron microscopy imaging
| Experimental equipment |  Model: Titan Krios / Image courtesy: FEI Company |
|---|---|
| Microscopy | Model: FEI TITAN KRIOS |
| Electron gun | Electron source:  FIELD EMISSION GUN / Accelerating voltage: 300 kV / Illumination mode: FLOOD BEAM FIELD EMISSION GUN / Accelerating voltage: 300 kV / Illumination mode: FLOOD BEAM |
| Electron lens | Mode: BRIGHT FIELD / Cs: 2.7 mm / C2 aperture diameter: 70 µm / Alignment procedure: COMA FREE |
| Specimen holder | Cryogen: NITROGEN / Specimen holder model: FEI TITAN KRIOS AUTOGRID HOLDER |
| Image recording | Average exposure time: 15 sec. / Electron dose: 50 e/Å2 / Film or detector model: GATAN K2 IS (4k x 4k) |
- Processing
Processing
| Software | Name: PHENIX / Version: 1.16_3549: / Classification: refinement | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| EM software |
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| CTF correction | Type: PHASE FLIPPING AND AMPLITUDE CORRECTION | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Particle selection | Num. of particles selected: 1431211 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Symmetry | Point symmetry: C1 (asymmetric) | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 3D reconstruction | Resolution: 4.3 Å / Resolution method: FSC 0.143 CUT-OFF / Num. of particles: 51573 / Symmetry type: POINT | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Atomic model building | Protocol: FLEXIBLE FIT / Space: REAL | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Refine LS restraints |
|
 Movie
Movie Controller
Controller



 PDBj
PDBj













